Motors, differences and types, part #1
Hi everyone in Steemit, in this post, I will be talking, as the title says about the engines, their differences and the different types that exist.
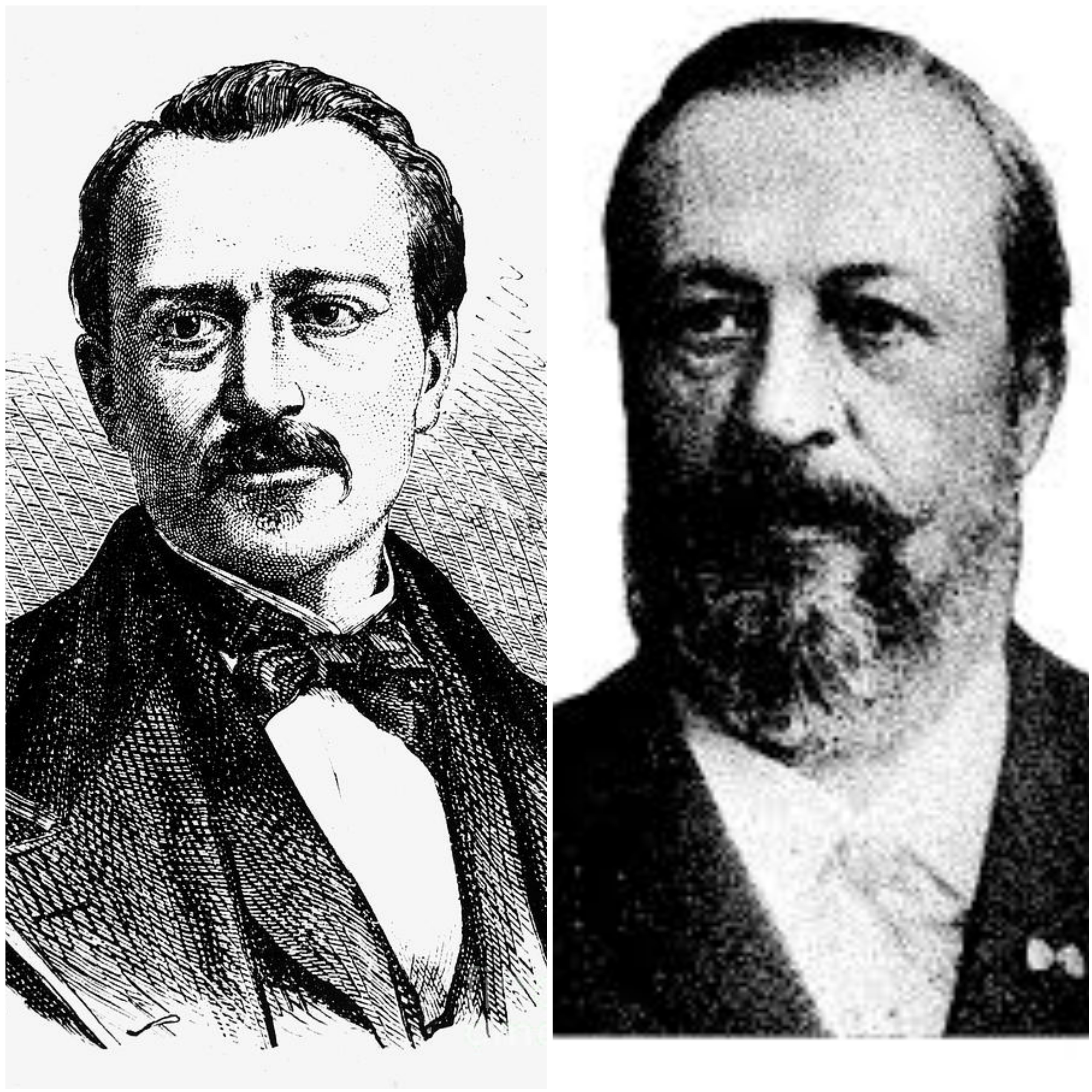
The year 1863 was a very important year for engineering, since in this year, the naturalized French Etienne Lenoir Engineer, invents the first internal combustion engine, later in the year of 1876 the German engineer Nikolaus Otto, invented the first engine of four-stroke cycle, and it is in his honor that this explosion engine is given the name Otto engine.

MOTORS
Thermal motors
WHAT ARE THE ENGINES?
An engine is the systematic part of a machine capable of operating the system, transforming some type of energy (electrical, chemical energy containing fuel, etc.), into mechanical energy capable of performing a job through a thermodynamic process. In automobiles, this effect is a force that produces movement.
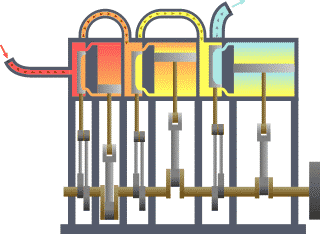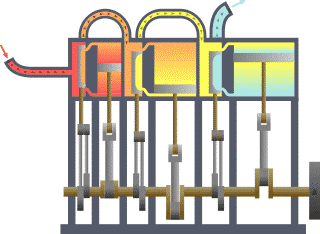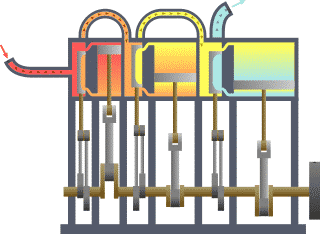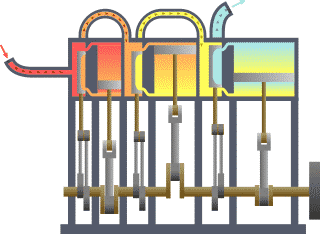
It is identified with the name of thermodynamics to the branch of physics that focuses on the study of the links between heat and other energy varieties. Analyze, therefore, the effects that have macroscopic changes in temperature, pressure, density, mass and volume in each system.
The piston accelerates due to the combustion of the fuel and air mixture. This rectilinear ascending and descending movement of the piston is transformed into a circular movement thanks to the mechanism of the crankshaft. Finally, the exchange of gases with the valves and channels is controlled in the cylinder head.
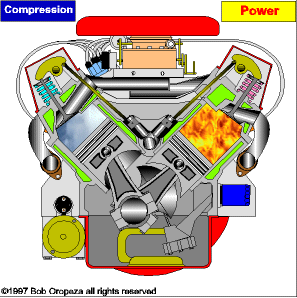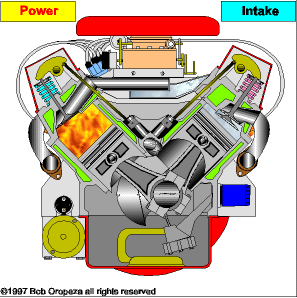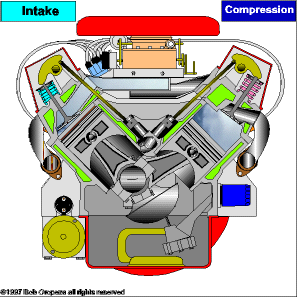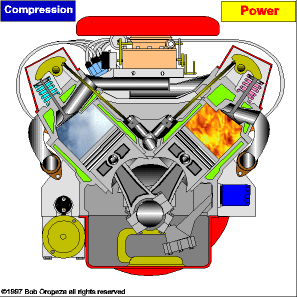
TYPES OF ENGINES
1. ELECTRIC MOTORS
An electric motor is a device that works with alternating or direct current and that is responsible for converting electrical energy into movement or mechanical energy.
Since its invention, electric motors have become very useful tools that serve to perform multiple jobs.
They are found in diverse applications, such as fans, pumps, electrical appliances, automobiles, etc.
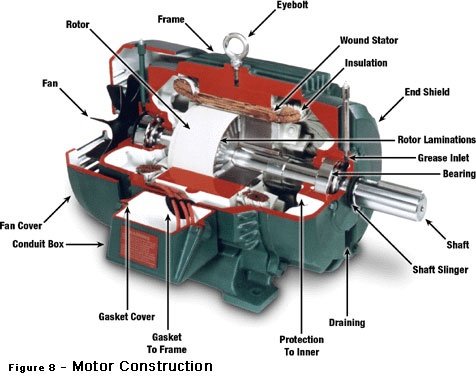
Every motor is based on the idea that magnetism produces a physical force that moves objects. Depending on how one aligns the poles of a magnet, it can attract or reject another magnet.
In motors, electricity is used to create magnetic fields that oppose each other, in such a way that they make their rotating part, called the rotor, move.
In the rotor, there is a wiring, called a coil, whose magnetic field is opposite to that of the static part of the motor.
The magnetic field of this part is generated by permanent magnets, precisely the repellent action to said opposite poles is what causes the rotor to start rotating inside the stator.
If the mechanism ended there when the poles were aligned the engine would stop. Therefore, in order for the rotor to continue to move, it is necessary to invert the polarity of the electromagnet.
The way in which this change is made is what defines the two types of electric motor.
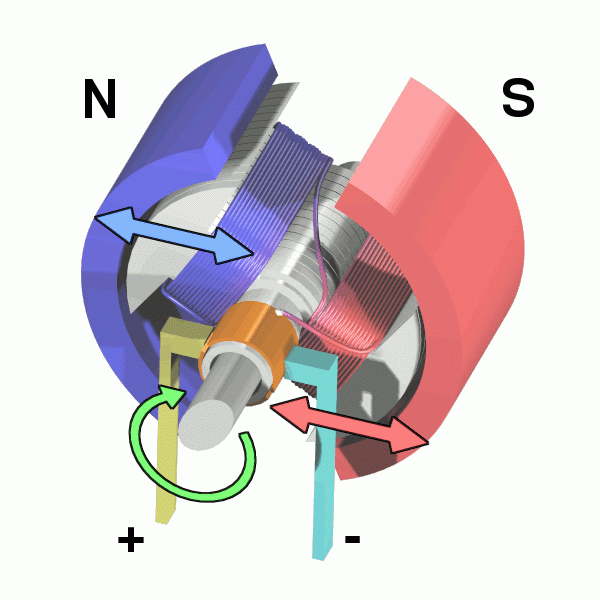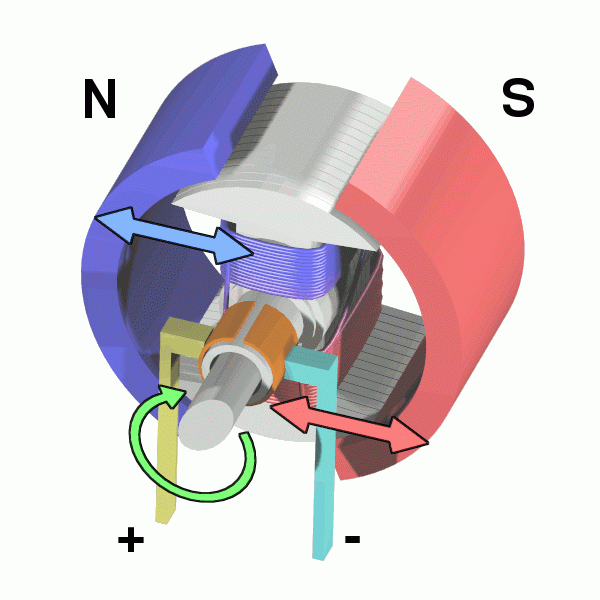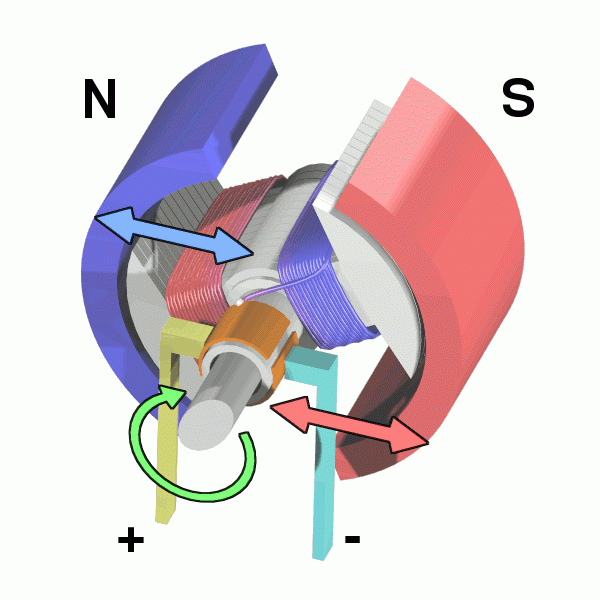
As far as electric motors are concerned, it depends on the current with which they work, they are divided into 2 types.
Most of these work with alternating current (AC), which changes the direction of the flow many times in a second.
The areas of positive and negative polarity in the electromagnet are reversed and alternating, which keeps the axis rotating.
Any equipment that moves and is connected to a wall outlet is driven by a motor of this type.
But there are also motors that work with direct current (DC). These get electricity from a battery.
To achieve the inversion process, they have a piece called a switch that alternates the direction of the current inside the electromagnet, a kind of artificial alternation, and changes the polarity of the magnetic field.
DC motors are more primitive than AC motors, but they can be very useful in contexts where there is no AC power source.
.gif)
AC motors
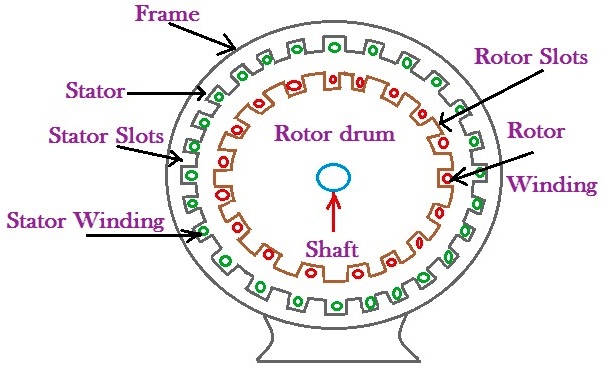
An AC electric motor operates by applying alternating current (AC), which feed the motor. AC electric motors are composed of several parts, but the Main parts are the stator and the rotor.
- The stator of the AC electric motor has coils that are supplied with the current alternates and produces a rotating magnetic field.
- The rotor of the AC electric motor rotates inside the coils and is attached to a shaft of output that produces a twist by the rotating magnetic field.
There are two different types of AC electric motors and each of them uses a type different from the rotor.
1.- The first is called induction motor (also known an asynchronous motor). An induction motor uses a magnetic field in the rotor that creates a current induced.
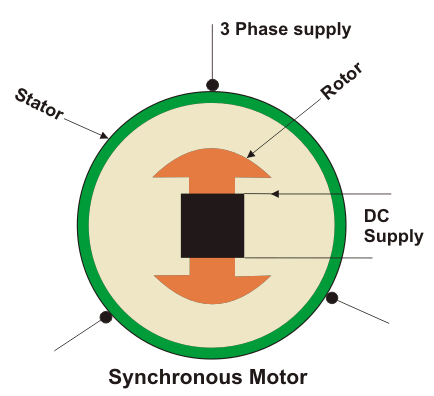
2.- The second is called synchronous motor and rotates precisely in the feeding frequency or in a sub-multiple of the frequency of supply. Asynchronous motor is capable of operate with a precision feeding frequently since it does not respond in the induction. The magnetic field of a synchronous motor is generated by the current supplied through the slip rings or a permanent magnet. The engines Synchronous run faster than induction motors because the speed is reduced by the sliding of the asynchronous motor.
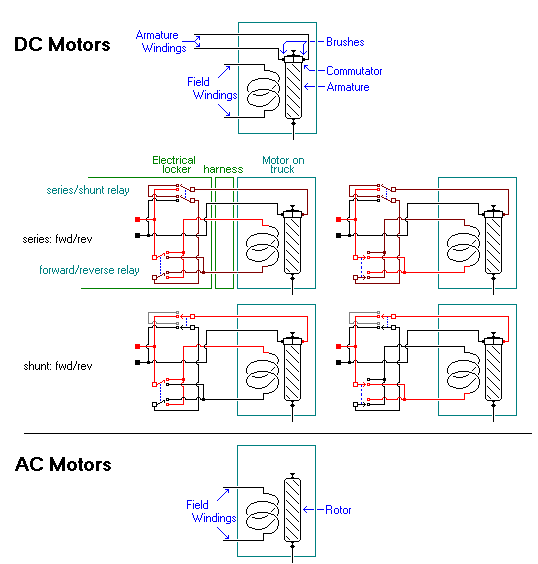
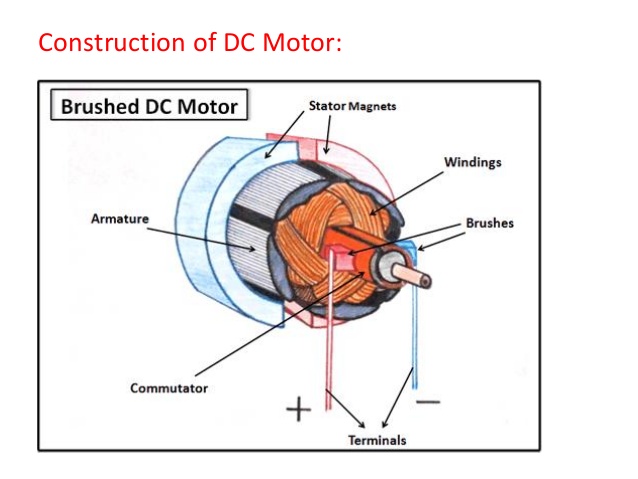
CD Motors
CD electric motors are switching machines that are powered by the direct current (CD) energy. Direct current electric motors have an armature induced rotary winding armature, and an induced field frame does not
rotate winding that is a static field or a permanent magnet. The engines electric CDs use different connections, and an induced winding to produce different speeds and the regulation of the torsion.
Unlike AC electric motors, the speed of the electric motor current Direct can be controlled inside the coil, by changing the voltage.
Because the theme of the engines is so wide decided to make several publications where I will be explaining and developing in more detail the operation as well as the parts and applications of each of the different engines, I hope you like this first post.
For more information visit this pages:
http://energyev.com/diferencias-entre-un-motor-ac-contra-un-dc/
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motor_el%C3%A9ctrico
super post, id like much more! :)
thank you I'm glad you like it ...
cool and informative :) nice one man.