DNA
DNA is the acronym of deoxyribonucleic acid, is an organic compound that contains the genetic information of a living being and some viruses, in prokaryotic cells and in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, inside chromosomes.

The main function of DNA is to store genetic information for the construction of proteins and RNA, which is essential for any vital function of an organism. The DNA stores and transmits from generation to generation all the information essential for the development of the biological functions of an organism.
The DNA segments that carry the genetic information are known as genes, but the other DNA sequences are for structural purposes or take part in the regulation of the use of genetic information.
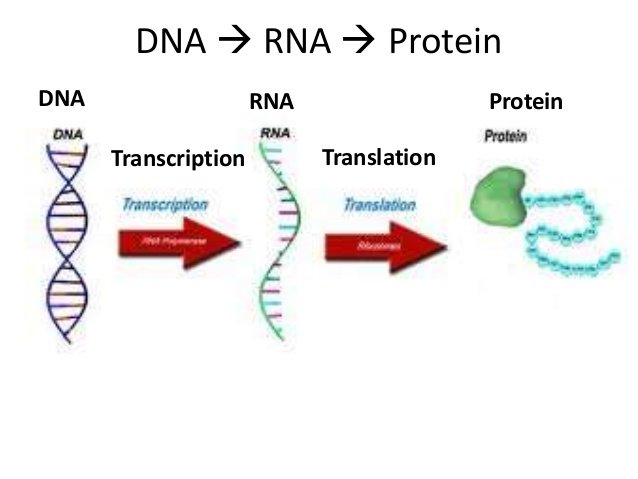
Referring to what has been said above, the coding DNA and the non-coding DNA can be observed. Also, in a gene the sequence of nucleotides established in a strand of DNA is transcribed to a messenger RNA and, in turn, it is translated into a protein that an organism synthesizes in one or some moments of its life and, finally, the replication of DNA consists in obtaining identical copies of a fundamental DNA molecule for the transfer from one generation to another, the basis of the inheritance.
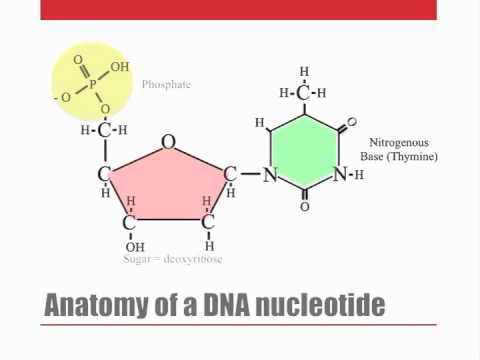
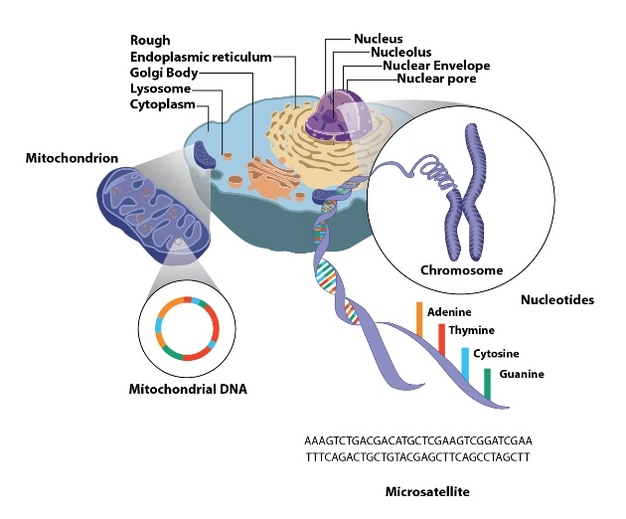
DNA is made up of bands formed by chemical compounds called nucleotides. In turn, each nucleotide is made up of 3 units: a sugar molecule, that is, deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a 4-base group: adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. In the center of the nucleotide is the deoxyribose molecule and is surrounded by one side of a phosphate group and the other a base, the linked deoxyribose-phosphate form what is known as the sides of the ladder.
The DNA of each human being is exclusive, each human being has 2 forms of each gene, that is, one that receives from the father and the other from the mother, but in spite of being the same genes among people, some DNA sequences vary from person to person. DNA is characterized by the position and quantity of these nucleotides along the chains, this sequence is known as genetic or genetic code.
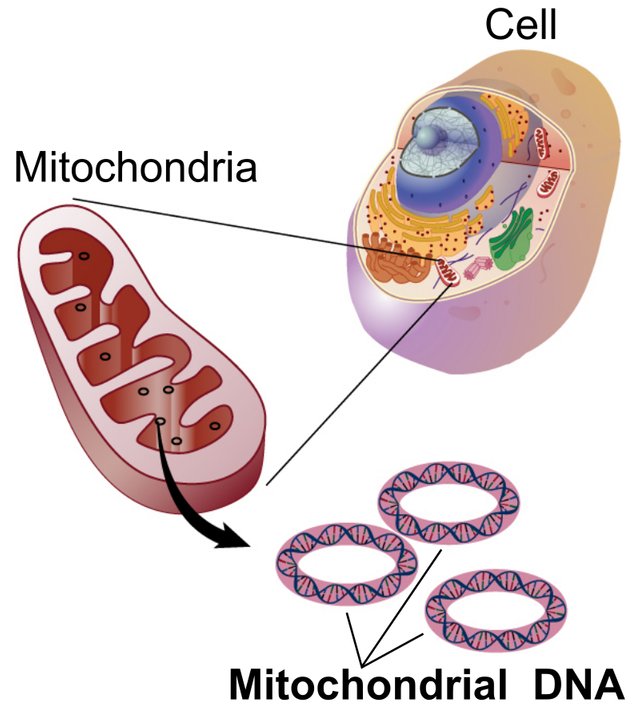
MItochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA is a fragment of nucleic acid in mitochondria. The mitochondrial genetic material is inherited exclusively by the maternal part. Mitochondrial DNA was discovered by Margit M. K. Nass and Sylvan Nass using electron microscopy and a marker sensitive to mitochondrial DNA.
Mitochondria are small organelles within eukaryotic cells, in order to produce energy for the cell to perform its functions. However, each mitochondrion has its own genome and its cellular DNA molecule.
Thank you for reading my post, for more information visit this page.
https://www.significados.com/adn/
Atte.
@jorge150785