LABORATORY: What inexperienced cause during scientific experiment................!
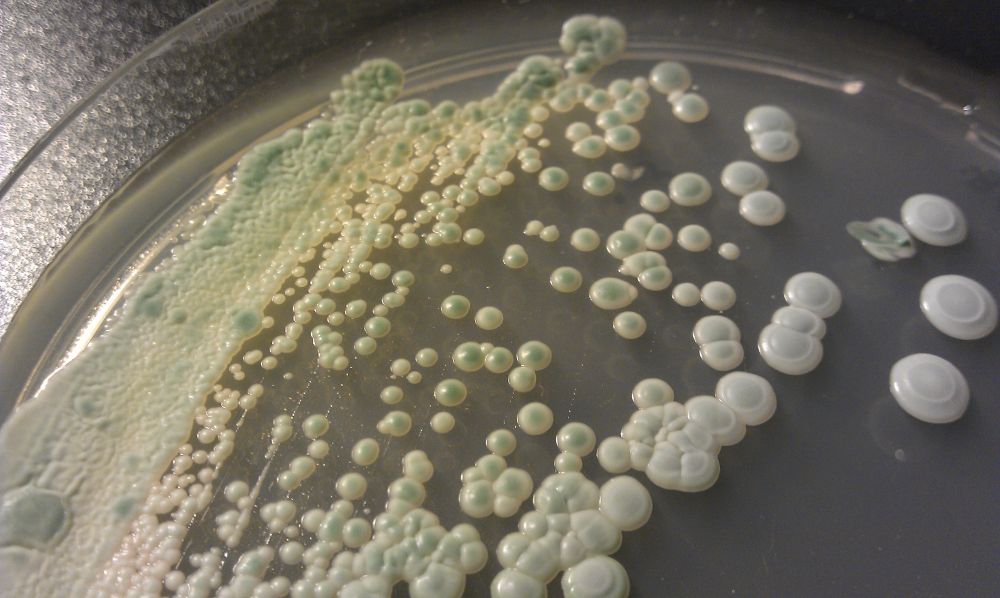
It is unbelievable that few of my students who carry out research on their own without any supervision, spent three weeks in the laboratory without result, according to narration, Nutrient Agar was prepared according to manufacturer specification or instruction and sample of organisms were streak on the surface of the Agar and incubate at 370C for 18 to 24hours. After incubation, they are expecting to have a very good colony or growth, but is something else they saw which is contamination…!
Later, they call my attention on the problems been enchanter on the materials and others equipment. Yeah, I asked them one or two questions are as follow, which kind of materials did they use? What is the nature of the problem? How do you prepare your media? How do you sanitize the Laboratory? Did you disinfect the bench work before used? Did you use distilled water or ordinary water?
One of them narrated that, they didn’t disinfect their bench work since the beginning of the research and then, I began to let them know the importance of disinfectants of bench work whenever researchers were been carry out. However, what are disinfectants and Antiseptic?
DISINFECTANTS AND ANTISEPTICS.
The term disinfectant means total elimination or destruction of microorganisms but not usually bacteria spores. It is generally applied to the process of making inanimate objects free from infection and safe to handle (e.g used laboratory glassware and hospital equipment) while Antiseptic is a term applied to an agent that destroys microorganisms but bacteria spores on the skin, mucous membranes or other living tissue, in order to prevent sepsis.
The terms disinfectant and antiseptic are usually applied to different types of chemical. Disinfectants are more potent and generally too toxic to be applied to skin or other tissue. They are used for disinfecting inanimate materials. Antiseptics generally have a weaker action and are sufficiently non-toxic to be applied to living tissue.
In general, chemicals are effective against a narrower range of organisms that are the physical agents and few of them are capable of killing spores within a reasonable period of time.
USE OF DISINFECTANTS
The important points of remembering when using disinfectants can be summarized as follow,
ACCESSIBILITY OF BACTERIA: A disinfectant fluid must be in contact with the bacteria cell and be absorbed by it in order to kill it. Dirt, grease and organic material will inhibit the accessibility of the disinfectant and some bacteria may remain unaffected. Therefore, it may be necessary to clean the materials with hot water and soap before applying the disinfectant.
TEMPERATURE: Disinfectants are more active at a higher temperature and for cleaning purposes; it will be helpful to use them in hot water.
CONCENTRATION: The disinfectant must be used at the recommended concentration.
TIME: All disinfectants take a certain time to the extent their effect.
TYPES OF DISINFECTANTS
ALCOHOLS: Ethanol, Industrial methylated spirit, and Isopropanol 70% are used to disinfect skin before injection and for the clinical thermometer.
ALDEHYDES: Formaldehyde that is Formalin.
DIGUANIDES: Chlohexidine (Hebitane) 0.5% solution of alcohol is used to disinfect the skin before injections.
HALOGENS: Hypochlorites, iodine in aqueous or alcoholic solution, povidone- iodine.
QUATERNARY: Ammonium, Compounds (QACs) examples follow, cetrimide (cetavlon) and benzalkonium chloride (Rocca).
They really appreciated the ways I though them because they followed the instruction. Thanks for taking much of your time on this post.