How will the new import tariffs affect the U.S. economy?
The White House has imposed an assortment of new regulations on future importations of natural resources. The initiative has been recently announced by the Trump Administration where an increase of taxation on imports of steel will promulgate at an affixed rate of 25% alongside other minerals such as aluminum which will be at 10%.
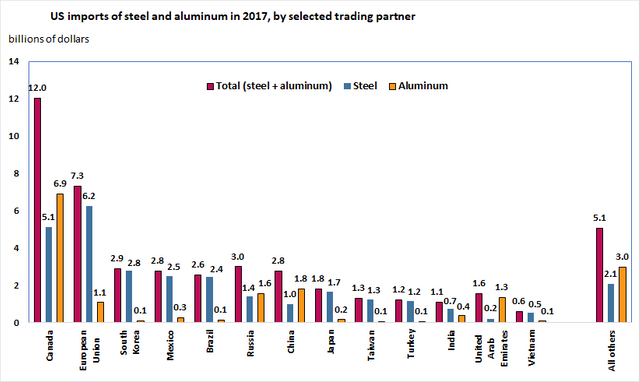
The move has angered several trading partners such as the European Union, Canada, and Mexico, which are expected to lose an accumulative amount of an estimated five billion dollars in steel exports and one billion dollars in aluminum exports for their total revenue.
The proposed policies have been seen as arguably restrictive by major trading partners as it does negatively influence the influx of trade between other nations and the United States. This move is seen as a provocation by other leading economies because it limits the number of products that are being exported to the U.S. and decreases the level of productivity in their countries where larger corporations could potentially be affected.
The objective was mainly launched to combat the increasing levels of unemployment in the U.S. labor market and increase domestic trade and growth within the economy.
The idea behind decreasing imports of metals have been introduced to encourage corporate entities to trade more within the country and with neighboring countries such as Canada and Mexico which are members of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and together make up the remaining participants of the free-trade association. The ongoing negotiations regarding the revisions of the NAFTA rules might alter the trade union significantly. Providing that the talks are successful, these new set of regulations would considerably benefit the domestic metal industries within the U.S. and neighboring states.
These activities can similarly compare to trade diversions where commercial activities divert from major to less efficient exporters. The respective country then becomes an essential supplier of consumer products for another country. There are potential risks to these measures as it would presumably broader the wealth distribution and lead to higher unemployment figures in nations which have traded with the United States due to the imposition of restrictive tax-schemes upon imported materials.
Furthermore, it forces other manufacturers to lower the marketed prices of their goods which may decrease the quality of their products due to inefficient management. This strategy is extremely beneficial for countries such as the U.S. with larger economies as they can control the markets of other nations through the influence on the value of natural resources as they are simultaneously a mass-producer and significant trading partner which gives them significant advantages when trading with other entities.
The most notable prospect of existing free-trade agreements is a comparative advantage that multiple countries have. Primarily, most of the participants subjected to these agreements enjoy the privileges of free trade to a certain extent.
Both countries accumulate large amounts of revenue.
The theoretical aspects are based on the scale of how massive the profitability can potentially be for the involved parties. The policies that have recently been introduced in the United States have considerably disregarded these factors.
Currently, any of these protectionist policies may restrict dozens of trading options within the country as it limits the importation of cheaper goods and destabilizes the market price of various consumer goods. Significant proportions of these more powerful economies produce more and consume less of the products they manufacture as most of them are exported overseas. The lower production costs are also a significant factor.
The idea encourages companies to move abroad or establish subsidiaries in other countries where production costs are lower rather than expensive. The monetary expenses of production are not taken into consideration and instead the opportunity costs producing goods among both parties are prioritized.
As long as the labor productivity levels of the two trading entities remain different, then the level of overall consumption of the product will increase in demand.
The leading economies of the world would most likely lose out on potential customers within the United States.
There will be a very noticeable revenue loss to other economic markets in other countries as well due to their dependency on trade with the U.S. and decrease in overall corporate expenditure.
Other nations would threaten and consider imposing retaliatory policies towards the U.S. in order protect their commercial interests. The EU has proposed a newly reciprocal tariff on cranberries, bourbon, and Harley-Davidsons which are estimated to amount up to 25% in import tariffs. It is a logical move which restricts trade between the United States and the European Union. The probable causes and effects of these new regulations would see a surge in the unemployment figures and prices to skyrocket in several countries due to limitations on partners to trade. It enables local companies to manipulate the prices of certain goods on the market.
The marketed prices of these products would increase causing many employees to lose their jobs.
The industries which are heavily reliant on materials such as steel and aluminum would be most negatively affected having to cut back on expenditures and dismiss employees.
If the United States wishes to pursue its initiatives in restructuring its labor force, then it must indeed be aware of the enormous effects it would have on other countries. First of all, the restrictive policies would decrease international trade for business partners In the U.S. presuming that other partners abroad retaliate.
It is hugely unbeneficial for world trade as it makes the prices of goods more expensive for both sides and harms the private sector of many other countries which are reliant on the United States.
There are multiple advantages to international trade such as that it creates jobs and increases economic growth. It also gives local firms the opportunity to expand into other economies and experience manufacturing in other markets abroad. The companies can function more efficiently when trading in multiple markets due to experiences of trading with various types of partners.
These factors can also lead to companies becoming increasingly dominant in their sector of production and gaining a competitive advantage in world trade. In many cases, these corporations would choose to prioritize their exports more than domestic business as it enables them to be more productive when serving more clients abroad. The importation of products from other nations also allows foreign competitors to decrease market prices of their goods and increases the varieties of products of goods and services available.
However, there may also be significant disadvantages to international trade as it reduces the local jobs of domestic industries which are unable to compete with larger businesses. This phenomenon eventually leads to job outsourcing where companies tend to move their headquarters or central offices elsewhere. Most of these relocated companies are based in countries where the corporative taxes are lower rather than those who are not. Those countries which are significantly reliant on traditional economies may be the ones to suffer most because most of the advanced nations tend to subsidize their agriculture sector which decreases the general income of local farmers as a result of government intervention.
The new import tariffs would drastically affect the general U.S. economy including individual states.
The initial plan to withdraw from the Trans-Pacific Partnership and renegotiate the terms of NAFTA. The economic effects which may follow afterward will subsequently put critical industries at risk.
Many economists believe that the tariffs are protectionist measures which have been introduced to level out the amount aluminum and steel that have been imported from other countries due to their low and attractive prices. This move puts American factories and industrial plants which are dependent on these raw materials in a disadvantageous position.
It may, however, serve as a relief for most of the producers of metals as they finally have their share of the market of potential consumers back. However, depending on how large the trade war will escalate, it will cause prices of steel and aluminum imports to rise. This action would critically endanger the construction, brewing, and automobile industries. Smaller states would quickly dominate the larger ones as they factories are more industrially orientated and can produce faster and on a larger scale.