Satellite Orbits.
Today we will see the concept of orbit, the various terms related to orbit and its path and the various types of orbit. First, let us understand what is an orbit.

Image by By NASA [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
What is orbit?
In above image, we have earth and a satellite and this satellite moves around the earth in the path which is known as orbit. Now, this satellite has two forces that act on it.
- Centripetal force
- Centrifugal force
one force that tries to bring the satellite close to the earth is the centripetal force. And the other force that tries to push the satellite away from the earth is known as centrifugal force and that is due to the velocity of the satellite. Now, at every position these two forces try to cancel out one another as a result the satellite is able to maintain its path and this path is known as the orbit.
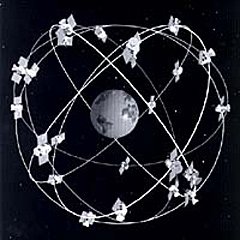
Image By NOAA [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
Now, the path of the satellite can be of two types. It can be either circular path or elliptical path. Now, whenever there is an elliptical path there are two edges, one edge is close to earth and the other edge is far away from earth. The edge that is far away is known as Apogee and the edge that is closer to the earth is known as the Perigee. Leat's say the section of the orbit that is closer to earth is Perigee section and the section of the orbit that is far away from earth is Apogee section. Now when I am saying this section is closer that means when the satellite is rotating into an elliptical path, the Perigee section would be covered at a faster rate so the duration of orbit in this path would be less because it would cover it very rapidly in contrast to Apogee, where it will remain for a longer duration as it has to cover more distance. So, this is the distance that satellite would be covering as a result it would take more time. So, this is the basic concept of orbit.
Now there are two terms that we usually talk about. One is Posigrade and the other is Retrograde. Posigrade means the satellite is rotating in the same direction as the rotation of the earth. So, it's moving in the same direction. In contrast to it, retrograde orbits move in opposite direction to the rotation of Earth. Now, in either of these cases there is a Geo center and that is the center of gravity. Whenever there is a path that satellite is following that orbit has its center of gravity and the point where the center of gravity lies is known as the Geo Center. These are some of the basic terms that we have learned about the orbit and the satellites in orbit. Now the next topic we will see is precision.
What is Precession?
Consider the top of a body that is spinning. When it's spinning it's into a motion. Now, precession occurs whenever there is a tilt and as the top spins around it starts to wobble and that wobbling is a procession. So, it's changing its axis from one point to another. Now let us understand what is the precession of the earth.
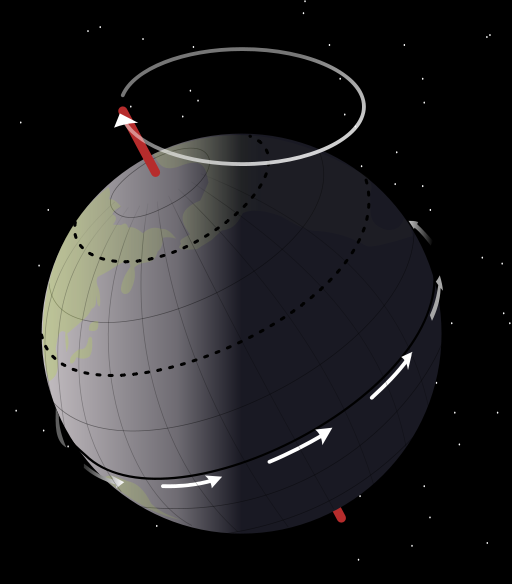
Image By NASA, Mysid [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
So, you can see above image of Earth. Here, earth is rotated earth is tilted at some degrees. if it wasn't tilted the line of shadow, as you can see in the image, would have been the axis. As I mentioned previously tilt is a necessary condition for precession to occur. So, Earth's precessional cycle completes in 26,000 years or I can say one degree precision takes place in 72 years.
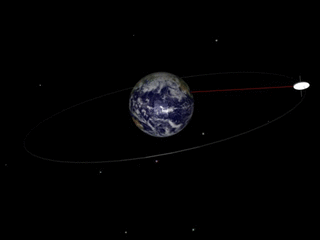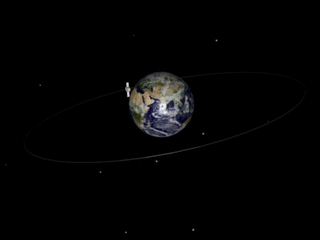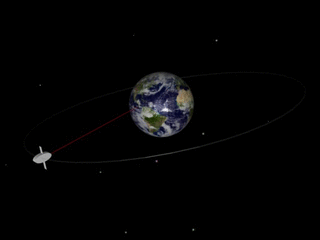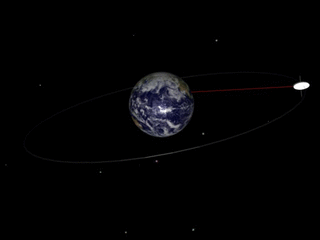
gif By Talifero (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
Now if you try to understand, the precision of orbit here is what is happening, as you can see, you have the earth and the satellite that is moving around on the earth. Consider, the original path of satellite was horizontal to the plane of above image and the axis of earth was perpendicular to your screen(I couldn't find the appropriate image for that) and now it has tilted. And this is the processional cycle of the orbit or I can say this is the nodal precision. Now nodal precision is important specifically in case of one type of satellites that is Sun synchronous satellite. Nodal precession is required in case of Sun synchronous satellite because there is a constant relative to the Sun. Sun-synchronous orbits usually fall under the category of either low or medium orbits. Now what is unique about Sun synchronous? As I said there remains constant relative to the Sun. So what is happening there is, for example, Sun synchronous satellite is over Brazil at, say, 10 a.m. So, every day at 10:00 a.m. it would be over Brazil. So what is maintained here is the time. Constant here is time. So, every time it would be coming on to the Brazil at the same time that's 10:00 a.m. Now Sun synchronous is based on sunlight as the name suggests. So, to understand this let's first understand the types of orbits.
Types of orbit :
- low orbit
- medium orbit and
- high orbit
Low Orbit :
Example of low orbit is a polar or a near polar orbit. Now, what is a special characteristics of a polar or a lower polar orbit? Consider, Earth is rotating along its axis. Now a polar orbit rotates perpendicular to earth all across the poles. So , that's a north-south rotation. So it completes in 99 minutes or I could say approximately 90 minutes, that is one and half hours so that's the approximate cycle of a polar orbit or a polar satellite. We also call it near polar orbits. Now, the best examples for polar orbits are space shuttles. What is the benefit of a low orbit satellite? When the satellite is at low orbit, that means the distance from the earth is very less. So, if the distance is Less what is the benefit? If I want to put any new instrument into the shuttle I can do that. So, installing of new instruments or repair of any instrument or equipment it becomes very easy in case of low orbit.
Medium orbit :
Medium orbits are usually classified into two types.
- Semi synchronous orbit
- Molniya orbit
Semi synchronous orbit :
Semi synchronous usually complete or usually go through the same place on the earth two times a day. A good example would be a kind of GPS navigation devices which require triangulation. In triangulation, you have three satellites that should be in line to locate a position. And semi synchronous satellites usually cause the same position two times a day.
Molniya orbit :
Now, molniya orbit is a kind of elliptical orbit. It has high eccentricity. Eccentricity means it's not circular it is kind of having an elliptical motion. Some of the examples of molniya orbit would be the cirius, radio satellite, and other Russian satellites which are placed into elliptical orbit.
High orbit :
High orbit is usually kind of geostationary orbits or geosynchronous and these geostationary or geosynchronous are located at a height of around 36,000 kilometers in contrast to semi synchronous which is around 26,000 kilometers. Now, at this height they try to cancel out the effect and they remain stationary with respect to earth. So, they are transmitting information about the same section of the earth always. So they are relative to earth. They remain constant. Now, what's the benefit of this? Geostationary satellites are used since they are into the same position. They have the rotation period similar to earth that is 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds and they capture the information of the same place every time so I can say they are best used in satellites communication, phone communication, in case of rescue and research operations. If one's ship is kind of sinking into a water this geostationary satellite can provide information about that region and relay that information directly. A common example of geostationary satellite is INSAT. Example of Sun synchronous satellite that we previously seen is radar. The other important benefits of this orbit is weather monitoring so geostationary is important for weather monitoring.
References :
- What is orbit
- Satellite orbit types
- Ellipstical and circular orbit
- Axial precession
- Book - Satellite Communication By Dharma Raj Cheruku
You received a 80.0% upvote since you are a member of geopolis and wrote in the category of "geopolis".
To read more about us and what we do, click here.
https://steemit.com/geopolis/@geopolis/geopolis-the-community-for-global-sciences-update-4
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by pratique007 from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Very interesting. Two things always intrigued me as a child. Space and geology. Now I'm doing the rock thing and I enjoy reading about space (non-fiction or fiction).
Love all things space and your post is helpful in explaining important concepts.
Congratulations @pratique007! You have completed the following achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCongratulations @pratique007! You have received a personal award!
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Congratulations @pratique007! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!