Urine research, Culture and Sensitivity.
Urine
Urine is a liquid waste material consisting of water, salts and organic compound, that is formed within the kidneys, hold on within the bladder, then free through the canal. it's one in every of the body’s waste matter, on a standard circumstance excreta doesn't contain important population of any microbes, but if any microorganism is introduced into the tract it will multiply and cause urinary tract infection (UTI). qualitative analysis is the comprehensive analysis of excreta
As a part of a qualitative analysis, the urine sediment is centrifuged and examined microscopically for crystals, casts, red blood cells, white bloods cells, and bacterium or yeast. as a result of examination of urinary sediment provides an immediate sampling of tract morphology, it provides vital data helpful for each diagnosing and prognosis.
Microscopic examination of excreta sediment is sometimes performed additionally to routine procedures particularly for pregnant mothers.
The specimen used for microscopic examination ought to be as recent as potential. Red cells and lots of shaped solids tend to disintegrate upon standing, significantly if the specimen is heat or alcalescent.
Preparation of excreta for microscopic examination.
To get a real worth of microscopic analysis of excreta, specimen should be properly collected and ready.
Patient ought to be schooled on correct techniques of fresh catch excreta assortment avoiding assumptions that the patient is aware of what to try and do from previous expertise or from others.
Review the way to cleanse the genital organ and instruct the patient to gather a eye specimen.
A volume of 5 to 10 milliliters of excreta ought to be poured into a tube. round shape bottom check tubes are most popular as a result of they permit for higher pellet formation.
Place the tube within the centrifuge and balance with a second tube crammed with another excreta specimen or water of equal volume. Spin the excreta for regarding 5 minutes.
Remove the tube and pour out the supernatant into the sink. Re-suspend the sediment within the residual excreta that adheres to very cheap of the tube by sound the tube against a tough surface many times. Place a drop of the re-suspended sediment on a glass sheet glass employing a pipet or by holding the tube the other way up and punctiliously sound it on the slide till one drop falls onto the slide. Place a coverslip over the drop and place beneath the magnifier.
How to look at the Slide
Review the instructions for your magnifier if you're unacquainted with its operation. Place the slide beneath the scope and start the examination below low power. make sure to use an occasional light (adjust the iris and condenser). an excessive amount of light-weight makes the cellular and crystalline components more durable to check. Scan the slide beneath low power to find areas of interest. explore for casts simply within the perimeter of the quilt slip. Then switch to high dry magnification and examine 10 random fields within the central a part of the coverslip. Count the numbers of red cells and white cells in every and report the vary of findings. If the sphere is roofed with cells, report as "TNTC" (too various to count). Estimate of bacterium density, any casts seen and alternative structures noted ought to be accessorial to the report.
Importance of microscopic examination
In healthy individuals, the excreta contains little numbers of cells and alternative shaped components from the complete tract, and animal tissue cells from the excretory organ, ureter, bladder, and canal.
A microscopic examination of excreta sediment detects the presence and amounts of Red blood cells, White blood cells, bacterium and yeast, Casts, animal tissue cells and Crystals.
Urine sediment is assessed beneath a high power field (HPF) for the presence of red and white blood cells. Normally, there ought to be solely an occasional red blood corpuscle within the excreta (2-3 per high power field).
Haematuria, the presence of abnormal numbers of red blood cells within the excreta could also be due to:
Tumors that erode any part of the tract
Kidney trauma
Acute cannular death
Upper and lower tract infections
Nephrotoxins
Traumatic catheterization
Passage of excretory organ stones
Physical stress
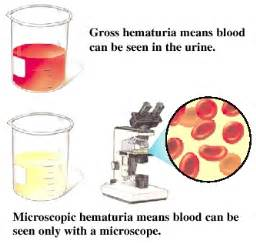
In women, it's vital to form certain that the excreta specimen wasn't contaminated by the menstrual blood. Inserting a tampon and assembling excreta midstream are ways to stop contamination. Red vegetative cells might remain and kind red blood cell casts.
The presence of oddly formed red blood cells within the excreta suggests a capillary illness like Bright's disease, because the odd form is caused by the passage of the cells through a distorted and abnormal capillary structure. White blood cells are usually not present within the excreta. The presence of white blood cells indicates infection or inflammation among the tract.
Bacterium or Yeast.
Excreta stored within the bladder is often free of bacterium or yeast, bacterium are unremarkably found in excreta specimens as a result of the abundant traditional microbic flora of the duct or external urinary passage and owing to the power of bacterium to multiply quickly in excreta standing at temperature.
Bacteria noted on a microscopic examination ought to be interpreted in sight of clinical signs and symptoms of tract infection. A colony count may be done to see if important numbers of bacterium are present.
Casts
Casts are collections of macromolecule, cells, and trash that are shaped within the tubules of the kidneys. cast dimension is described as slim (one to 2 red blood cells in width), medium broad (three to four red cells in width), and broad (five red blood cells in width). Broad casts sometimes indicate a major reduction within the purposeful capability of the uriniferous tubule and indicate severe excretory organ injury or "end stage" excretory organ illness.
Some hyaline casts are normal, however all alternative casts ought to be evaluated. once cellular casts stay within the nephrons for a few time before being flushed into the bladder excreta, the cells might degenerate to a coarsely granular cast, later to a finely granular cast, and eventually, to a waxy cast. Granular and waxy casts are believed to be derived from excretory organ hollow casts. the quantity of casts are according as "number and kind seen per low power field (LPF)". AN example of a report would possibly read: "5-10 hyaline casts/LPF."
Some animal tissue cells from the skin surface or from the outer canal will seem within the excreta. Some sorts of crystals seem within the excreta of healthy people. Abnormal crystals will indicate disease or some sorts of genetic abnormalities.
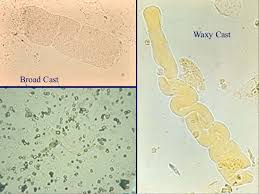
Image source
References
https://www.labtestsonline.org.au/learning/test-index/urine-culture
http://www.glowm.com/lab_text/item/94
https://www.rcpa.edu.au/Library/Practising-Pathology/RCPA-Manual/Items/Pathology-Tests/M/MCS-urine
https://labtestsonline.org/tests/urine-culture
tps://www.drugs.com/cg/urine-culture-and-sensitivity.html
https://www.healthline.com/health/urine-culture
http://www.austinpathology.org.au/test-directory/index.php?testid=1476
https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/what-is-urine-culture#1
##Images
1
Urine test can be conducted if you've got pain in your belly, chills, fever, or burning once you urinate, you may have a tract infection. The tract is formed of the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. urine culture and sensitivity tests are done to seek out which microorganism is inflicting the infection and also the best medication to treat it.
Thanks for taking out time to read this, remember health is wealth.

Being A SteemStem Member