Matic Network announced its mainnet is Live Now
Mainnet is Going Live! Announcing the Launch Sequence
Matic Network is a well known blockchain application platform that provides developers with the ability to deploy applications with faster and cheaper transactions than Ethereum while still maintaining a high level of security, by utilizing a novel combination of the hybrid Proof-of-Stake and Plasma-enabled sidechain.
Architecturally, the beauty of Matic Network is its elegant design, which features a generic validation layer separated from various execution environments. This architecture provides Matic Network with a huge breakthrough for growth for Matic and increases its addressable market size, along with the addressable developer community size, many fold ad many possibilities. More on this hugely exciting front later.
When Matic Network started in 2017, the initial hypothesis was to build a platform that all developers would find easy to develop on, and would work as a Layer 2 solution to Ethereum only. Now they understood early on that there would be various scaling approaches that could apply and Matic Network did not want to tie it to a specific solution. With this in mind, Matic architected solution to have a core Proof-of-Stake layer with the MATIC token securing it.
Currently, developers can use Plasma for specific state transitions for which Plasma predicates have been written such as ERC20, ERC721, asset swaps or other custom predicates to a new level. For arbitrary state transitions, they can use PoS. Or both! This is made possible by Matic Network's hybrid construction.
Design Decisions
Some decisions that they have made early on in Matic design have proved to be very beneficial during the course of implementing platform over the last 2+ years:
- Implementation of a Proof-of-Stake(PoS) protocol
- EVM sidechain based on the Proof-of-Stake implementation
- Plasma sidechain support with restricted contracts on the same EVM sidechain (account-based Plasma implementation)
- Division of validation and block production into 2 layers
- Periodic checkpointing of sidechain state to Ethereum
- Staking management with MATIC ($Matic) ERC20 tokens on Ethereum Network
- Liquid delegation managed on Ethereum
- Novel Bor sidechain consensus implementations
- Usage of existing, battle-tested tools for modules that didn’t need reinventing (e.g. peer-to-peer gossiping, Tendermint consensus)
- Block producer committee selection via a pluggable randomization algorithm (to ensure future upgradeability with newer randomization techniques)
- Native mechanism for interoperability with other chains (e.g. sidechannel implementation for communication between Matic and Ethereum)
- Ability to integrate newer and yet unknown types of scaling approaches into the Proof-of-Stake layer of Matic Network
Counter Stake Progress – Incentivised Staking Testnet
Counter Stake is Matic Network’s experimental testing event for everyone wishing to participate in the testing of the Matic network, by validating, conducting economic or other attacks, testing the network’s limitations and earning rewards by showcasing technical skills. Counter Stake allows anyone to compete with other validators on Matic's testnet and earn rewards.
Counter Stake comprises of 3 stages:
Stage 0 (status: complete)
Matic Network received an overwhelming response for this stage. Stage 0 was initiated in November 2019 by the team. In this stage the objective was to become familiarised with setting up a node for Matic Network. This would later be a foundation for Stage 1 once the community was familiarised with the process, components and requirements.
During this stage validators were able to:
- Understand the core components of the chain
- Get their hands on setting up theMatic testnet nodes
- Run their nodes and keep them synced
- Get more familiar with the setup process and core components
Stage 1 (status: complete)
Matic Network started Stage 1 on February 13, 2020. During Stage 1 the tested out running the actual blockchain. There were 300+ registrations for Stage 1 and they onboarded more than 150+ validators throughout 6 testnets. Our current testnet, CS-2006, is running with 100 Validators.
During Stage 1, validators were able to:
- Set up their node
- Stake on Matic through CLI or Dashboard
- Delegate to a validator
- Claim and re-stake their rewards
- Replace validators via an on-chain auction process
- And unstake from the network
For more details on Stage 1, they released a blog post highlighting all the important points and milestones they achieved: https://blog.matic.network/counter-stake-stage-1-is-complete-the-final-stage-begins-matic-network/
Stage 2 (status: ongoing)
Even though Stage 2 is currently underway, Matic's current testnet (CS-2006), running with 100+ validators, has been carried over to Stage 2, and this testnet has been running for 3+ weeks. This gives us enough confidence to initiate the network with the initial set of validators.
Stage 2 is an adversarial stage where testnet of the Matic Network is being “stress-tested” thoroughly in terms of attempts to break it. It will be an ongoing process which, along with a year-long (separate) bug bounty program, will ensure that we are made aware of any adversarial attack scenarios on the network. In Stage 2 in particular, this basically means is that we are encouraging validators to:
- Test the network for resilience against explicit exploits that take down the network
- Try to successfully execute an economic attack and find bugs in the network's system/code
Although Stage 2 has been running for 2 weeks now, with no issues found as of yet, in the case that in the later weeks of Stage 2 any issues are found, the mainnet with the initial restricted validator set will allow us to upgrade the network quickly and iterate in the live environment, which in itself is a learning process for a nascent network like Matic.
Please refer to Matic dedicated article here for a detailed overview of Counter Stake – Stage 2.
What Matic Want to Ensure for the Matic Mainnet Launch
- Developers have access to a high-performance blockchain with low-cost transactions, while still ensuring a high level of security
- Developer tooling is as close to Ethereum as possible
- That the Matic Network chain(s) runs without halting
- Applications run as expected
- Monetary value does not get lost or hacked
- Multiple validators are staking MATIC tokens, thereby running and maintaining the network
Mainnet Release Steps
The mainnet launch will be spread over multiple steps as detailed below. This multi-step process will ensure that the mainnet deployment and validator onboarding is achieved as smoothly as possible.
More importantly, it ensures that right from day 1 that DApps are able to deploy their products successfully on Matic and that their user experience is stable and robust. That’s also one of the reasons why we are choosing to start with DApp partners as early validators.
The network will move from one stage to the next based on the goals for each stage. The intent is to ensure that early issues get addressed and resolved quickly. We do expect our network software to function well, but we believe the most pragmatic approach is to gradually rollout the network to address any unforeseen issues.
Mainnet rollout strategy
These are the steps which we will be taking to ensure our network rollout is as smooth as possible:
Description of steps:
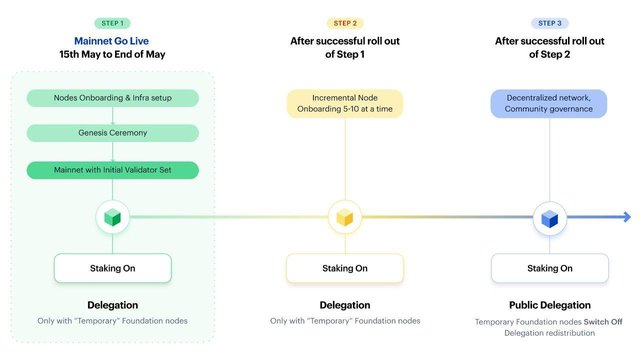
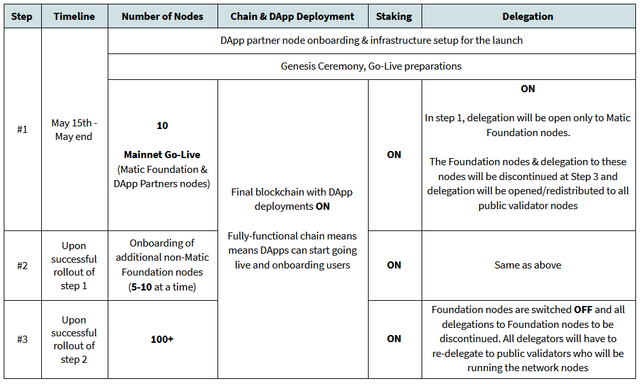
Step #1: DApp partner onboarding, Genesis Ceremony & mainnnet Go-Live with initial validator set (only Matic Foundation nodes and nodes run by select validators invited by the Matic team will be active)
Step #2: Additional validator slots to be opened gradually (in batches of 5-10) to public validators
**Step #3: **Full-blown public validator-run decentralized network
#1 – Mainnet with Initial Validator Set
Timeline: May 15th to end of May
During step 1, we will onboard the nodes run by our selected DApp partners and will ensure our infrastructure is set up for the launch of the network. We will then hold our Genesis Ceremony, and make the necessary preparations before going live.
The first step of the Matic mainnet will be launched with an initial set of validators including the Matic Foundation nodes and some select validators who have been working closely with the Matic team. These include professional validators and marquee DApps who will be deploying to the mainnet. The list of DApp Partners which are going to be in the first cohort is being finalized and will be released shortly.
A very important point here is that the state of the network will be persisted and maintained by the Matic Foundation in this step. This will continue until the final step.
Developers will be able to deploy their applications on Matic directly by acquiring MATIC tokens on Ethereum from an exchange of their choice.
ETH, MATIC and other ERC20 tokens can be moved to Matic from Ethereum and vice versa.
The Betav2 mainnet and Alpha-mainnets will be retired. Appropriate support will be provided to migrate state and tokens from both of these mainnets to the final v1 mainnet.
Validator slot auction and replacement will be disabled during this phase. Slashing is also disabled in this phase – this will be enabled in later stages.
The final testnet of Counter Stake – currently CS-2006 – will be transitioned to be a testbed for developers and will replace all current testnets, including Testnetv2 and Testnetv3.
The goals for this phase are to:
- Ensure that the mainnet is working with a restricted set of validators, with >⅔ of the stake controlled by Matic Foundation and the select set of validators
- Enable developers to deploy applications right away
- Make sure the network continues operating even if native network calls for fetching Ethereum staking contract state or other network calls fail
- Ensure any bugs/issues are addressed with smoother validator coordination
- Continue code and security reviews
- Upgrade nodes based on any bugs reported via the Bug Bounty program
#2 – Validator Slots to be Gradually Opened for Public Validators
Timeline: Upon successful rollout of step 1
This is not a discrete, but continuous phase in which additional validators slots are being opened gradually in batches of 5-10.
This ensures the smooth addition of external validators into the network, and the resolution of any unforeseen issues that may be encountered.
The validator slot auction process will be enabled and validators can be replaced. Interested validators will need to participate in the staking slot auction process, if a slot is not empty, by staking a higher amount of MATIC tokens compared to the incumbent.
Slashing is disabled in this stage.
The goals for this phase are to:
- Enable a limited set of validators to join the network and ensure the ability of the Matic team to address any bugs/issues in the network nodes and/or contracts
- Test the validator community governance process
- Ensure any bugs/issues are addressed with smoother validator coordination
- Continue code and security reviews
- Upgrade nodes based on any bugs reported via the Bug Bounty program
#3 – Full-Blown Decentralized Public Network Run by External Validators
**Timeline: **Upon successful rollout of step 2 & validator community governance
Once this phase is reached, the network is decentralized and will be entirely run by external public validators only. The network will not depend on the Matic Foundation nodes to be running.
Entry onto this phase will be decided by validator governance.
**Matic Foundation and the initial set of nodes will be switched off and delegation will be enabled **for all external validators.
NOTES:
- All delegators to Foundation nodes have to mandatorily switch their delegations to public validators. This will ensure that public validators exclusively receive delegations from the Matic community, and there is now no necessary role of the temporary Foundation nodes.
- Matic Foundation may or may not run nodes after step 2, depending on the overall feedback.
Slashing is expected to be enabled in this stage. More details regarding the details of the slashing mechanism and the rationale behind it will be explained in a later blog post.
This phase is when the network reaches true decentralization and the governance will be handed over to the community via an on-chain governance mechanism.
What will be Present by Stage #3?
- One EVM-based sidechain with fast block times and low gas fees
- High throughput (~1k to 4k transactions-per-second expected on mainnet – upto 17k TPS found during benchmarking tests)
- Moving ETH, ERC20 and ERC721 assets from Ethereum to Matic and vice versa
- Full Proof-of-Stake implementation spread across Ethereum staking smart contracts and the Heimdall validator layer
- Staking of MATIC tokens (albeit for the restricted set of validators only)
- Delegation of MATIC tokens
- Liquid delegation or staking derivatives on Ethereum staking smart contracts
- Pseudo-randomized block producer committee selection
- Side-channel mechanism to ensure sync between staking contracts on Ethereum, Heimdall validator node and Bor sidechain
- State sync mechanism to pass generalized contract state between Ethereum and Matic
- Plasma MoreVP account-based implementation
- Plasma predicates – ERC20, ERC721 and atomic swap predicates present by default
- Upgradeability of contracts on Ethereum (staking, delegation, plasma)
More Network Features for Future Stages
- Multiple sidechains
- Unbiasable randomness
- Optimization of historical state storage
- Upgradeability of the chain without hard forks
- Inter-sidechain communication
- And more…
Staking Economics
The Matic ERC20 token lives on Ethereum and this will continue being the case after mainnet launch. The token is not inflationary and a fixed percentage of the token supply is reserved for staking rewards for the first 5 years.
For a detailed overview of the Matic Network staking economics, please refer to the following articles:
- https://blog.matic.network/matic-network-staking-economics/
- https://blog.matic.network/matic-network-staking-update-and-becoming-a-validator/
What Does This Mean for our Stakeholders?
Developers (from day 1 of mainnet – step #1)
- Deploy your DApp on a high-performance blockchain with a ~1-2 second block time, and transaction costs lower than 1/100th of that of Ethereum gas fee costs
- Be assured that state will persisted across steps
- Move assets from Ethereum to Matic and vice versa
- Pay gas fees on behalf of users or let users pay for gas
Validators
- Select validators invited by Matic Foundation to run nodes initially (day 1 – step #1)
- Additional validator slots will be opened up gradually with advance notice (step #2)
- Stake with MATIC tokens on these validator slots when opened (step #2)
- Earn staking rewards based on the Matic network economics (step #2)
- Once the network is run by 100 external validator nodes, and the Matic Foundation nodes are shut down, all delegators will need to move their staked MATIC tokens to the public validators (step #3)
Token holders and delegators
- Delegate with the initial set of validators (from day 1 – step #1)
- Start earning staking rewards based on delegation and validator performance (day 1 – step #1)
- Move delegated tokens to public validators (step #3)
Let the fun begin! “pew pew” 🙂