Mining and its effects on the environment (part 2)
Mining and its effects on the environment
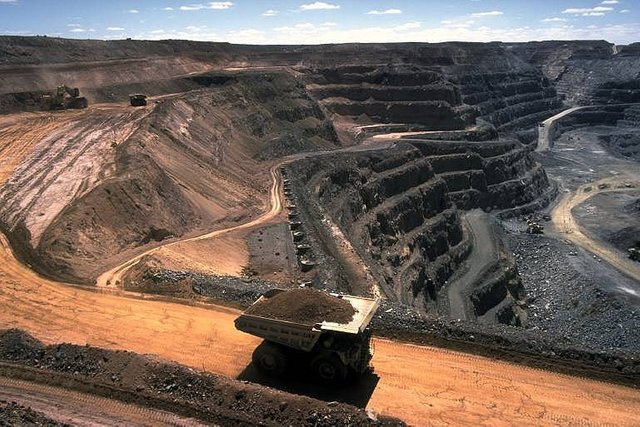

SURFACE COAL MINING
In my latest post, I introduced the methods of mining as well as the minerals that are mined and the procedures taken to mine them. In this post I’m going to be introducing the effects of mining on the environment and how it causes a negative impact.
Environmental impact of mining
Mining uses large amounts of electricity and water. If the mining process is not managed properly the acid and other chemicals can enter nearby Water Systems such as rivers and dams. This water pollution can cause extremely harmful damage to Aquatic animals and plants as well as humans who may rely on that water for drinking. Mine dumps and open pit mines change the shape of the land. Dust from open pit mines and mine dumps as well as harmful gases such a sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide from mining processes contribute to air pollution. Mining activities often encroach on protected areas and threaten biodiversity. Mining activities compete with other land use activities, such as farming.
Mine rehabilitation
There is a growing emphasis on the need to rehabilitate old mine sites that are no longer in use. Any mine rehabilitation program should:
• ensure that the abandoned mining site is safe and stable
• Remove pollutants that are contaminating the site
• Use plants to remove metals from polluted soils and water
• Use plants to stabilize the soil for vegetation
• Restore the biodiversity that existed before mining started
• Restore waterways to what they were before mining had begun
• Use land contouring to help restore drainage in the area
The atmosphere
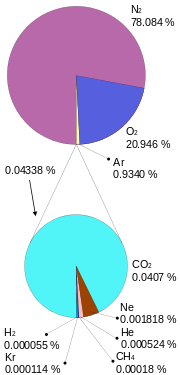
COMPOSITION OF THE EARTHS ATMOSPHERE BY VOLUME
The atmosphere is the layer of air around the Earth. Air, which is a mixture of gases, consists of nitrogen(78%), oxygen(21%), carbon dioxide (<1%) and other gases, such as inert gases and water vapour(1%).
At sea level the density of air is very high. The density decreases as the distance from the earth increases (the further away from the Earth, the thinner the air). The atmosphere is divided into 4 layers
Each layer has a different temperature gradient.The definition of temperature gradient, is how much the temperature changes with height above sea level, which is more commonly known as altitude.
The troposphere extends from sea level to approximately 10 km above the surface of the Earth. The troposphere contains more than 70% of the mass of the atmosphere and it has the greatest density of air particles. Temperature decreases as the distance from the surface increases which means that the further away you are from Earth, the colder the air. It contains most of the water vapour, clouds are formed in this layer. This is the sphere in which living organisms are found.
The stratosphere extends from about 10 km to approximately 50 km above the Earth’s surface. The air in the stratosphere is extremely thin. It includes a layer of ozone gas(O3) which absorbs Ultraviolet(UV) radiation from the Sun and Shields life below from harmful ultraviolet rays.
The unnecessary airis extremely thin and very cold. There’s enough air in this layer to burn up small rocks and dust entering from space. When a meteor enters the mesosphere, friction and pressure causes it to heat up and give off light. They are often referred to as shooting stars.
The temperature in the thermosphere can reach up to 2000 degrees Celsius at the top of the layer. Certain radio waves are reflected back to Earth off the bottom of this layer. Satellites orbit much further away. The International Space Station (ISS), orbit the earth at heights of approximately 370 km. The lowest part of the thermosphere absorbs ultraviolet radiation and dangerous rays from the sun.
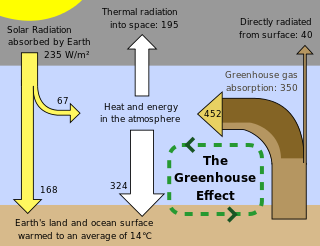
The greenhouse effect
In a gardeners greenhouse, heat from the sun enters through the glass roofs or walls. The heat does not escape and is trapped by the roof and walls and the temperature inside of the greenhouse is raised.Carbon dioxide, water vapour and methane in the atmosphere behave in the same manner as the roof and walls of a greenhouse. The atmosphere is warmed sufficiently to maintain life on Earth. This phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect maintains a stable and steady temperature on Earth.
However, over the years there has been a large increase in the emissions of greenhouse gases by Industries and Agriculture. This is having a global impact on the temperature and weather patterns on the Earth. An increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere leads to an increase in the temperature around the earth and this results in global warming. Global warming is a potentially life threatening situation.
Greenhouse gases
The major greenhouse gases include ozone, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and fluorocarbons. They come from both natural processes as well as human activities and are responsible for the disruption in the balance of the gases in the atmosphere.
Effects of global warming

SURFACE TEMPERATURE CHANGE FROM 1880 TO 2017
The effect of global warming are strongest at the poles. Ice and glaciers start melting with the increase in sea level and this causes flooding of low lying areas.
Irregular weather patterns
Irregular weather patterns have an effect on humans. Heavy rains and storms damage human property and agriculture. Plants may not survive high temperatures and this can cause ecosystems to collapse as plants are the main producers in all food chains.
Changes in food production
As temperatures around the world change, plants will find it difficult to adapt to the change in weather and some of these plants are used by humans for food and may result in a food shortage.
Droughts and desertification
Droughts are more likely to occur in the world due to higher temperatures. It means that there’s no water for plants to grow and Agriculture would be severely affected.
Changing ecosystems
Ecosystems will not change, some animal species will migrate to more suitable conditions while some will stay and try to adapt. Not all will succeed and many species will become extinct.
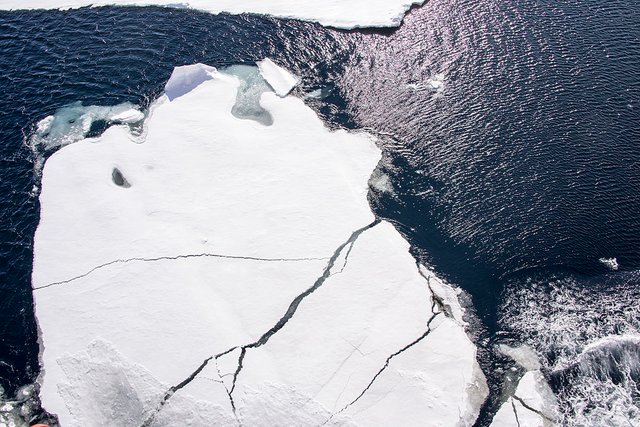

THE DARK OCEAN SURFACE REFLECTS ONLY 6% OF SOLAR RADIATION INCOMING, SEA ICE REFLECTS 50%-70% SOLAR RADIATION
Human health
Rising temperatures have an effect on the health of humans and the diseases that they are exposed to. High temperatures and humidity can lead to diseases such as malaria to start spreading rapidly. Massive flooding will enable waterborne diseases such as cholera to infect a greater population of humans.
The End
References
1.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mining
2.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atmosphere_of_Earth
3.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greenhouse_effect