U.S. Nuclear Weapons Are Controlled By 1970s Computers With 8-Inch Floppy Disks
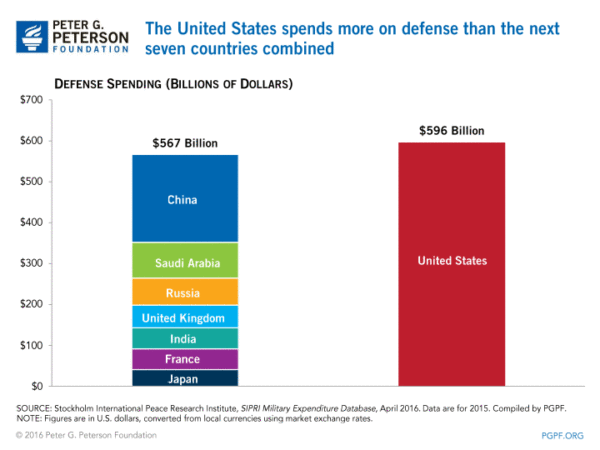
The U.S. spends over half a trillion dollars on defense each year. In 2011, for example, the U.S. spent more (in absolute numbers) on its military than the next 13 nations combined. Currently, it has dropped to the next 7 nations combined.
The U.S. unofficially has taken the responsibility of defense for Europe through NATO. Many key nations in Europe today count on the U.S. to sail through a global conflict. This puts a huge burden on the country. With such a responsibility, observers expect the U.S. to have an up-to-date warfare technology that can aptly face its adversaries.
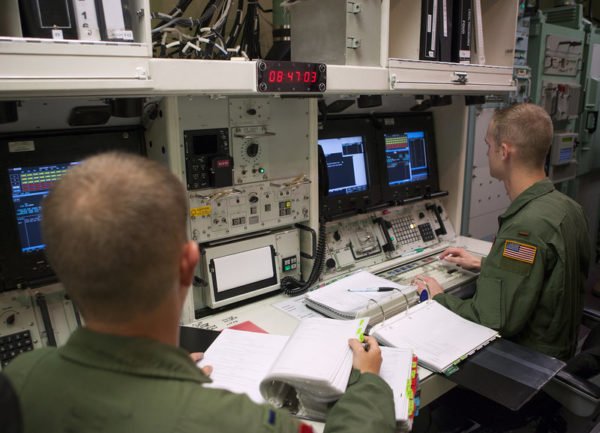
But a U.S. national document prepared for congress has revealed that the country’s nuclear weapons are still being controlled by an outdated technology. According to the document, the military’s nuclear arsenal is controlled by computers built in the 1970s that still use 8-inch floppy disks.
In addition, the country is spending around $60 billion each year to maintain museum-ready computers. Moreover, creators of these computers have retired, and many personnel maintaining the computers do not even know how to operate them anymore.
The Defense Department’s Strategic Automated Command and Control System (DDSACCS), which is used to send and receive emergency action messages to U.S. nuclear forces, runs on a 1970s IBM computing platform that still use 8-inch floppy disks.
“We’re not even talking the more modern 3.5in floppy disk that millennials might only know as the save icon. We’re talking the OG 8in floppy, which was a large floppy square with a magnetic disk inside it. They became commercially available in 1971, but were replaced by the 5¼in floppy in 1976, and by the more familiar hard plastic 3.5in floppy in 1982”, a comment published on the Guardian said.
The U.S. Government Accountability Office has admitted that the computers operating such an important national asset are outdated. It added that parts for the computers can not be replaced as they are obsolete.
Reacting to the document, the Pentagon said it was instigating a full replacement of the outdated computers. It further said the entire upgrade of the country’s nuclear weapon systems would take longer, but the floppy disks would be replaced by the end of this year.
This revelation has made some observers to question whether the U.S. has the capability to even launch a nuclear weapon in case the need arises. The American economist and journalist, Paul Craig Roberts said the U.S. is ready for war but not prepared for it.
What do officials at the Defense Department do with the huge military spending if the country is still using such an outdated technology to operate its nuclear weapons?
This article has been shared from our website: http://anonymous-news.com/u-s-nuclear-weapons-are-controlled-by-1970s-computers-with-8-inch-floppy-disks/



Great article!
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with us, I am going to be less stupid again tonight! ;)
Namaste :)
Thanks for appreciating it!
oh SNAP..

This post received a 4.1% upvote from @randowhale thanks to @anonnews! For more information, click here!
I thought it was 1980s technology!!
At least they cant be hacked remotely.
Exactly.
Great post man! :)
This should have been a classified information until the replacement or upgrade is made, those terrorists are reading this also.
If the computers are outdated, then you're absolutely right that the U.S. is ready for war but not prepared.
I'm thinking that the reason that they are spending the 60 billion per year to keep the current technology viable is because it would cost in the mid-trillions to replace/change the computers. Changing any technology platform takes years in order to scope it out properly. They also have to be careful from a security perspective on how they engage any upgrades. I'm sure that the global expectations that the US be the sheriff of the world (and paying for it) also takes its toll on the amount of R&D procurements that they intend to complete in any given year.
Very good assessment.
great info i was surprised to know that but at that time it was the latest technology this thing look ocvard now but at that time it was an advanced technology for using and handling the nuclear weapons . it a sensitive topic and i hope you will explain it in more deatail