AMERICAN CIVIL WAR - History of USA #8
- INTRODUCTION
During the years 1861-1865 US witnessed one of the severest struggles between North and the South, which turned out to be the greatest civil war in history. The issue of whether to expand slavery into federal territories and new states provoked existing tensions within the established states. When this War, also known as the War Between the States or War of the Rebellion finally broke out, the tensions create a geographic split of the states. It was precipitated by the decision of a number of states of south to secede forming the Confederate States of America, also known as the Confederacy from the Union and ended in the defeat of South and the preservation of the Union. It also resulted in abolition of slavery and acceleration of the economic development of the country.
- TENSIONS BETWEEN NORTHERN & SOUTHERN STATES
The idea of secession from the US was not new. At various times in the nation's history, other states had threatened to sever ties to the Union in protest of federal policies. As Northern and Southern economies grew in very different ways, however, the slavery issue began to create particularly severe disagreements between the states. When US territories expanded westward during the first half of the 19th century, the spread of slavery became the subject of national debate. The southern states built their economy on plantation crops of cotton and tobacco. Plantations thrived in the South with the support of slaves, and the southern economy would collapse if slavery was abolished. Since these states needed to protect their interests, and what they considered to be their property, the southern states were intent on keeping and expanding slavery. Southern states wanted state laws , not federal laws, to decide whether slavery was allowed or not. Under popular sovereignty, a state's legislation is more powerful than the federal government's legislation. Northern states built their economy on the labor of immigrants within factories. Slavery, which did not cost as much to support, was an economic threat to the northern communities and industries. Instead of slavery, they supported the concept of "free labor," which allowed jobs to be available to the community. Because factories sent their goods to other states, the northern states wanted a strong union. They favored a strong central government that would unite the states and their economies.
- DIFFERENCES BETWEEN NORTH & SOUTH

- ROAD TO SECTIONAL DIVISION
EXPANSION OF SLAVERY
When the United States purchased the Louisiana territory in 1803, the question of slavery expansion arose.
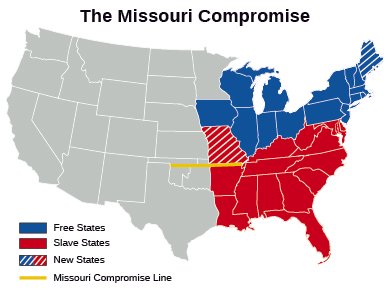
MISSOURI COMPROMISE 1820
Missouri's application for statehood heated the situation and friction increased between the two poles. It quickly became a heated debate but was temporarily calmed when Congress passed the Missouri Compromise. The Compromise allowed Missouri to be admitted into the Union as a slave state and Maine to come in as a Free state, while providing that no more slave states could be created north of Missouri's southern boundary. Under the Missouri Compromise, an uncertain peace was maintained for nearly three decades. But it also created a geographic line that split the rest of the purchased territory into northern and southern halves. The northern half would not allow slavery, but the southern territories would have the right to chose for themselves.
COMPROMISE OF 1850
The peace was disrupted at the end of the Mexican-American War (1846-48) when the US won California, Arizona and New Mexico territory south of the Missouri Compromise line, but not specifically covered under the compromise. So compromise of 1850 was given by Henry Clay. It is known as inter-sectional compromise. Numbers of measures were introduced to reduce conflict between north and south poles.
- Commission was appointed to review conditions of both sides.
- It admitted states to the Union in slave/free state pairs to maintain the balance
- To satisfy South, Fugitive Slave Act was passed which made the provision for capture & return of escaped slaves to their owners.
THE 1793 FUGITIVE SLAVE LAW
The 1793 act allowed a slave owner to seize an alleged fugitive slave and bring him or her before a judge to determine if he or she was a runaway slave of the claimant. If the judge agreed that the person was the slave of the claimant, he would issue a certificate of removal, which allowed the slave owner to take the slave back to his home state. The law introduced a $500 fine for anyone interfering with the return of a fugitive slave and allowed the slaveholder to sue anyone who had helped the fugitive.

DRED SCOTT DECISION
Dred Scott, a shiftless and illiterate Negro slave, had lived with his master for five years in Illinois and Wisconsin. He sued for his freedom on the ground that resistance in free territory relieved him from slavery. Supreme Court gave a decision that being a Negro he cannot file case in court because founders of the United States did not intend Negroes to be citizens.
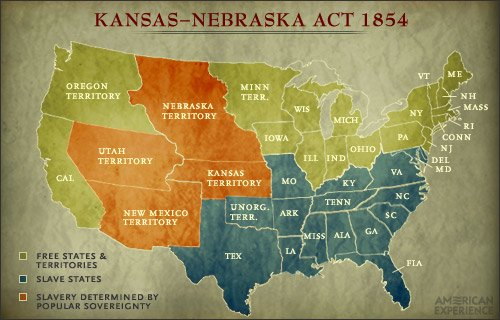
KANSAS-NEBRASKA ACT 1854
The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 played a large role in bringing about the American Civil War (1861-65). Within a year of its passage, proslavery and antislavery settlers were at war in Kansas a confrontation known as "Bleeding Kansas" and the nation's political parties had turned from positions of compromise to outright opposition.
PANIC OF 1857
In 1857 economic crisis overtook United States because of inflated currency, speculation of land and rail road etc. It gave rise to unemployment. The North was hit harder than the South which managed to come out of storm because of favorable cotton prices abroad.
ROLE OF ABRAHAM LINCOLN
The presidential elections of 1860 were very complicated one that had four candidates . Former US representative Abraham Lincoln (1809-1865; served 1861-65) of Illinois, a Republican, was elected.

The Republican Party wanted to stop the expansion of slavery. Its members also believed in a strong federal government. Though it had no interest in abolishing slavery where it already existed, the Southern states feared Lincoln's upcoming administration. Before Lincoln's inauguration, South Carolina was the first state to secede from the Union on December 20, 1860. Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana and Texas followed by February. Before Lincoln took office, they formed the Confederate States of America and elected their own president, US Senator Jefferson Davis (1808-1889) of Mississippi......Before Lincoln various efforts have been made to wipe out slavery from American land but final step was taken by Abraham Lincoln in 1865. He eliminated the deeply rooted slavery from America.
BEGINNING OF WAR
When he entered office in March 1861, Lincoln was intent on maintaining and protecting federal property throughout the rebellious states. In April, he sent supply ships to the troops at Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, and told the Confederate troops not to interfere. Confederate forces, however, opened fire on the fort; Union officials surrendered there the next day. When Lincoln called for volunteers to put down the rebellion, Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee and Arkansas joined the Confederacy. The American Civil War had begun.
BATTLE OF BULL RUN
Lincoln called 75,000 state militiamen into service for ninety days and later called for men to enlist for three years. Winfield Scott (1786-1866), commander of the US Army, crafted Lincoln's military plan to cut off Confederate access to supplies and to respond to rebellious attacks. Scott knew Confederacy would eventually collapse without the important supplies from the outside. Though Lincoln incorporated elements of the plan. both he and the public were impatient. He sent General Irvin McDowell to attack the Confederate capital of Richmond. At the Battle of Bull Run, July 21, 1861, the two armies met for the first time. The Union army was soundly defeated and forced to flee back to Washington. With defeat, Lincoln began to prepare for a longer war.
- Union General: George B. McClellan
- Confederate General: Robert E. Lee
THE SECOND BATTLE OF BULL RUN & BATTLE OF ANTIETAM
By August 1862, the Confederate army's superior tactics had dealt the Union army multiple defeats. The Confederates had protected their capital of Richmond and were pushing the Union army back towards Washington. The Second Battle of Bull Run, August 23, was a Confederate victory that inspired General Lee and Thomas J. Stonewall Jackson to move their troops into Maryland. Union general McClellan followed. The two armies met on September 17 at Antietam. The resulting Battle of Antietam was the single bloodiest day of the American Civil War. While McClellan forced the Confederates back to Virginia, he refused to pursue them aggressively. The Confederate Army escaped damaged, but intact. After the battle, Lincoln removed McClellan from command in November 1862.
BATTLE OF GETTYSBURG
In June 1863, General Lee moved his army into Pennsylvania. Union general George Meade moved to block him. The two armies clashed on July 1 in the Battle of Gettysburg. After three days of fighting, Lee was forced to retreat with a loss of nearly a third of his men. It was a major victory that marked the turning point of the war for the Union.
THE SIEGE AT PETERSBURG
In May 1864, General Grant, now in charge of the Army of the Potomac, led his army in a push towards Richmond. they engaged General Lee in several battles and refused to allow him to withdraw. Grant hoped to cut off Richmond and force its surrender by capturing the vital rail junction at Petersburg, Virginia. General Lee, however, refused to surrender Petersburg, and the two armies settled into a siege. The siege continued into the spring of 1865. On April 1, the last rail link into the Petersburg was captured, and Richmond was cut off from the rest of the Confederacy. Grant blocked Lee's retreat into North Carolina. Lee's surrender to Grant on April 9 at Appomattox Courthouse, Virginia was the last major defeat of the war. The remaining Confederate troops surrendered nine days later, and the American Civil War was over.
ELECTION OF 1864 & THE 13TH AMENDMENT
Lincoln's reelection in 1864 was not certain to happen. The Union was growing weary of the war and the Union army was struggling. The victories at Vicksburg and Gettysburg, however, instilled confidence in Lincoln, and he was elected for a second term. It was a clear signal that the American people valued the Union and were ready to abolish slavery. With Lincoln's reelection, the Republican Congress presented the 13th Amendment for ratification, or approval by the states, on January 31, 1865. Ratified on December 6, 1865, the amendment officially ended slavery throughout the US and made emancipation permanent.
SECESSION POLITICAL RIGHT OR WRONG
Most Northerners viewed the act of secession as rebellious and those who supported it as traitors under the law. Southerners argued that secession was legal, consistent with the belief that the people of each state have the power of self-government to organize as they see fit. Each state had willingly entered the Union with a vote to ratify the Constitution.
- CAUSES OF CIVIL WAR
1. The Devil Theory
This theory regarding the cause of civil war was popular from 1861 to 1900. According to this theory, the war was caused by Southern and Northern devils. Southern writers accused north of designs to destroy the south and its institutions. Likewise Northern writers accused South of designs to rule the union or break it.
2. Constitutional Theory
War was caused by different interpretations of the Constitution on question of State Sovereignty. North wanted to establish highly centralized national government exercising vast powers, the southerners stood for retention of power in the states where the framers of the constitution intended it to be. The southerners while denying slavery as the cause of war, had stressed the concentration of power at the center as the main cause of war.
3. Economic Theory
After WW-I, a new theory regarding causes of civil war emerged, which emphasized the importance of economic factors for the outbreak of Civil war. This theory rejected the moral basis of slavery and instead emphasized that different labor systems prevailed in North and South and those posed a threat to each other.
4. Nationalism as a Factor
Another cause of civil war is difference in the spirit of nationalism. Nationalism took hold of northerners due to economic growth and interests, the South was comparatively lacking in it. No doubt there was a spirit of nationalism in South like Unionists loyal to American Nationalism but they were very less in number.
5. Social & Political Factors
In South, entire economy was controlled by the big planters, formed a sort of Aristocracy. On the other hand North had strong faith in democracy and they considered slavery as a stumbling block in the way of achieving true democracy.
6. Conflict between Romanticism and Materialism
According to another opinion, civil war was the result of conflict between romanticism showed by South and materialism expressed by North. In view of their different outlook, a proper understanding could not be established between two poles and hence war broke out.
- LAST MEASURES
Between 1868 to 1870, all former Confederate states were readmitted to the Union with new governments. Though Congress continued Reconstruction with a series of enforcement acts through 1871, support for Reconstruction faded in the midst of economic concerns. President Rutherford B. Hayes (1822-1893; served 1877-81) withdrew the last federal troops from Confederate states in 1877, and southern states once again assumed full control. The vast majority of African Americans and many small farmers remained poor, without property and practically without enforceable rights. A system of sharecropping replaced slavery. Life under the oppressive state governments was made worse by the terrorist acts of white supremacist groups such as the Ku Klux Klan. The federal government would have to return to the south in the middle of the 20th century to compel integration of African Americans into Southern society.
- THE RECONSTRUCTION ACTS
They were a series of legislation passed by Congress in 1867, after the American Civil War (1861-65). Together they outlined the Republican Party's plan for reintegrating into the Union the Southern states that made up the Confederate States of America and for protecting basic rights for the newly freed slaves. The acts represented the wishes of a strong Republican Congress and were passed over the vetoes of President Andrew Johnson.
- CRITICAL ANALYSIS
From the above discussion it is crystal clear that various causes contributed in civil war of 1861. If we analyze depth of each cause, we may say that a sociopolitical difference between two poles is the major cause of civil war. Differences in practical life and mindsets widened the gap between the two parts. As a result, the level of understanding dropped to a negligible level. In such an unbalanced situation people from both sides rushed to fight for their rights. This triggered the American Civil War.
In my next article of this series, we shall discuss the Westward Expansion :)
If You Liked this Post, please UP VOTE this article and FOLLOW me for more informative stuff on offer!
Junaid Khalid
Very nice article! Highly informative. Good work :)
Thanks dear :)
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by Junaid from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews/crimsonclad, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows and creating a social network. Please find us in the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
Thanks :)
This post has received a 1.04 % upvote from @drotto thanks to: @banjo.
Resteemed your article. This article was resteemed because you are part of the New Steemians project. You can learn more about it here: https://steemit.com/introduceyourself/@gaman/new-steemians-project-launch
A very comprehensive and informative article about the American History. Keep up the good work.