Technical Criteria For Classifying a Power Plant as Either a Peak or Base Load Power Plant
It is worthy to keep in mind that there are different classifications of power plants which could be as a result of the type of fuel it uses, whether the fuel is exhaustible or inexhaustible, the mode of conversion from the raw energy to electrical energy, whether it is conventional or non-conventional.

Some classifications hinges on whether the fuel for the power plant is renewable or non-renewable by nature, other criteria could be whether it can deliver bulk power or just small output as is witnessed in most of direct energy conversion generators.
No matter the criteria for classifications, the primary classification of a power plant that is relevant to a power engineer is mostly whether the plant can run continuously for long hours without incurring much cost with regards to fuel consumed. Secondly, of importance is the speed in which one can start a power plant from the cold condition and its ability to pick up load immediately.
Those power plants that can run for days at a minimal running cost is described as a baseload power plant. We should not confuse high capital cost with low operating or operational cost.
A power plant can have a high capital cost but with a negligible running cost. A typical example of such power plant with high capital cost and the low running cost is the hydropower plant.
Another power plant close to it with regards to low operational cost is the Nuclear power plants which makes use of a small quantity of fuel to achieve a much higher output. It has been estimated that the complete fission of 1kg of uranium-235 is capable of producing equivalent energy as would be produced by 4500 tons of high-quality coal. Is that not impressive?
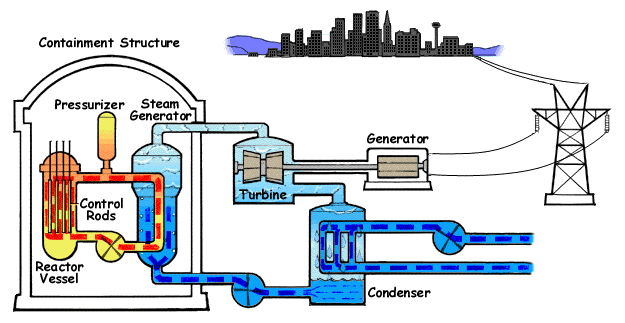
Such power plant will have a lower running cost as compared to a steam power plant of the same capacity owing to the money that will be saved regarding transporting coal from the coal mine to the power plant, assuming the steam power plant is not located close to the coal mine.
Another reason for ranking nuclear power plant over steam power plant from the economic point of view could come from the fact that there will be no need to handle large quantities of ash as the by-product of combustion of coal.
Before we venture further, it is imperative, we explain the meaning of a base load and a peak load. After which we describe the characteristics of an ideal base and peak load power plants. This description will help in highlighting the attributes of the power plant that put them in a position to be described as either a base load or a peak load power plant.
The load on any power plant can be conveniently grouped into two, namely:
- The base load
- The peak load
Base Load
The base load is the unvarying and steady load which occurs almost the whole day on the power plant (this load is often regarded as the steady component).
The power plants to be employed as base load power plant should have the following attributes:
- Low operating cost
- Capacity for working continuously for long periods
- Quick starting capability and ease with which it can be synchronised with other plants in the system coupled with quick loading capability.
Peak Load
Peak loads are the various peak demands of the load over and beyond the base load of the power plant. The peak load depends on the time of day and days of the week as well as factors that results in the majority of the consumers having similar load patterns such as is experienced during public holidays or popular television programmes.
Classification of Power Plants According to the Load Supplied
- Base Load Power Plants: These are power plants which can take up a load on the base portion of the load curve of the power system. Such plants are usually of large capacity.
Base load involves the constant, less varying load in a power system which the power plant must carry continuously. As a result, the load factor such plant is high. Notice that the load factor is the ratio of the average load and the maximum demand on the power plant.
High load factor implies that the maximum demand on the station at any particular time will be clipped and tend to the less varying component. The base load should be supplied by the most efficient plant especially regarding lesser money incurred in fuel (lowest operating cost).
This plant should be capable of running 24-hours a day, while the up-shoot or the load above base load should be catered for by the less efficient plants (with lower capital cost).
Before progressing to describe a peak load power plant, it is worthy to mention that a plant can also supply what is called the spinning reserve. It is common practice to hold a specific part of the power the plant is capable of producing in reserve to accommodate any uncertainty or contingency that could materialise such as generator unit tripping or a sudden rise in load demand.
In as much as hydropower plants are baseload power plants, they are also used to supply spinning reserve. A part or all of this reserve must be primed to come into operation immediately and as an outcome, some machines are run at about 75% of their full output to cater for this spare generating capacity known as the spinning reserve.
It is customary to allow reserve margin in the total generation plant that is commissioned to accommodate the sudden loss of plants due to faults, scheduled outages for maintenance and errors in forecasting load or the output of renewable generators.
It is not unusual to allow a margin of generation of about 20% beyond the annual peak demand. A higher penetration of renewables suggests that a higher reserve margin is prudent owing to their intermittent and non-reliable nature.
In a well-designed power system, it is essential to have a generator mix consisting of hydro, thermal, renewable, nuclear and gas turbine. The best combination offers the most economical operation, but this is highly reliant on fuel prices which can fluctuate over time and with a change in location.
Plants that can be used as a baseload power plant include:
- Hydroelectric Power plants
- Nuclear power plant
- Steam power plants
Peak Load Power Plants
These are plants used to supply peak loads of the system which comprises of the load at the top portion of the load curve.
Plants that can be used as peak load power plants include:
- Gas turbine power plants
- Hydroelectric power plant
- Pumped Storage plants
We will consider every one of these power plants and delve into the attributes that make it either a base load or peak load power plant.
Hydroelectric Powerplant
Hydroelectric power plant utilises the hydraulic energy of falling water to generate electricity. Once the water has the potential energy, it can do some useful work if it is allowed to drop from the height it was positioned.

It can be likened to a person that has water placed in an overhead tank which is channelled to the house and secured through taps. Whenever he needs water, all he just needs to do is to open the tap, and the water will flow. He does not need extra energy to bring the water down, neither does he expend any extra power to maintain the water in the overhead tank.
Such is the setup of hydroelectric power plants that makes them attractive as a peak load power plant. We know that water is free and as such the running cost of hydroelectric plants is considerably low. It is self-starting. Hydroelectric plant has quick starting capability and the advantage that no energy losses are incurred when at a standstill.
It can be used as both a peak and base load plant for power generation because of this ability to meet peak loads at minimum operating cost and can work in conjunction with thermal stations.
It does not need external power from the grid for it to start. This property of starting without relying on external power is known as Black Starting Capability.
Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants can be used as base load plants. They are not suited for variable load operations as the reactor cannot be quickly controlled to respond to load variations efficiently. The reactor comprises of the fuel that comes in the form of rods or pellets housed in an environment (moderator) which can slow down the neutrons and products of fission and in which the heat is released.
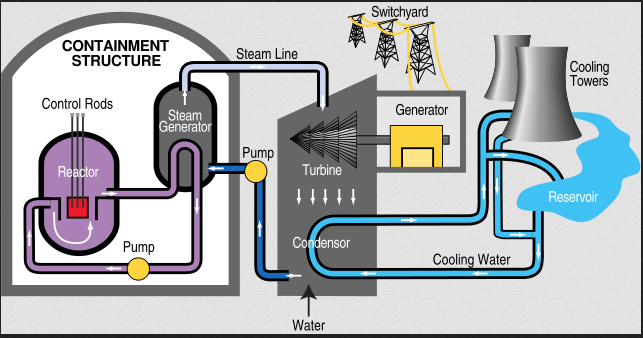.png)
The moderator can come in the form of light or heavy water or graphite. Also located in the moderator are movable rods known as control rods which absorb neutrons and as a result exert control over the fission process.
Nuclear fission comes in the form of a chain reaction of which care should be taken in the control of neutron release or absorption. This control is not quite easy as to adjust immediately as the load varies and the effect is that nuclear power plants are better off used as a baseload power plant with an almost unvarying constant load.
Steam Power Plant
The steam power plant is used as a baseload power plant because one of the attributes it falls short on as a peak load power plant is the ability to start up quickly and pick up load immediately.
The steam power plant has its raw energy in coal which is burnt in the boiler furnace to produce heat; this heat is used the raise steam from water. When you examine these processes, you will notice that for steam to perform as a peak load power plant it must have its boiler in operation before the time it will need to be called into operation.
This concept of running the boiler and keeping it hot is not an economical one and as a result, it is better suited as a base load power plant.
Gas Turbine Power Plant
The gas turbine power plant is not self-starting because external power is needed to keep the compressor running before the part of the power of the turbine takes over supplying the compressor. Recall that the compressor, gas turbine and the alternator is mounted on the same shaft for ease of operation.
Gas turbine power plant despite having low efficiency is ideally suited as a peak load power plant because of its fast start capability (2–3 minutes). Another reason is the flexibility with which it can follow load variation, the relative speed of installation because of its modular nature and factory-supplied units and its ability to run on oil in the event of a shortage of gas.
Pumped Water Storage
Pumped water storage plants are typical peak load plants by nature of its design. It can even be likened to a storage system such as the battery. During the period of light load, excess power available from the grid is utilised to pump water up from the lower reservoir to the upper tank.
When the demand is high on the system, the water is allowed to fall from the upper reservoir to the lower reservoir from where the kinetic energy is harnessed using water turbine which drives the alternator to generate electricity.
Conclusion
The trend is to adopt the interconnected system where different generator mix are connected to the grid. The interconnection of power plants allows the power system engineer to choose the right generator mix to achieve economy, efficiency, reliability and security of the power system.
To achieve economy, we need to choose the plant that has the least running cost as baseload plant. This is because base load plant operate continuously throughout the hours of the day and as such its cost per kilowatt of power generated must be low.
On the other hand, a peak load plant must have the ability to start up quickly from cold condition and pick up load in a very short time. It should also be easy to be paralleled and synchronized with other generators in the grid system to maintain stability of the system.
Electricity is produced and is consumed at the same time without efficient means of storage, and this is a massive challenge to the operator as it gives the operator limited control over the load.
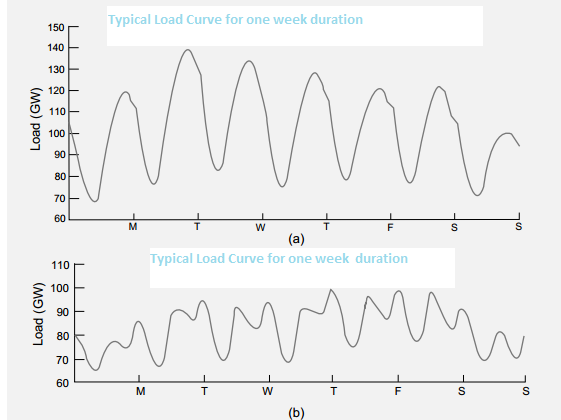
The control engineers strive to keep the output from the generators equal to the connected load at the specified voltage and frequency which is quite tricky from a glance at any typical load curve. The load curve consists of a steady component known as the base load, plus peaks that fluctuate with the demand of the consumer which has no accurate way of predicting to a certainty the pattern it will take.
This is so a detailed effort from the boss. This got me
This has been a problem in most power generating system. Efficient storage hasn't been well done and most times we would have to run emergency systems to cater for high load requirements.
Nice compilation boss @kaydee
StemngFamily #KeepTheTrend #KeepUsGrowing
Many thanks for making out time to visit my blog despite your busy schedules. I appreciate your input and time immensely.
You're welcomed sire. You're really putting alot of efforts here.
Keep writing sire.