the nuclear phenomena
The nuclear reactions
The chemical reactions that we observe in our environment are due to the arrangement of the electronic configuration of two or more atoms to form different compounds. However, another type of reaction occurs in the atomic nucleus of the elements.
The nuclear reactions that occur as a result of the instability of the nuclear composition and give rise to different elements because the number of protons is altered.
Nuclear reactions are characterized by:
• Nuclear reactions are produced by nuclear particles; Chemical reactions are produced by electronic interactions.
• Nuclear reactions cause transmutation of the elements, that is, conversion of one element into another; chemical reactions do not change the identity of the atoms of the elements.
• Nuclear reactions are independent of environmental conditions, while chemical reactions do not
• The nuclear radioactivity of an element occurs independently of the way it is found, whether free or combined.
• The isotopes of an element have different nuclear properties, but equal chemical properties.
The mass of a nucleus is actually smaller than the sum of the masses of the protons and neutrons that constitute it. This difference in mass is called binding energy. This energy is what is needed to break a nucleus in its protons and neutrons.
The greater the binding energy, the more stable the core will be.
For example, iron (Z = 26) has a very high binding energy, and therefore its core is very stable.
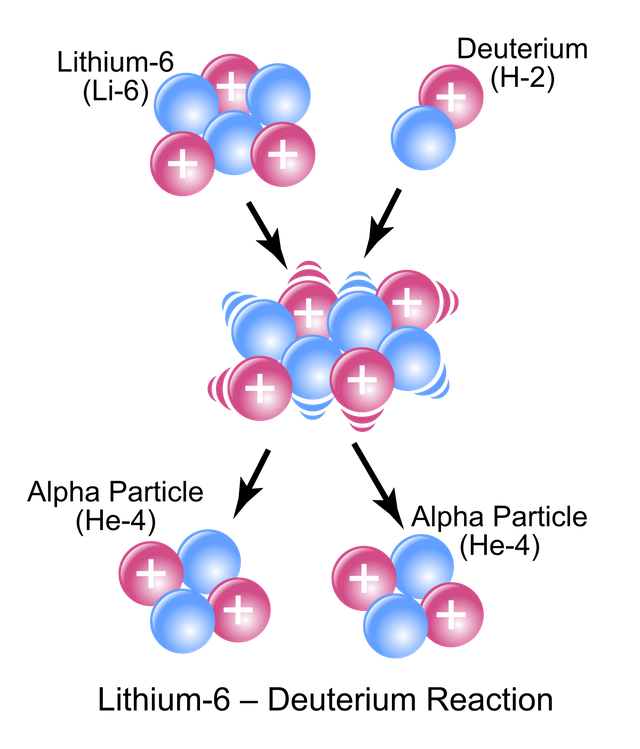
Source
The stability and nuclear instability
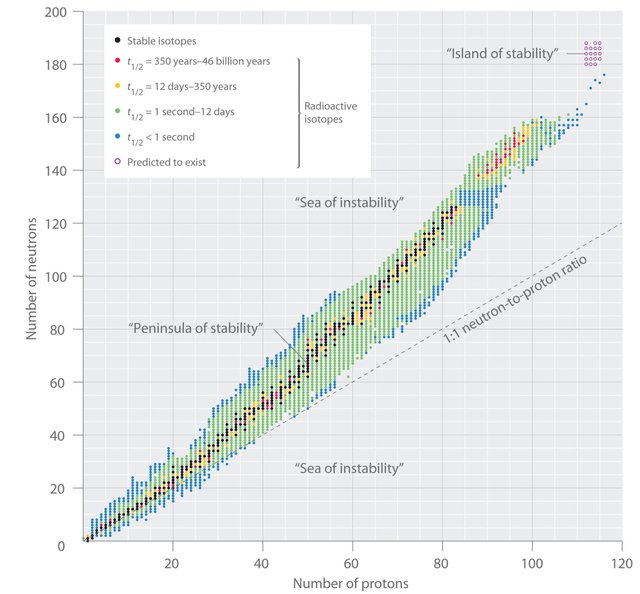
The stability of a nucleus depends on the number of neutrons and protons it has (neutron/proton ratio).
Because protons are positively charged and repel each other, it seems that more neutrons are needed to decrease this repulsion. For a nucleus to remain stable, the number of neutrons must be equal to or greater than the number of protons (neutron/proton ratio must be 1 or greater than 1). Nuclei with this condition are called stable nuclei or isotopes. However, when a nucleus has a greater number of protons than neutrons, the Coulomb forces of repulsion prevail over the nuclear forces or strong interactions that hold the nucleons together, so that the unstable nucleus or isotope undergoes a process of spontaneous disintegration with the emission of radioactive particles to form stable nuclei. Isotopes of heavy nuclei with an atomic number greater than Z = 83 are unstable and decay in radioactive form; they are radioactive isotopes.
Source
The radioactivity
The disintegration of a nucleus emits radiation and changes its nature, a process called radioactivity. This phenomenon was first observed by Henri Becquerel (1852-1908) in 1896 when he accidentally discovered that uranium compounds (Z = 92) produced radioactive emissions of alpha, beta and gamma type. Subsequently, the Polish chemist Marie Sklodowska (1867-1934) and her husband, the French physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906), isolated in 1898 two other radioactive elements: polonium (Po, Z = 84) and radium (Ra, Z = 88).
The natural and artificial radioactivity

Source
The natural radioactivity
Natural nuclear disintegration occurs randomly in an unforeseen time; However, scientists have managed to calculate the period of disintegration. This period refers to the time it takes for half the unstable nuclei of the isotope to disintegrate, which is why it is best known as the half-life time. This can be better understood through the following example: When analyzing a certain amount of the radioactive isotope or iodine-125 radioisotope, scientists have observed that half of its nuclei have disintegrated at 58 days, and half of the mass remains initial of this isotope; this means that the half-life of iodine-125 is 58 days.

Source
The radiations emitted during the disintegration of a nucleus have the following characteristics:
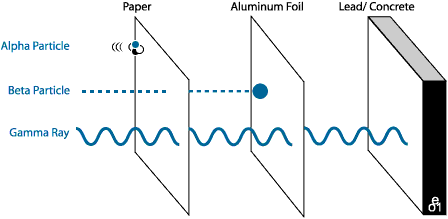
Alpha radiations(α): Helium nuclei with positive charge +2. They are formed of two protons and two neutrons. Its mass is equal to that of a helium nucleus.
They have low penetration power of matter; They pass through the epidermis and dermis of the skin to about 0.05 mm and are stopped by a sheet of paper. They are formed when radium-226 disintegrates.Beta radiations (β): They are formed by electrons, so they have negative charge -1. Its mass is the same as that of the electron and its velocity is close to that of light. They are more penetrating than alpha radiations: they penetrate the epidermis and the dermis between 0.06 mm and 4 mm. They are formed by disintegrating polonium-218
- The gamma radiations (ƴ): They are not formed by particles but by electromagnetic radiation of speed equal to that of light. They do not have mass. They have a high energy and are more penetrating than beta radiation; they easily cross the body and cause serious damage to the cells. They are stopped by a block of lead. They are formed by disintegrating tellurium-125.
Source
Artificial radioactivity
The first case observed on artificial radioactivity was in 1919 when Rutherford bombarded the isotope nucleus nitrogen-14 with alpha particles and formed an isotope of oxygen. In 1934, Irene Joliot-Curie and her husband Frederic isolated the first radioactive core produced by artificial means, for which they won the Nobel Prize in 1935.
Artificial radioactivity is called artificial transmutation and has allowed the synthesis of new elements with atomic numbers greater than uranium, called transuranic elements. These elements have a very short half-life of a few seconds.
Source
Applications of nuclear energy
Peaceful use of nuclear energy
Nuclear energy is considered the fuel of tomorrow. It has multiple uses such as the following:
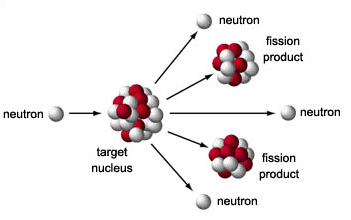
• Obtaining electricity: Electricity is generated in nuclear power plants, which are complexes that have a nuclear reactor connected to an electric generation system. The energy obtained in them is higher than that obtained in a thermoelectric power plant. The nuclear fission of 1g of uranium generates the same amount of electricity as the combustion of 2500 kg of coal. Nuclear energy is transformed into electrical energy in a similar way to how heat energy is transformed into electricity in a thermal power plant.
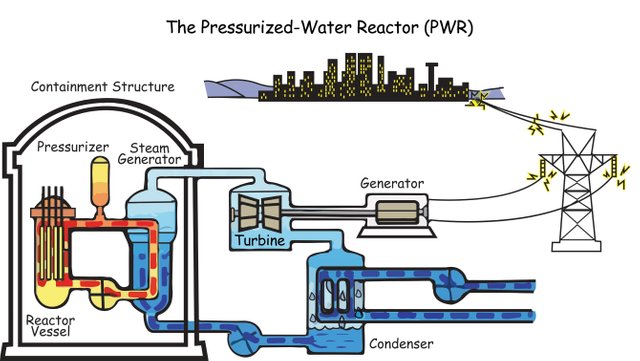
Source
• Production of radioisotopes: the radioisotopes produced in the nuclear reactors are used in different fields: medicine, industry, agriculture, geology, archeology, and so on. Radioisotopes are used as tracers of chemical and biological processes, by monitoring the radiation that is emitted. Some examples are:
- in medicine, iodine is used in the detection of abnormalities of the thyroid gland: cobalt and Y and X rays in the treatment of cancer; the technetium to obtain images of organs, such as heart, liver, and lungs; X-rays and gamma rays are also used to obtain radiographs; Ionizing radiation is used for the sterilization of instruments.
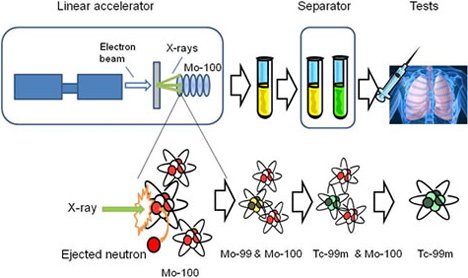
Source
- In the industry, tracers allow locating leaks of liquids or gases transported underground through oil pipelines.

Source
- In agriculture, radioisotopes are used to keep vegetables fresh for a longer time, to delay their sprouting period and to eliminate microorganisms, without affecting the quality of the product.
Source
- In geology and archeology, carbon is used to estimate the age of organic materials, such as fossils; Potassium is used to determine the age of rocks.
Source
- In chemistry, sulfur and phosphorus, among others, are used to dilute mechanisms.
Source
Dangers of nuclear energy
The use of nuclear energy must be very careful because the exposure of living beings to certain levels of radiation is harmful to health. Some facts that illustrate this are:
• The discoverers of the radioactive elements of the beginning of the century never suspected the risks of working in contact with radiation and many of them died due to the continuous radioactive exposures they received.
• The atomic bombs of Hiroshima and Nagasaki are an example of the danger of nuclear energy: Their genetic damage to humanity is so serious that they still persist after 100 years.
• Nuclear reactors are a potential danger: A serious accident occurred in 1986 in Chernobyl, in the former Soviet Union, when a cloud containing radioactive products escaped, the effects reached Europe, Asia, and even the United States.

Source
Hola @daniel1511, upv0t3
Este es un servicio gratuito para nuevos usuarios de steemit, para apoyarlos y motivarlos a seguir generando contenido de valor para la comunidad.
<3 Este es un corazón, o un helado, tu eliges .
: )
N0. R4ND0M:
8972 6322 7386 9112
8976 9562 8269 6946
3487 5860 8944 1524
8755 3956 5138 1617
Congratulations @daniel1511! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Congratulations @daniel1511! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!