The Mitosis and Meiosis // Analysis
Mitosis
The process of the mitosis splits into four stages: In the profase the cromatina countess and it forms the chromosomes, each one has doubled during the interface and it is formed by two cromátidas, calls cromátidas join, joined by the centrómero. The centriolos go separating, leaving a bundle of microtúbulos, which form the husomitótico and it disintegrates the nuclear membrane.
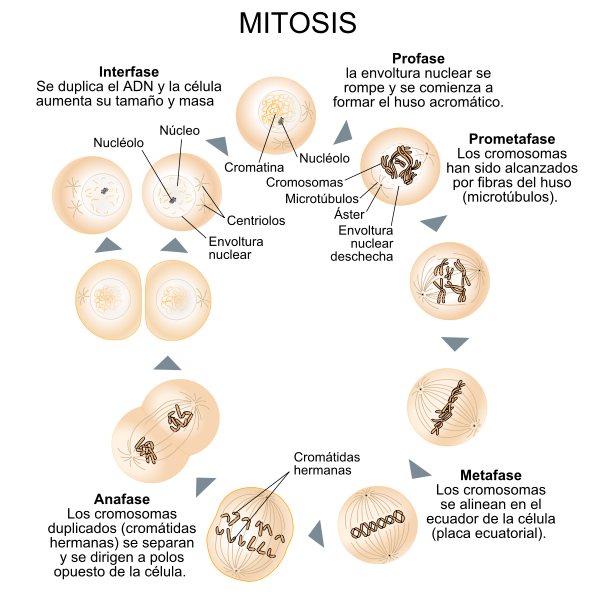
Diagram showing the changes that happen in the centrosomas and the nucleus of a cell in the process of the division mitótica. The Ist the IIIrd, profase; the IVth, prometafase; the Vth, metaphase; the VI and VIIth, anafase; the VIII and IXth, telofase, source of image of mastery of wikimedia commons
In the metaphase the chromosomes remain arranged as form, that all the centrómeros are in the same on the halfway plane of two pairs of centriolos, the plane in which the centrómeros are placed is the equatorial badge.
In the anafase the cromátidas of every Y-chromosomes separate they are located each one in the poles put up of the bone. In the telofase the cromátidas of every chromosome approach the centríolos and the nuclear membranes form, the cellular division ends with the segmentation of the citoplasma or citocinesis.
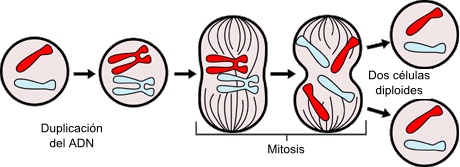
Scheme that shows in an abridged way what happens during the mitosis, source of image of mastery of wikimedia commons
The meiosis
The miosis consists of two divisions successive similar to the mitosis, these divisions of the alone nuclei are accompanied of a few divisions of the chromosomes. Each of the divisions meióticas split into four phases, profess, metaphase, anafase and telofase.
The profase of the first division has split in turn into five periods as they it are: leptotena, cigotena, paquitena, diplotena and diacinesis, at the beginning of the first division meiótica every chromosomes, forming for two cromátidas sister, it approaches his counterpart.
Next the exchange of genes takes place or entrecruzamiento on having mated the homologous chromosomes, which further on separate and two cells form, at the end of the first division meiótica two obtains cell 2n with following peculiarities, that distinguishes clearly d the cells diploides formed for mitosis: two copy of every chromosomes derive from the only one of the homologous existing chromosomes in the cells originally and sisters joined by his centrómeros are inherited in forman of cromátidas, forming this way only one chromosome. As soon as the first division was finished meiótica and without the replicación of ADN happens, the second division begins meiótica, whose stages it corresponds to a division meiótica conventional, it is possible to sum up that the whole process saying, that the meiosis consists of two cellular divisions successive, that take place after the only phase of chromosomal replicación, from what four cells originate haploides from cells diploide, that the meiosis suffers.
sexual and asexual Reproduction implies the miscellany of the chromosomal endowments proceeding from two individuals different from the species to produce progeny, the cycle of the sexual reproduction implies an alternation of generations of cells haploides, each of the cells haploides, each of which contains a simple endowment of chromosomes, with generations of cells diploides and it is in turn they contain a double endowment of chromosomes of the ancestors cells are achieved by the merger of two haploides cells or sperm cells, that they form one diploide of the zigoto.
The cell diploide this way formed will split mitóticamente to give to place to the adult organism, new cells are generated haploides when a few cells diploide it divides by the process known for meiosis. This process of cellular division for which from a cell diploide, four cells are obtained haploides. The divisions mitóticas lead to lineages of cells, which have the same number of chromosomes, that the mother where the division mitótica of a cell diploide (2n), it generates two cells daughters diploides. The mitosis is the system for which they grow multicellular, even some organisms use organism, to reproduce in an asexual way.
Secondhand bibliography.
Mitosis and Apoptosis - Page 17 for Ivor D. Bowen, Century. M. Bowen? Sandra Maureen Bowen - 1998.
General biology - Page 132 for Julián Monge-Nájera - 2002.
Mitosis: Methods and Protocols for Andrew D. McAinsh - 2014.
