#A Brief Introduction to Microorganisms • A Glimpse into the Field of Study - Microbiology.

Today I am going to try to shed a little light for the non Illuminati among the readers on the branch of science known as Microbiology.
While some of you might have an idea of what the word means using the knowledge of etymology (mikros + bios + logos translated from Greek as small, life, science/study respectively). In simple a simple sentence, it translates to - the study of small, tiny, living things. But if you ask me, i'd tell you that "Microbiology is the branch of biology that is concerned with the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, viruses, algae, protozoa, and fungi, and their effect on humans" just to sound smart and haughty.
First, Microorganisms are tiny organisms which cannot be seen with naked eyes (unless you're Superman or something) which exist individually or in collections known as colonies. These organisms show and perform characteristics and functions required to be called "living" and are found everywhere on earth, even in space! These little things often have a good or bad effect on humans and other things like food, animals and plants e.t.c. depending on their alignment. Think of them as fairies, small, tiny and sometimes unseen. We have the good ones like the nature fairies who cause the seasons, fairies who cause good luck (and of course, Cinderella's fairy godmother) and we also have the naughty ones who cause naughty things (duh!) like the pixies and Maleficent? Like so, there are microorganisms do good things like aid digestion, help in food manufacturing e.g Yeast, and there are also some which do bad things like cause food spoilage and diseases e.g Salmonella (pronounced as spelt) which causes food poisoning.
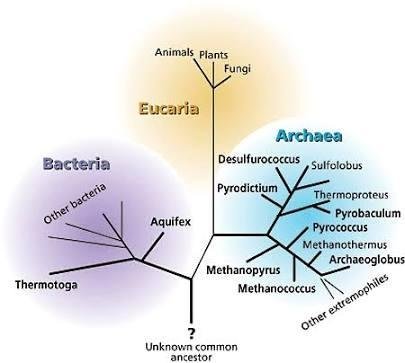
Microorganisms are mainly classified into three domains :
So, a microbiologist's job is majorly to study these miniature organisms, look into their structure, growth and development among other characteristics and how we can use them.
Microbiology as a discipline is pretty relevant in aspects of society like - food, hospitals, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, biotechnology, environment, education and other aspects which I might have failed to mention. Some of these aspects are described below.
Microbiology in Food Industry
Food microbiology does not only include study of microorganisms which produce food due to their high nutritional value, but also involves study of microorganisms which use our food as a source of nourishment for their own growth and development thereby leading to spoiling of food by certain enzymatic changes. Like I said, good and bad microorganisms.Microbiology in Production of Industrial Products
This involves the study of how microorganisms can be exploited to commercially produce vitamins, antibiotics organic acids and even alcohol. For example, Aspergillus niger produces citric acid which is used in food preservation and as animal feed additives since they enhance growth.Microbiology in Biotechnology
This involves the use of molecular techniques for manipulation of genetic info called Genetic engineering and the use of such genetically engineered microorganisms in industrial processes, all these using the knowledge of microbiology.Microbiology in Environment
Microorganisms are found everywhere on earth and even in areas of harsh conditions like extreme cold or extreme heat. These little things have the ability to adapt to situations over time. Microorganisms are also found in soil, water, and air (everywhere). These microorganisms play essential tolerating recycling of environmental elements such as oxygen, nitrogen (e.g Nitrosomonas ) and carbon.Microorganisms in Medicine and Hospitals
This involves the use of microorganisms to try to create a "disease free world" and since there also "villain" microorganisms, Microbiology also tries to find new ways of efficiently fighting them (sort of a hero corporation).
Microbiology also has types which include :
- Medecine
- Research
- Agriculture and Food Safety
- Environment and Climate change.
And also, as Batman has his batarangs and Wolverine has his claws, Microbiologist also have some cool tech which they use in their line of work. While their gadgets are not as cool or badass, they still do some pretty interesting things, for example :
Autoclave - this is a very important instrument used to sterilize glassware and liquid substances. It is important because the study of microorganisms is fragile business requiring neatness and meticulosity on the part of the individual.

Microbial Incubator - this is used for growing microorganisms in the lab. It provides a suitable environment in which microorganisms can effectively grow.

Refrigerator - no, not the one in the kitchen for your food and drinks but similar. It serves as a storage for chemicals, serums, reagents e.t.c all part of stuff used in a microbiology lab.
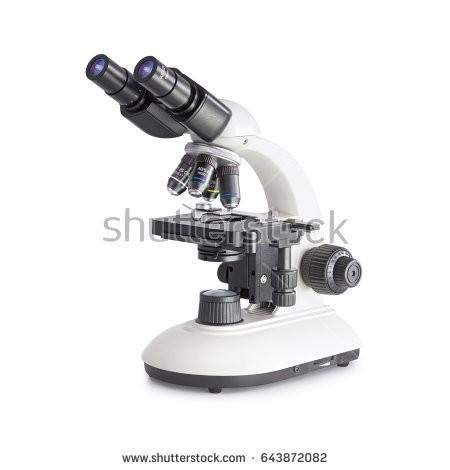
Microscopes - highly essential and widely known, they are used for the observation of items that cannot be seen with naked eyes.
Computers - unlike your Windows PC and other variants, these computers are specialised for the analysis of lab results and are also used for the identification of microorganisms. Examples are the Apple II, IBM PC and TRS-80 and their modern variants.
There are still more equipments like the spectrophotometer, Automatic Bacteria Identification System (you can already guess what it's used for), Dry air oven, Hot air oven for sterilization e.t.c.
Finally, in the unlikely event that you partake in a microbiology themed trivia, these might help :
Anton Van Leeuwonhoek is regarded as the "father of microbiology" and one of the notable names among pioneers of microbiology. Other notable names are Louis Pasteur, Robert Koch and Joseph Lister.
Noteworthy events and their time of occurrence in Microbiology.
Date Event
1857 - Louis Pasteur showed that Lactic acid formation is due to microorganisms .
1881 - Louis Pasteur developed anthrax vaccine.
1885 - Louis Pasteur gave rise to rabies vaccine.
1887 - Buchner discovered that yeast extract ferments sugar.
1921 - Fleming discovers lysozyme.
1923 - First edition of Bergey's manual.
1929 - Fleming discovers Penicillin.
1933 - Ruska develops electron microscope.
1935 - Domagk discovers sulfa drugs.
1937 - Chatton divided living organisms into prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
1941 - Beadle and Tatum give one gene, one enzyme theory.
1944 - Waksman discovers streptomycin.
1982 - Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine developed.
1986 - First vaccine (hepatitis B vaccine) produced by genetic engineering approved for human use.
Hopefully you've gained something of value from this post, thanks for reading 😃.
Image Sources :
pixabay
shutterstock
Article sources :
Wikipedia
A textbook of microbiology by R. C. Dubey and D. K. Maheshwari.