Oral Cancer: Risk factors and Management.
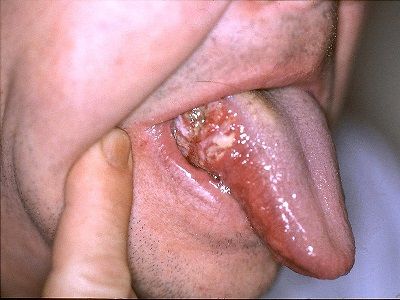
Today I will be discussing the risk factors associated with oral cancer and in my next post I will discuss ways of preventing and treatment options for Oral Cancer.
Oral cancer is a malignant growth found on the lips,tongue, floor of the mouth, buccal mucosa, para-oral sites such as salivary glands, the oro-pharynx and nasopharynx. Oral cancer constitute a global health challenge as reported new cases worldwide exceeds 640,000 annually.
It is known to be 6th of the 10 most common malignancies in the world. It constitutes about 40% of all cancers in Asia, while in the UK the incidence is 2 in 100,000 population per year. In the USA over 30,000 new cases of oral cancer are diagnosed yearly. In Nigeria however, study has recorded low prevalence of between 1.2%-2.5% (Lawal et al., 2013)
About 80% of all cancer affecting the oral cavity is Squamous cell carcinomas arising from the lips, tongue and oral mucosa. Age predilection is above 40 years in low prevalence areas,but 35yrs in high prevalence areas (India, Brazil, Papua New-Guinea, France and Western Europe). The reason for this is as a result of use of oral snuff/smokeless tobacco as teenagers that is common in these regions. It is said to be more common among Males because Males are involved with risk factors and occupational exposure (out door exposure- UV light) than Females.
What are Precancerous lesions?
The WHO in 1978 described these lesions as a “generalized state associated with a significantly increased risk of cancer”. This means that whenever these lesions are seen in any part of the mouth, it raises a high index of suspicious for oral cancer.
Types of precancerous lesions:
- Leukoplakia- a white patch or plaque not easily wiped off arising not by chemical or any physical injury and can not be classified clinically or histologically as any other disease.
- Erythroplakia is a red patch that can not be classified clinically or histologically as any other disease. Its less common, has increase potential for malignancy.
Malignancy potential of both types of lesion is the evidence of epithelial dysplasia on histology.
Lesions on the floor of the mouth, lateral borders of the tongue, lower buccal sulcus, alveoli ridge and angle of the mouth are high risk sites.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Tobacco
Smoke contains a lot of carcinogens which include Nitrosamines and initiators such as 3, 4 1Benzo pyrene a polycylic hydrocarbons and promoters such as phenols. Polonium and Carbon 14 (radioactive element) may also be found. See my previous post on cigarette smoking Here.
Also thermal irritation from use of clay pipe or reverse smoking can predispose the oral mucosal to malignant transformation
Alcohol
Alcohol is converted into acetaldehyde (carcinogenic) by the liver. This is toxic (cytotoxic forms free radicals) and interferes with repair of alkylated DNA (Ogden and Wight, 1998) leading to the development of Oral cancers.
Alcohol is an irritant to oral mucosa and solvent (vehicle) to many carcinogens.
Risk of alcohol causing oral cancer depends on the content, quantity, level of impurities and some protective additives in the alcohol.Usually it causes cancer of the floor of the mouth and tongue (serves as trough). Its potentiate the effects of tobacco or other topical carcinogens.
Sunlight/ Ultraviolet rays
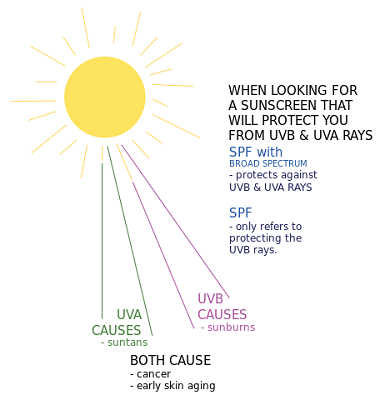
However, the degree of risk depends on the type of UV rays, the intensity, and quantity absorbed (melanin protects absorption of UV light).
Solar UV has 3 types:
- UVA (320-400nm),
- UVB )280-320 nm) and
- UVC (200-280nm).
The UVC is the most deadly among them but the Ozone layer have filtered out this.
UVB is attributable to the formation of pyrimidine dimers in the DNA which is a form of DNA damage.
Ionizing radiation
This causes direct and indirect effects on the DNA. The indirect effects is via the formation of free radicals leading to DNA damage. It also can directly damage the DNA on its own.
Infections
Various Fungal and Viral infections has been implicated in the aetiology of oral cancer.
Virus
Recently Human Papilloma virus(HPC) and Herpex Simplex Virus(HPV) have both been established as etiological factors in oral cancer. In about 24% of cases of Oral cancer, HPV has been identified and the major implicated type of HPV is types 16 , 18,31 and 33.HPV is usually transmitted in people who engages in oral sex and also multiple sexual pattners.
The virus causes insertion of specific viral DNA fragments (early genes E5, E6 and E7) into the host cellular genome thereby expressing oncogenic proteins that initiate tumor suppresors, activate cyclins, inhibit apoptosis and combat cellular senescence.
Herpex Simplex Virus type 1 causes various types of mucosal ulceration which can predisposed to malignant transformation.
Fungi
Malnutrition and Diet
Deficiency of dietary Vitamins such as A (B carotene),D,E, C and K are associated with cancer formation due to lack of anti-oxidant effects of these minerals. Iron deficiency is associated with upper aero-digestive cancers.
Eating of raw vegetables and fresh fruits are preventive measures
Other Factors include
Habits
Bethel nuts chewing , areca nut etc. are associated with sub-mucous fibrosis.
Kolanut is also found to be associated with cancer changes in cells in Nigeria (Lawal et al., 2013)
Chronic Irritation caused by ill fitting dental prostheses, jagged edges of restorations, presence of dental calculus and poor oral hygiene
Immune deficiency/suppression
Conditions such as HIV/AIDS causes Kaposis sarcoma of the oral cavity and also chronic use of immune suppressants
Occupational hazards
Workers in asbestos company, nickel, cement, coal, wood dusts, organic chemicals such as pesticides, insecticides, herbicides, fumigants etc. Farmers, road workers, miners are all vulnerable to oral cancer.
Let me stop here for today. I will be discussing the various preventive measures and options of treatment of oral cancer in my subsequent post. Till then, enjoy your day.
Thank you for reading.
Please Note: All pictures used in this post are free for usage.
References
Being A SteemStem Member
Since when does asbestos cause oral cancer? And how?