Alcohol and its Effects on the Body
Alcohol, any of a class of organic compounds characterized by one or more hydroxyl (−OH) groups attached to a carbon atom of an alkyl group (hydrocarbon chain). The most common form is ethanol or ethyl alcohol which is an ingredient found in beer, wine and spirits that causes drunkenness.
It has been a part of us with lots of cultures using it for one thing or the other. It has saved the lives of some lost in the wilderness by using it as a combustible. The higher the concentration, the more combustible alcohol is with the highest percentages seen in drinks like vodka, rum, gin and the lowest being in some light beers and wine.
Alcohol is formed when yeast ferments (breaks down without oxygen) the sugars in different food. For example, wine is made from the sugar in grapes, beer from the sugar in malted barley (a type of grain), cider from the sugar in apples, vodka from the sugar in potatoes, beets or other plants.
Why do People Take Alcohol?
For the Euphoria:
Alcohol, like most addictive drugs, give some people a feeling of euphoria when they take it. I can't exactly attest to that affect of alcohol as I have never liked the taste of alcohol; the closest I got to getting drunk ended in me confused, dizzy and passing out.
Sedative effects: this effect on the body goes up as amount consumed increases. Like I said earlier, my only experience getting drunk made me pass out. It's quite a strong sedative. The downside is the hangover you get when you wake up. Fortunately for some people, they don't get this headache and photo- and phonophobia on waking up.
As a Painkiller:
This isn't exactly used often nowadays, however, during the preanesthetic era, alcohol was the go to choice for pain relief. These days we all simple go for tylenol or aspirin whenever we have a little pain. Imagine having to chug a pint of whiskey to get the pain from a wound down.
Peer pressure, social factors:
Mostly concerning teenagers and young adults, some are pressured into drinking; it might even be at an age when it is illegal. It's amazing though how the legal drinking age is 21 years in US, Canada and some other countries while it is 18 in Europe and lots of African countries. In some places it isn't even regulated or the law is never enforced as kids below 10 can buy alcoholic drinks without hinderance.
Addiction:
A lot of us know how addiction works or at least the idea of it. Those addicted can't help but drink. It may start as an occasional bottle or two at a party or as a way to forget things, maybe relax but with time, the person just continues and just can't stop the daily ritual of wanting to have a taste of it. This particularly ruins lives.
Positive effects /Health benefits
It's important to know that any possible benefit of alcohol to the human body depends solely on little to moderate consumption. Definitions of moderate consumption varies but on average a bottle of beer, a glass of red wine, or a shot of spirit a day falls in that category.
The bulk of possible positive effects of alcohol are on the cardiovascular system.
Over a hundred studies on alcohol show an inverse association between moderate drinking and risk of heart attack, ischemic (clot-caused) stroke, peripheral vascular disease, sudden cardiac death, and death from all cardiovascular causes. This effect is somewhat consistent, corresponding to a 25 percent to 40 percent reduction in risk.
Some studies found out that Gallstones and type 2 Diabetes Mellitus were less likely to happen in moderate drinkers than in non-drinkers. The emphasis here, as elsewhere, is on moderate drinking.
As with a lot of things in this world, some people still argue and strongly believe that alcohol has no positive effect on the body.
Negative Effects of Alcohol in the Body
The risks of negative effects of alcohol on the body increases with each sip.
Effects on the Mouth, esophagus
The effects of alcohol consumption start with the entry point. Alcohol is an irritant; it burns when it touches any bodily surface. It is the burn that would subsequently destroy the body’s living tissues. Taking 5 drinks or more a day can increase your risk of developing cancer in your mouth, throat, or voice box by about three times.
Stomach and Intestines
As alcohol travels to the stomach, it’s absorbed into the bloodstream or passes through to the intestines.
However, some alcohol does none of the two. Some remain in the stomach. This increases the acidity of the stomach and irritating its protective lining. This irritation, when experienced for a long time and repeatedly, can lead to corrosion of the stomach lining. Even moderate alcohol consumption can give rise to or exacerbate existing stomach and intestinal ulcers. It also increases the chances of developing stomach cancer.
When it goes down to the small intestine, it does a lot of damage by interrupting the digestive system. It prevents the intestines from absorbing folic acid, Vitamin B1, B12, and amino acids and even fats.
Effects on the Brain
Alcohol affects the central nervous system in a lot of ways, causing a lot of short-term effects like slurred speech, blurred vision, weakened muscles, decreased reaction time and impaired memory.
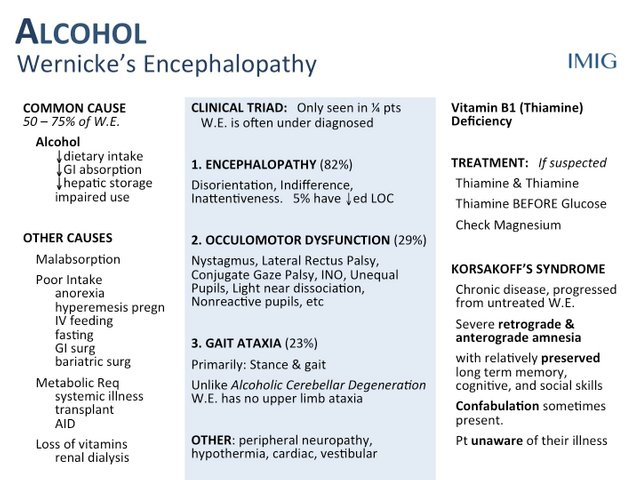
The amount of havoc alcohol unleashes on the brain is astonishing. The brief periods you don’t recall from the crazy party – that’s temporary amnesia. Continue this and you can develop Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS). This is a syndrome characterized by the memory impairmenter, vision and speech disorder, difficulty standing or walking in a straight line (ataxia) and even seizures. Those affected will not be able to form new memories. Mumbling involuntarily and frequent twitching of the eyes is also observed in people with this condition.
The Liver
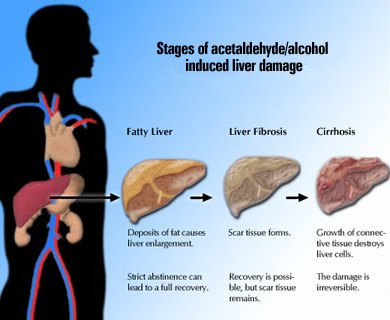
The Liver is where alcohol gets metabolized if and when a person takes more than a drink per hour, on average. Drinking excessively makes the liver to accumulate fat and this can lead to a condition known as fatty liver disease. When the liver is clogged with too much fat, it's function will be impaired. It is responsible for the metabolism of most chemicals and food groups that enter the body, even clotting factors are produces in the liver. Therefore if it underperforms, the body would be in jeopardy. From there alcoholic hepatitis and subsequently liver cirrhosis happen.
The liver turns alcohol into something called acetaldehyde, which is toxic and can cause cancer.
Breasts
Alcohol consumption raises the risk for breast cancer. Studies suggests that even so little as one drink a day may increase of person’s risk of developing breast cancer. Estrogen levels are increased following alcohol consumption and raised estrogen level is strong factor involved in the development of breast cancer.
Pancreas
Excessive alcohol consumption has been found to be a common cause of pancreatitis, (inflammation of the pancreas) and this is a major risk factor for pancreatic cancinoma. Drinking heavily can also impair the ability of the pancreas to produce insulin which is necessary for glucose metabolism. Without insulin, there is a resulting impairment of glucose metabolism- Diabetes.
Bladder and Kidneys
Alcohol is a diuretic. The more you drink, the more you urinate. This may not be seen as much of a problem but long-term drinkers experience a more sinister effect of alcohol in the urinary bladder. It can irritate the inner lining of the bladder and cause it to increase in size. There would be a subsequent blockage of the ureters which in turn can result in renal failure.
The Heart
On a short-term basis, alcohol does not do much damage to the heart. It is long-term drinking and surprisingly short term binge drinking that cause most of the negative effects on the heart.
Chronic alcohol use in large quantities can lead to a condition called alcoholic cardiomyopathy. This condition – which can include the conditions of cardiomegaly or dilated cardiomyopathy (the heart muscles become bigger and do not perform well) – overtime the toxic effects of alcohol makes the heart weaken and the heart will not be able to pump blood to the whole body. Binge drinkers are over 50 percent more at risk of developing an ischemic stroke over a ten year period.
Pregnancy
Folic acid is a very important vitamin which plays a vital role in the development of an embryo’s spinal cord. It is also important in the building of DNA in our cells. This is why it's always recommended that pregnant women avoid alcohol consumption. As mentioned above in effects of alcohol in the intestines, there's an impaired absorption of folate in the intestine. Alcohol also inactivates folate in the blood and tissues. Lack of folate can cause neural tube defects in the fetus.
The effects of positive effects of alcohol on the body however the negative effects of long-term alcohol consumption in the body are so much that I sometimes wonder why people go so crazy about it.
Thanks for reading!
Sources:
Grate write up. The negative effect on the body is more than the positive effect. Its better not to take it at all because not all can control the small intake that benefit the body. But, if you can, why not.
Also, I believe alcohol is classed as a depressant to. The euphoria ends up leading to a depression phase.
Is this correct @stanleyc-md?
Good post mate! You should have gone into metabolism and the MEOS system, that stuff is so interesting :)