Where Does The Solar Wind Come From?
Like any other star of the yellow dwarf category, the Sun is a huge ball of low-temperature plasma. Which not only sustains life on our planet, but is constantly involved in the formation of Interstellar medium.
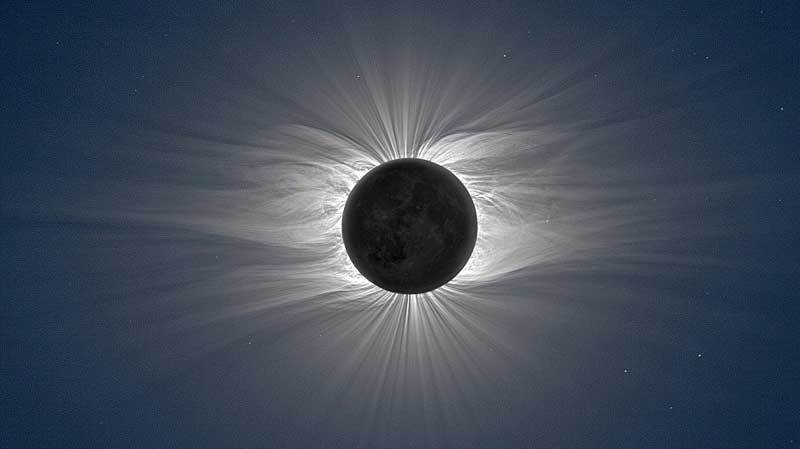

image source
The barely perceptible streams of ionized gas flow along the lines of the magnetic field of the sun at a speed of 300-1200 km/s. These flows extend beyond the orbits of all the planets of the solar system, gradually reducing speed. The name of this phenomenon is a Stellar wind. In our case- the Solar wind.
Every second the Sun burns 700 million tons of matter, and only 1 million tons are able to overcome the attraction of the giant and leave the atmosphere of its progenitor, to later become part of the interstellar space.
In the solar Corona region, billions of particles are combined into laminar flows, the ordered, continuous streams. A powerful magnetic field of the star pushes the particles from the center along the magnetic lines. Huge masses of matter move evenly, in large volumes. It looks like a calm and steady flow of the river. Some of these streams return back to the Сorona.
The motion of the solar wind near the Sun. image source
But, some flows (away from the Sun) lose their integrity, becoming gusty, irregular currents with changes in speed and density. They become like real wind, not water. These flows escape from captivity of the magnetic field and overcome billions of miles at supersonic speed.
Only recently the scientists have been able to understand at what point the laminar flow of ionized particles turns into a turbulent flow, and what happens at the boundary of separation of the flow from the Corona [source].
At a distance of 30 million kilometers from the center of the Sun, the most powerful emissions of plasma begin to lose their stability. At some point the pressure of matter dominates over the magnetic field and the flow of charged particles begins to behave as a gas and not as plasma.
From that moment, this is not a concentrated flow, but a scattered cloud moving in a certain direction at a tremendous speed.

The moment of transition of flow from laminar to turbulent regime. Views of the solar wind from NASA's STEREO spacecraft (left) and after computer processing (right). source
It is important to note that the solar wind is actually an extension of the magnetic field of the star. How far does it extend?
Only breaking the mark of 11-13 billion km., the solar wind loses its supersonic speed and first encounters with the interstellar medium. This event greatly reduces its speed, and gradually ionized solar particles mix with particles from across the universe. Here ends the heliosphere.
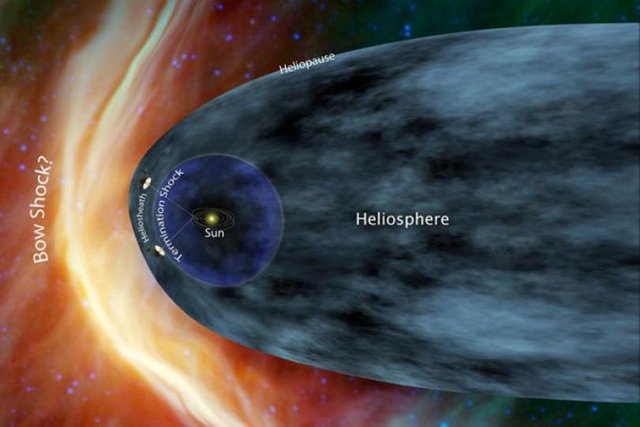
The Heliosphere is the area in which the solar wind moves at supersonic speed relative to the Sun. image source
In 2013, the world got the news that Voyager-1 finally left the solar system. In fact, this is a contentious issue. Voyager really escaped from the zone of the main influence of the solar wind, left the heliosphere.
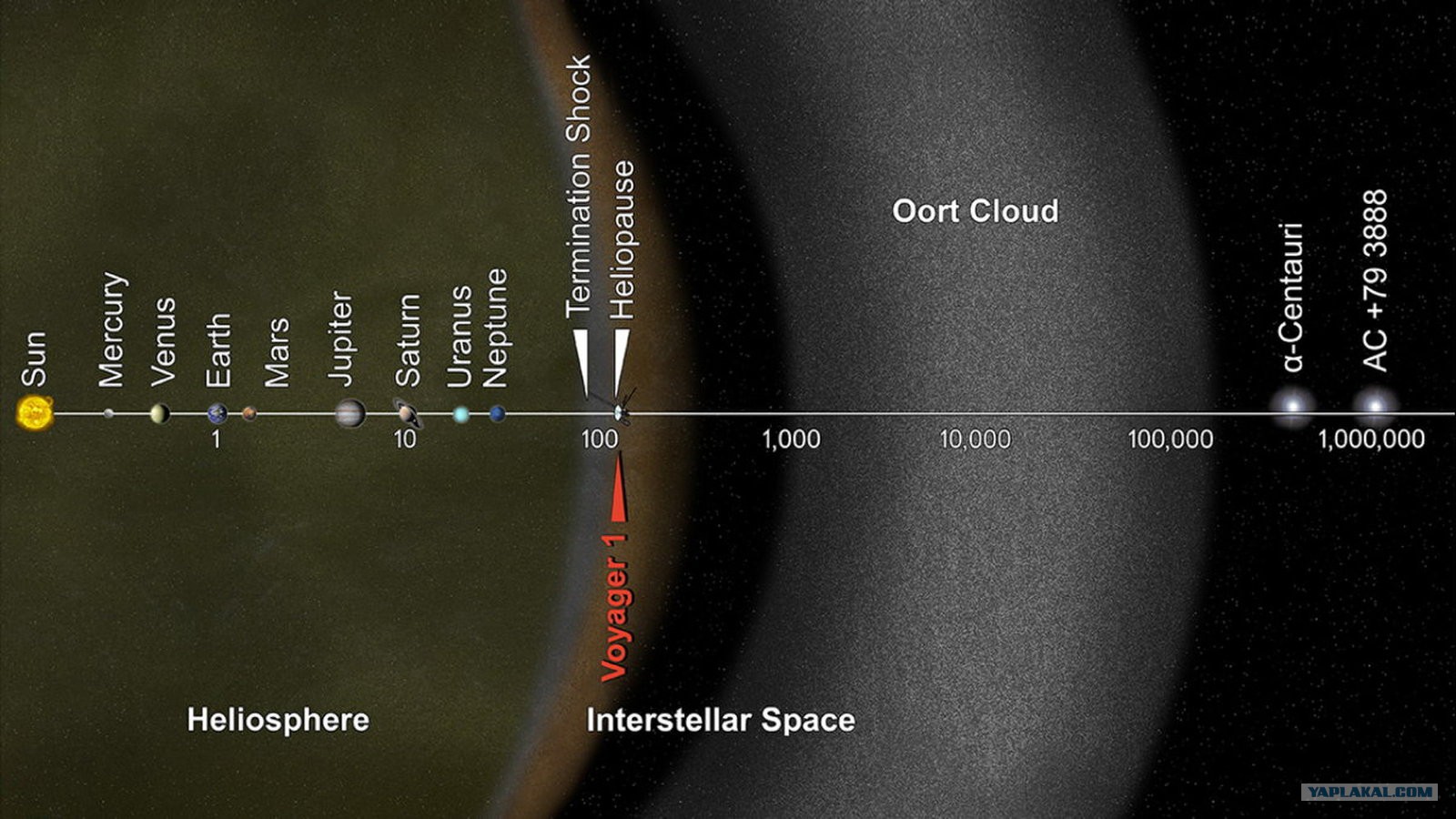
image source
But, if we consider the gravitational influence of our star, the radius of which is 1 light year (9460 billion km), then Voyager did not overcome even 1/1000 of the whole way.
Is the solar wind dangerous for our planet? No, while the magnetic field of the Earth is strong enough to hold the atmosphere.

source
We can observe the direct impact of the solar wind in the form of the Northern lights. During strong solar flares can occur so-called magnetic storms, which have the small impact on our electronics.
But in the long term, the solar wind can become the executioner for the planet with a weak magnetic field.
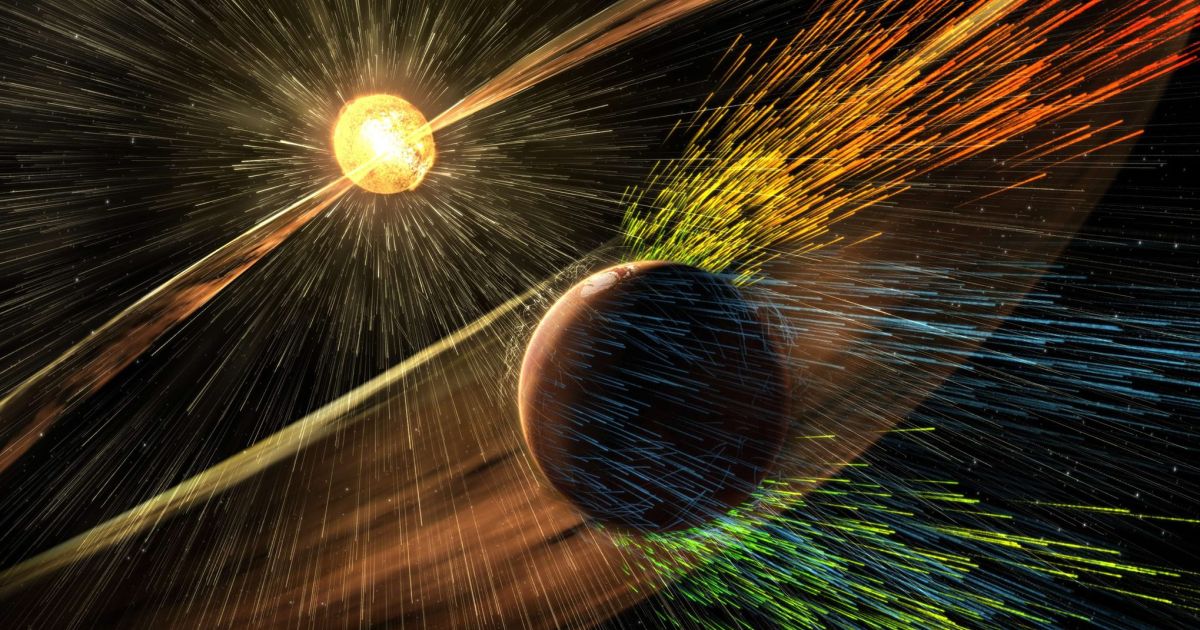

image source
The solar wind finally turned Mars into a lifeless planet. When its magnetic field weakened and the density of the planet's atmosphere decreased, the solar wind literally blew away the remains of the atmosphere into space. The surface of the planet became completely defenseless against the influence of solar and cosmic radiation.
Ironically, at the same time, the solar wind serves as a protection for the whole solar system. Within the boundaries of the heliopause, the pressure of the solar wind prevents the penetration of interstellar gas and cosmic rays deep into our system. Meanwhile, radiation effects of the sun far below the levels of radiation of interstellar matter.
In 2018, NASA will send Parker Solar Probe in the solar Corona, and we will get more data about the origin and influence of the solar wind in the scale of our system and galaxy.
sources: Images From Sun’s Edge Reveal Origins of Solar Wind, FADING CORONAL STRUCTURE AND THE ONSET OF TURBULENCE IN THE YOUNG SOLAR WIND, Sciencenews, NASA Uses New Test To Determine If Voyager 1 Has Left Heliosphere To Enter Interstellar Space,WiKi, Elements and other references in the text.

well job👍👍 brother@natord
Thank you! :)