SLC21 Week2 - Programming arrays
Assalam-o-Alaikum!!!
Greetings to my all STEEMIT members. Hopefully you all are great and enjoying your best life on STEEMIT. I am also fine ALHAMDULILLAH
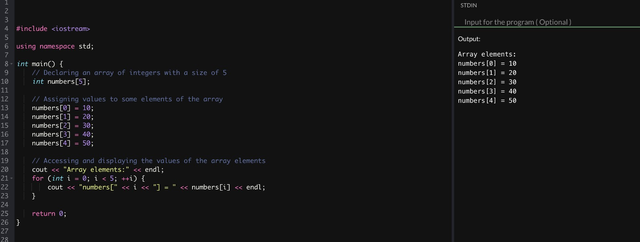
We can say that Array is the addition if elements of same data type. We can access array through data types. And through this effieicient method, we can access and stored many items of the same data type
Advantages:
Arrays is a single variable that not only allows elements to be stored, but is also very organized, and in individual cases it also reduces need of indivisual variables. It handles searching or debugging tasks very well. It allows quick access and organizes a fixed set of elements. It groups related data and keeps code clean and tidy. Makes it much easier to understand
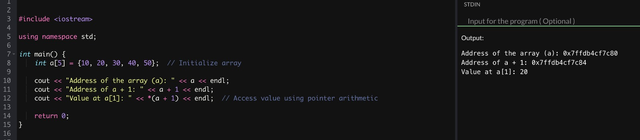
- Array Name as Pointer:
The array name a is actually a constant pointer to the first element of the array (a[0]).
If you use cout << a;, this will output the memory address where the array starts, not the array elements themselves. The address is displayed as a hexadecimal value (like 0x7ffc...).
Pointer Arithmetic (e.g., a + 2):
- Since a is a pointer to the first element, expressions like a + 2 or a - 2 perform pointer arithmetic.
- a + 2 means the address of the element that is two positions ahead of a[0], which is a[2].
- a - 2 would attempt to move two positions backward from the start of the array, which is invalid for array boundaries and will result in undefined behavior if accessed.
Using cout << a + 2; and cout << a - 2;:
cout << a + 2; displays the memory address of a[2].
cout << a - 2; displays the memory address two integer sizes before the start of the array, which is generally invalid.
If cout << a; Displays 4000:
Assuming a is an int array and cout << a; displays 4000 (as a hypothetical memory address), a + 1 would be the address of a[1], which would be 4004.
In C++, each int is typically 4 bytes, so moving to the next integer address increases the address by 4. Therefore:
a points to 4000
a + 1 points to 4004
a + 2 points to 4008, and so on.
Let’s break down what happens with cout << a + 2;, cout << a - 2;, and the effects of pointer arithmetic in general.
Understanding cout << a + 2; and cout << a - 2;
- Pointer Arithmetic:
a + 1 points to the address of the next element (a[1]).
Since a is an int array, each element typically occupies 4 bytes (assuming int is 4 bytes on this system).
Thus:
a + 1 points to 4000 + 4 = 4004
a + 2 points to 4000 + 2 * 4 = 4008
a - 2 would point to 4000 - 2 * 4 = 3992
Using cout << a + 2; and cout << a - 2;:
cout << a + 2; will display the memory address 4008, which is the address of a[2].
cout << a - 2; will display the memory address 3992. This is technically two int positions before the start of the array (a[0]). Accessing a - 2 is invalid and leads to undefined behavior if dereferenced, as it’s outside the array bounds.
Example Explanation
If cout << a; displays 4000, then:
cout << a + 1; will display 4004
cout << a + 2; will display 4008
cout << a - 2; (while invalid for accessing values) would display 3992
Yes, an array has 2D we display and organize the data in columns and rows which are arranged in our table. It is also supposed to handle any data for which it is capable of 2D indexing.
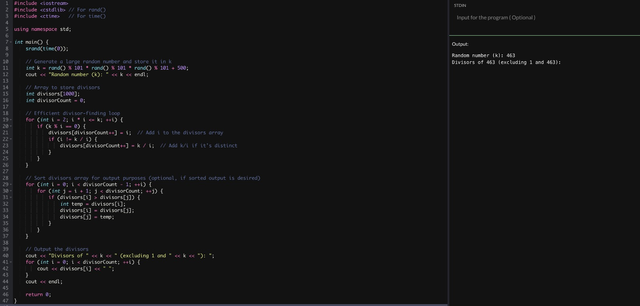
While solving this problem, we will let a number k. And we will also store it in an array. After that we will generate this as specified. and then found a divisor by using efficient method by without using the function. then our result will be stored in an an array
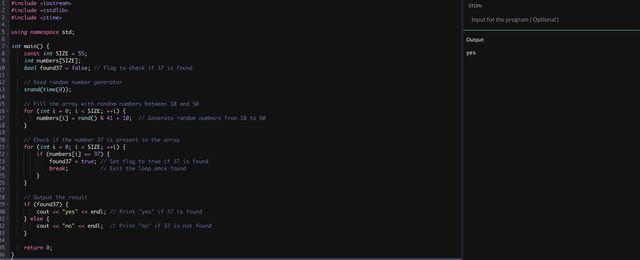
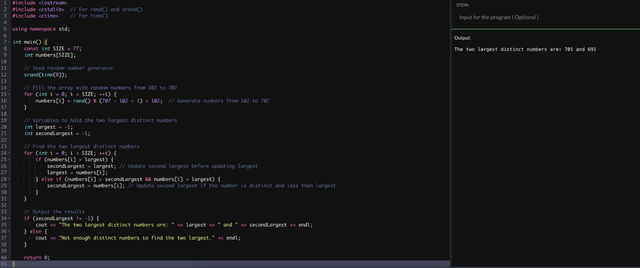
In this problem we will fine the required number in the array. And if we find the required number in the array then print yes. But if we did not fine the required number then, it will print No
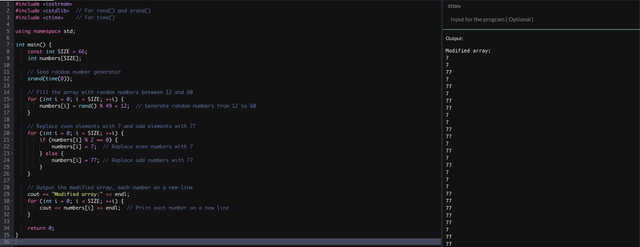
I found this is very interesting. In which we founds an array from number 12 to 60. And we have to show it in this way that it will show thw even number replaces to 7 and odd number replaces to 77
Here is the program with Output
So here I am trying to do my all tasks. And I do my level best. I hope you will appreciate me.
Special Thanks to @sergeyk
Invite friends @maryamnadeem , @uzma4884 @drhira