Oral Vitamin D Supplementation Drastically Reduces Inflammation From A Sunburn
Summer is just beginning, and with summer comes the beach, pool parties, or a variety of other outside activities. This means spending time in the sun and trying our best to protect our skin from the harmful UV radiation that it emits. Wearing sunscreen is important but lets face it, we are all human, sometimes we forget to apply, sometimes we don't apply often enough. This leads to sunburns.
Today lets take a look at an article published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology titled "Oral vitamin D rapidly attenuates inflammation from sunburn: an interventional study." This article is available for use under a creative commons attribution license, as such all material from the article will be appropriately credited.
Sunburns
A sunburn is a radiation burn (in this case the radiation is ultra violet light), when the ultraviolet light hits your skin it penetrates into the cells and actually induces changes to their DNA. It results in a variety of deleterious DNA lesions including thymine-dimers (when two stacked T's (thymines) actually form a chemical bond to one another). These forms of damage wreak havoc on cellular DNA replication processes and will stop DNA polymerases (the replicative ones, not certain specialized repair enzymes) in their tracks.
If you have a little bit of damage, the cells have the necessary enzymes to conduct a repair mission, restore DNA replication to normal functioning and continue on their merry way. However if there is just a whole crap ton (to use a very scientific term) of damage (from longer sun exposure) they can't fix everything. When cells can't fix the errors, which spells trouble and can lead to a whole host of potential issues (including cancer). Our cells are programmed to kill themselves in this situation, thus they begin the process of doing so, called apoptosis. The cells killing themselves results in an inflammatory response, and this inflammatory response is what we all know of as a sunburn.

Vitamin D
Vitamin D actually does not refer to just one compound, rather a few (D3([Cholecalciferol)(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecalciferol), D2(Ergocalciferol and the less important D2 which is actually a mixture of D2 and the compound Lumisterol). The D vitamins are fat soluble compounds with a whole host of important biological functions including calcium shuttling, bone development and influence on inflammation levels [2]. Vitamin D is only a vitamin by technicality as our bodies are able to synthesize all that we need from 10 minutes daily exposure to the sun [3].
What Were The Researchers Studying
Due to the recent finding that a single dose of vitamin D3 was capable of rapidly decreasing inflammation in a mouse model for chemical skin injury [4] the authors hypothesized that it could be used to reduce the inflammation of a sunburn. So they designed a proof of principle double blind clinical trial to test this hypothesis [yes @lemouth, the sample size here is also small, only 20 people ;)].
In their study the participants received either a placebo or a high dose of vitamin D3 one hour after they were blasted with enough ultra violet radiation to cause a “sunburn” though in this case the sun was not used… so it was more of a lab burn? This sounds like a great study, I wonder what the participants were asked… “Come participate, will give you sunburn for $$$.” Regardless, the results might interest you.
What Did They Find?
They blasted the participants skin with UVB radiation, then waited 48 hours and took a look at the skin redness. In the figure below you are seeing 4 spots on a participants arm where they were blasted with increasing amounts of UV radiation (from left to right).
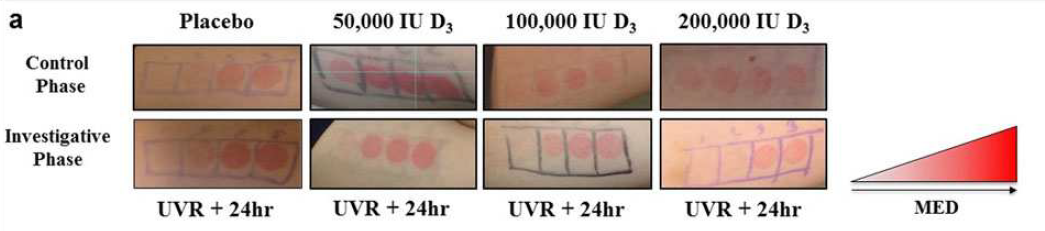
What you can make note of from the figure above, is the last group on the right, for the very high dose of vitamin D3. The top set is a control where the participant did not receive the vitamin D, and the bottom is where that same participant did. You will notice that there is significantly less redness (especially at lower amounts of UV) in the bottom set. This indicates that a high dose of vitamin D did have an effect in reducing the inflammation from the sunburn. (For this result the authors report a P value of 0.02, where they were concluding statistical significance for any P < 0.05)
In addition to visual queues, the authors also took a look at the amounts of proteins that are expressed in inflammatory processes. These were 'Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) and cytokine inducible Nitric Oxide Synthetase (iNOS).
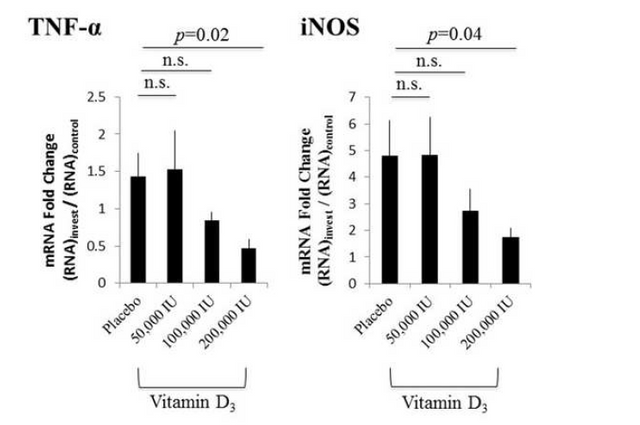
Here they were looking at the expression levels of these proteins based upon how much mRNA was being generated (remember mRNA is the instruction sheet telling the cell to make a protein, more mRNA = more protein generated, because there are more instructions floating around). What we can see here is that both of these proteins involved in the inflammatory response are reduced in expression levels as the amount of vitamin D supplemented goes up.
Other Important Observations
- The overall cellular gene expression profile for those receiving the high (200,000 IU) dose of vitamin D3 was very different from the placebo group.
- NOT all participants receiving higher doses of Vitamin D3 showed a response. As a result the authors classified the participants into two groups (Responders and Non-responders)
- Non responders had very different gene expression profiles then people who did respond better to the vitamin. They expressed a lot more proteins which are pro-inflammatory (IE lead to and participate in the inflammatory response).
Brief Conclusions
- The authors here have illustrated evidence that a single high dose of vitamin D3 administered one hour after sun exposure helped to alleviate the inflammatory response associated with sunburn.
- The administration of the single high dose of the vitamin did not negatively alter the participants calcium levels.
The simplicity and safety of high dose oral vitamin D3 treatment, combined with its rapid and sustained therapeutic efficacy, suggest that these proof-of-concept findings may ultimately be translated to routine clinical use once larger studies are performed on diverse populations of subjects.
The results reported here are interesting and do hold promise for future research.
Should I Self Medicate With Vitamin D After Sun Exposure?
NO, this data is not sufficient to justify self medication.
It is just some interesting science that I hope you enjoyed learning about.
# Sources
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X17315580
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/
- http://health.usnews.com/health-news/family-health/heart/articles/2008/06/23/time-in-the-sun-how-much-is-needed-for-vitamin-d
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26288355
All Non Cited Images Are From Pixabay.com or Flickr.com And Are Available Under Creative Commons Licenses
Any Gifs Are From Giphy.com and Are Also Available for Use Under Creative Commons Licences
If you like this work, please consider giving me a follow: @justtryme90. I am here to help spread scientific knowledge and break down primary publications in such a way so as to cut through the jargon and provide you the main conclusions in short (well compared to the original articles at least!) and easy to read posts.
That is one way to start a conversation, haha.
I realize this was a double blind clinical trial but the results are intriguing.
Do you have any thoughts on why the gene expression of the non-responders was different than the responders group?
Genetic variations leading to a differing response to vitamin D supplementation is a previously identified phenomenon.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23935129
So that part isn't surprising, however as to why this genetic difference occurs between people? That I don't know. More information is probably out there in the literature that sheds some light on it somewhere. I haven't looked though.
Great research i love your post however did you know that tomatoes are goid for sun burns and skin issues. Yes by eating lots of it.... Do a research let me know if you enjoyed that
I did not know that. Apparently eating a bunch of tomato paste resulted in about an spf 1.3 for the participants in a 2012 study.
Amazing post, thank you for posting this valuable information !!
Thank you for your comment.
Firstly, Shame I hope the participants where rewarded well because those sunburn spots look mighty painful!
I do find articles like these so informative, I only realized last year how important vitamin D3 is to our body's
I hope they were paid too! I wouldn't want someone to give me a sunburn for nothing (I mean I understand for science...but still, it's physical harm.)
Yes haha for sure..
I found this writeup very interesting, making good research like this will go along way solving some problem we are having,i have upvoted you already and equally following you. I am looking forword to woking with you and a lot of people that have good content and need people to support them.i am always there for them.
Thank you!
Your welcome, i realy enjoy the writeup, feel free to let me know whenever you have a post, so that i can enjoy the pics and equally upvote you as usual
Animation is excellent
Thanks man :)
Thank you for sharing this! Vit D3 is very important but we shouldn't forget about using sunscream also! xX Karolina
Well of course, sunscreen is imperative.
Nice and very educative...keep it up...upvoted and following...I shall send quite a lot on health...follow me too for ur informed comments
Thank you for reading :)
welcome @justtryme90
do check my blog as i sent first into post along with a nice joke
will appreciate if you upvote and comment...plus follow..tks
Great post master of biochemical, be fancy with your article @justtryme90
Thanks man :)
welcome @justtryme90
You can get vitamin D from the sun? or from fruit or vegetables. taking vitamins to me like trying to run mac software on a windows computer. it won't understand what it is and is pretty much useless to the body. Why not use what nature provided. cool article but
Vitamin D is naturally produced by our bodies from exposure to uv light from the sun, and a bit of processing in our livers.
Vitamin D supplementation does in fact work, uptake is okay. However it is only necessary for specific cases. Your analogy isn't any good in this case.
Cheers.