How does electricity become part of electronics?
The first use that was given to electricity, around 1880, fueled the daylighting. The old gas lamps and candles were replaced by electric bulbs.
Towards 1920 came the valve radios, predecessors of modern electronic devices. Currently, the latter includes televisions and complex control systems for the latest generation of spacecraft.
Electric current
Electric current is a physical phenomenon that consists in the displacement of negatively charged particles, or electrons, through a conductor. The substances that allow electrical charges to move easily are called conductors. Metals, such as copper, iron or aluminum, are good conductors of electricity, and that is why they are used to make the inner part of the cables. Insulating materials such as glass or plastic, on the other hand, prevent the circulation of electrons, they are bad conductors. A plastic cover is used to insulate the electrical cables from the outside.
There are other materials that belong to an intermediate group, called semiconductors. These conduct the electrical fluid better than an insulator but not as well as a conductor, and are widely used in electronic circuits. Some examples are silicon, germanium, and selenium.
Source
Electronic circuits and their components
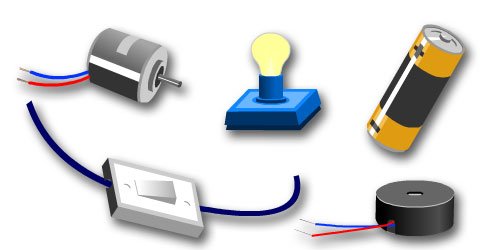
Electric circuits are systems where a current flows. Basically, they are composed of:
Source: Which provides an electrical voltage.
Conductor wires: That conduct electricity.
Receiver: That transforms electrical energy into another form of useful energy, for example, a lamp.
Control element: That interrupts or allows the circulation of the current through the circuit. These had transistors inside, components made of semiconductor materials that work.
Source
Difference between alternating current and continuous
When the circulation of electrons by a conductor is always in the same direction, we speak of direct current. DC generators are found in batteries, accumulators, and dynamos.
When the direction of the circulation of the electrons changes many times per second, we speak of alternating current. The generators of this type of current are called alternators.
Electronic systems
Electronics is the physical branch that studies the conduction of electricity, or flow of electrons, through materials that are not the usual conductors used in electrical installations. In particular, electronics study the conduction of electricity in semiconductors, gases, and vacuum.
There is an extraordinary variety of products on the market that are the result of electronic technology: radios, videos, calculators, computers, audio equipment, communication systems, camera, among others.
Electronic components are elements with whose combination electronic circuits are obtained.

Source
Main electronic components
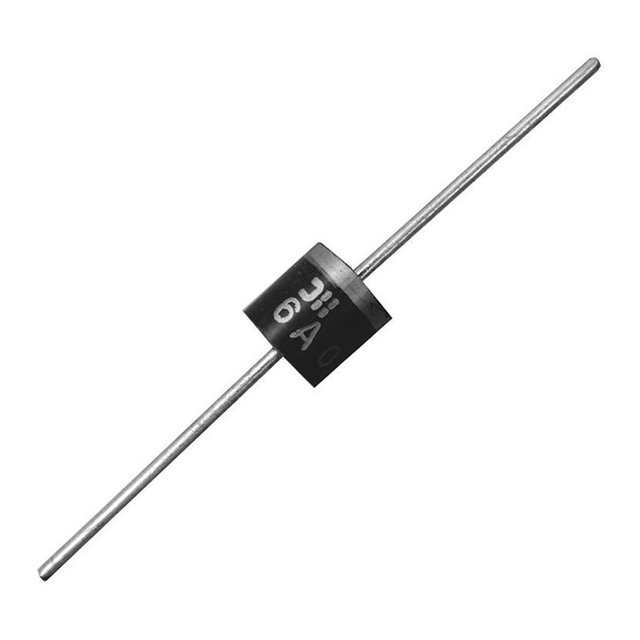
• Diodes:
Diodes are two-terminal electronic valves that allow the flow of electrical current in only one direction.
- Driver diode: It allows the passage of the current in a certain direction and prevents circulation in the opposite direction. One of the main applications is to convert alternating current to continuous. This is fundamental, since all electronic equipment needs a DC supply, and the one that reaches the homes is alternating.
- LED diode: Also allows the passage of the current in one direction but, in addition, has the property of emitting light. That's why they are used mostly for signaling: they are the lights that indicate, for example, that a computer or a camera is on.

Source
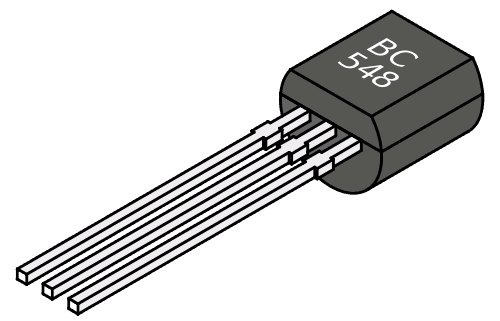
• Transistors:
Towards the end of the 1950s, old valve radios fell into disuse when the first portable radios began to be manufactured as amplifiers or as switches (a switch is a device that allows modifying in succession the connections between several circuits).
Nowadays, transistors are the fundamental parts of almost all electronic circuits destined to the most diverse applications (communications, computers, process control, etc).
Source
The era of integrated circuits or chips
An integrated circuit or chip is an electronic component formed by a silicon base material, of small dimensions, in which, by means of a complex manufacturing system, they are integrated in a single piece of set of interconnected components, to fulfill a certain function. The chips are composed of hundreds, thousands or even millions of transistors interconnected by thin wires. Among the main advantages of the chips is its small size and its lower weight.

Source
For more information visit the followings links
-https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_circuit
-http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/circuits/Lesson-2/Electric-Current
-https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/systems/electronic-system.html
-https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/integrated-circuits