Nervous system manipulation by electromagnetic fields from monitors --- US Patent 6506148 B2
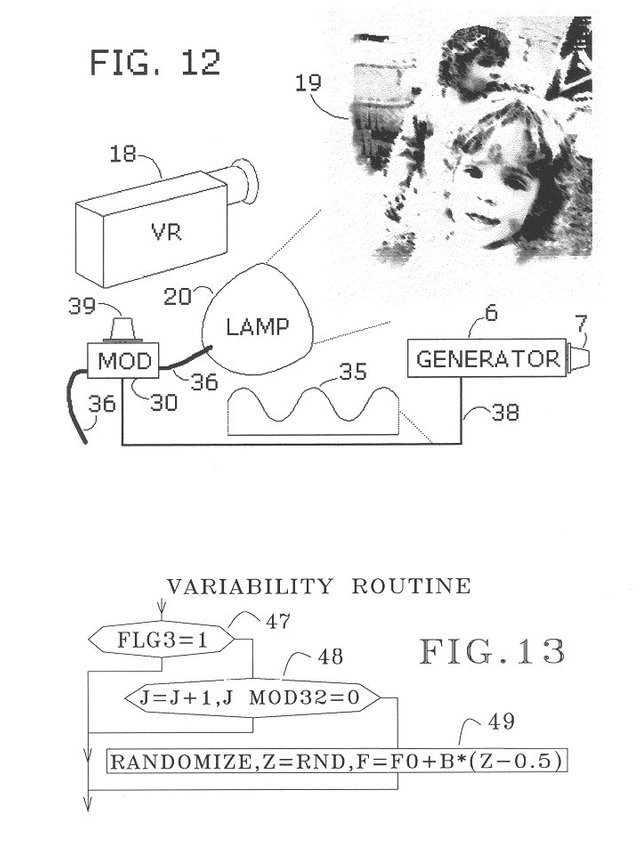
As you stare into your monitor, relax with the knowledge that as far back as 2001, grants were being awarded to complete patents on technology aimed at manipulating your nervous system by simply being close to your computer monitor or TV screen. One of the graphics describing this technology even features children as the subjects. It's been nearly two decades since someone pursued this capability, which begs the question -- what do they have now?
As the patent describes itself:
Publication number: US6506148 B2 Publication type: Grant Application number: US 09/872,528 Publication date: Jan 14, 2003 Filing date: Jun 1, 2001 Priority date: Jun 1, 2001 Fee status: Paid
Nervous system manipulation by electromagnetic fields from monitors
US 6506148 B2
Abstract
Physiological effects have been observed in a human subject in response to stimulation of the skin with weak electromagnetic fields that are pulsed with certain frequencies near ½ Hz or 2.4 Hz, such as to excite a sensory resonance. Many computer monitors and TV tubes, when displaying pulsed images, emit pulsed electromagnetic fields of sufficient amplitudes to cause such excitation. It is therefore possible to manipulate the nervous system of a subject by pulsing images displayed on a nearby computer monitor or TV set. For the latter, the image pulsing may be embedded in the program material, or it may be overlaid by modulating a video stream, either as an RF signal or as a video signal. The image displayed on a computer monitor may be pulsed effectively by a simple computer program. For certain monitors, pulsed electromagnetic fields capable of exciting sensory resonances in nearby subjects may be generated even as the displayed images are pulsed with subliminal intensity.
"The invention relates to the stimulation of the human nervous system by an electromagnetic field applied externally to the body. A neurological effect of external electric fields has been mentioned by Wiener (1958), in a discussion of the bunching of brain waves through nonlinear interactions. The electric field was arranged to provide 'a direct electrical driving of the brain.'"
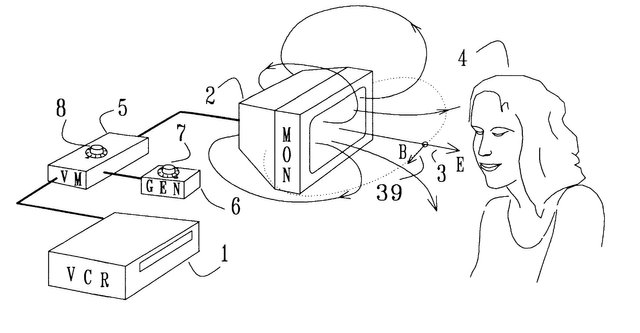
"Computer monitors and TV monitors can be made to emit weak low-frequency electromagnetic fields merely by pulsing the intensity of displayed images. Experiments have shown that the ½ Hz sensory resonance can be excited in this manner in a subject near the monitor. The 2.4 Hz sensory resonance can also be excited in this fashion. Hence, a TV monitor or computer monitor can be used to manipulate the nervous system of nearby people. The implementations of the invention are adapted to the source of video stream that drives the monitor, be it a computer program, a TV broadcast, a video tape or a digital video disc (DVD)."
"A DVD can be edited through software, by introducing pulse-like variations in the digital RGB signals. Image intensity pulses can be overlaid onto the analog component video output of a DVD player by modulating the luminance signal component. Before entering the TV set, a television signal can be modulated such as to cause pulsing of the image intensity by means of a variable delay line that is connected to a pulse generator. Certain monitors can emit electromagnetic field pulses that excite a sensory resonance in a nearby subject, through image pulses that are so weak as to be subliminal. This is unfortunate since it opens a way for mischievous application of the invention, whereby people are exposed unknowingly to manipulation of their nervous systems for someone else's purposes. Such application would be unethical and is of course not advocated. It is mentioned here in order to alert the public to the possibility of covert abuse that may occur while being online, or while watching TV, a video, or a DVD."
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
http://www.google.ca/patents/US6506148