Hydrogen its importance and application
Hello, my dear friends of Steemit, I am happy to share this research with you, I hope you like it.
Although Hydrogen is one of the most abundant materials on the planet earth and even in the whole universe, and taking into account that our sun is clear evidence, of the importance of hydrogen for all, I want in this report, to talk a little about what is and represents hydrogen for us.
Hydrogen is one of the most important elements in our day to day. There are two hydrogen atoms in each water molecule and a good part of the atoms that make up the molecules that support life are hydrogen.

Hydrogen is the lightest element, being the nucleus of its isotope more abundant constituted only by a proton. Hydrogen is the element with the greatest abundance in the known Universe and one of the most abundant on Earth.
But besides its importance in the natural world, it is also of enormous industrial importance and its production is frequently a limiting factor in the industry.
High amounts of hydrogen are needed in the chemical and petroleum industries, nominally in the "Haber" process for the production of ammonia, the fifth compound with the highest industrial production.
In addition to the production of ammonia, hydrogen is also used in the hydrogenation of fats and oils, hydrodesulfurization, hydrocracking, hydrodealkylations, as well as in the production of methanol, among others.
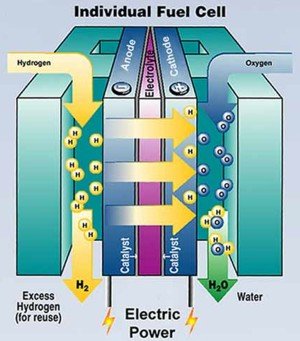
Hydrogen is currently being tested as a source of "clean" energy for use in transportation. The reaction of hydrogen with oxygen, to produce water, carried out in fuel cells is one of the most promising ways to generate energy for automobiles, avoiding the release of greenhouse gases, contrary to what happens with current engines that they use the combustion of hydrocarbons of fossil origin.
Another huge promise of hydrogen at the energy level is nuclear fusion. This process, which feeds most of the stars that shine in the sky, produces helium from hydrogen nuclei, releasing huge amounts of energy.

This reaction, which was already used in its "uncontrolled" way in the hydrogen bombs, was carried out in a controlled manner, it could allow having an almost inexhaustible source of energy.
Other relevant applications of hydrogen are:
Production of hydrochloric acid (HCl).
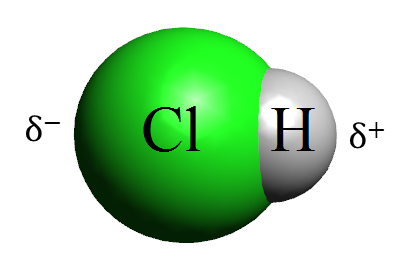
It is an acid that receives different names according to the place where it is mentioned. Known as etching or salfumán in Spain or muriatic acid in South America, and can even be purchased as chloric or marine acid.
Regardless of the nomenclature, the properties of hydrochloric acid are the same. The liquid that composes it has a yellowish color and breathing its vapors irritates the mucous membranes, so then we indicate all its characteristics:
1.-The gas it produces weighs more than air.
2.-It is irritating to breathe it.
3.-Burns the living tissues.
4.-It is corrosive of hard and soft materials.
5.-It works as a reagent when dissociated in water.
6.-pH less than 1.
7.-Not flammable.
8.-As it has a very low pH it is very dangerous for people and cellular tissues. It must be handled with care and avoid contact with the skin.
Rocket fuel
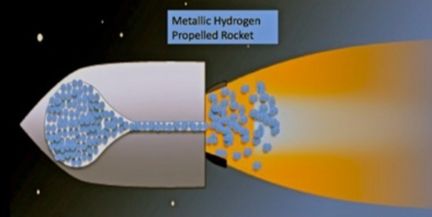
Hydrogen is a compound with a great capacity to store energy, being a low molecular weight fuel, it has the highest amount of energy per unit of mass than any other known fuel and when cooled and in a liquid state, hydrogen occupies a space equivalent to 1/700 of the one that would occupy in gaseous state.
That is one of the reasons why hydrogen is used as a fuel for the propulsion of rockets and space capsules, which require low weight, compact fuels with a large energy storage capacity.
Cooling of rotors in electric generators in power stations, given that hydrogen, has a high thermal conductivity;
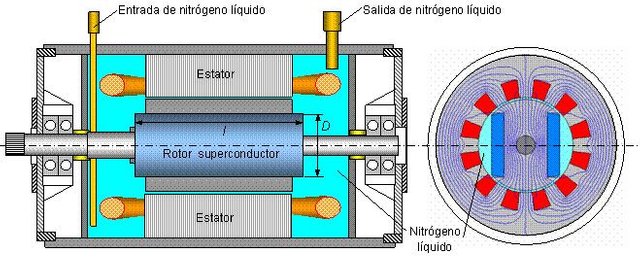
In the conventional cooling system the hydrogen gas is circulated by means of an internal fan and once the heat loss produced in the generator is absorbed by the cooling water, the gas circulates 30 to 40 times per minute. Using hydrogen gas it is possible to increase the assigned power by increasing the gas pressure, later the advances obtained in the rotor materials and other components have allowed a constant increase in the power of these units. In hydrogen-cooled generators in a conventional manner, however, pressures greater than 2 Kg / cm2 are used, it is difficult to increase the power due to the thick thickness of the insulation wall of the excitation coil. To avoid this problem, internally cooled turbogenerators are already used, in this case, the stator and rotor conductors are drilled and fed through the hydrogen gas holes at high speed and at a higher pressure than the conventional system.
In the liquid state, it is used in cryogenic investigations, including superconductivity studies.
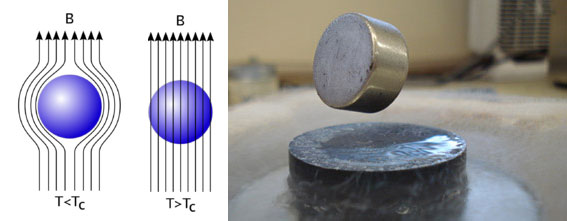
The super drivers that operate at room temperature would make much more efficient the transmission not only of electrical energy but also of information infrastructures improving their transmission and efficiency, as well as giving a great impulse to the current uses of superconductivity such as huge magnets used in medical imaging machines.
The results are the work of Mikhail Eremets, Alexander Drozdov and his colleagues at the Max Planck Institute of Chemistry in Mainz, Germany. They found that when samples of hydrogen sulfide are exposed to extremely high pressures - around 1.5 million atmospheres (150 gigapascals) - and cooled below 203 K, the samples exhibit the classic characteristics of superconductivity: resistance zero electric and a phenomenon known as the Meissner effect. The Meissner effect occurs when a superconducting material is placed in an external magnetic field and there is no field inside the sample, unlike in normal materials.
Since it is 14.5 times lighter than air, it is therefore often used as a lifting agent in balloons and zeppelins, although this use is reduced due to the risks of working with large amounts of hydrogen, which was clearly evident in the accident that destroyed the Zeppelin "Hindenburg" in 1937.

Deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen in which the nucleus is constituted by a proton and a neutron, is used in the form of the so-called "heavy water" in nuclear fission as a neutron moderator.

.jpg)
My thanks, for all those who follow me and read my work, I thank you for being willing to support me, see you.
For more information, consult the following pages:
https://quimica.laguia2000.com/conceptos-basicos/aplicaciones-del-hidrogeno
https://quimica.laguia2000.com/conceptos-basicos/uso-del-hidrogeno-como-combustible
http://qubit7.com/el-sulfuro-de-hidrogeno-superconductor/