Biomass
Generally, biomass as matters can be considered as Garbage, Without energy conservation, manufacturers will pass the production cost to consumers Convention forms of energy are: i. Mechanical ii. Chemical iii. Heat energy iv. Nuclear and energy of electromagnetic radiation The non-conventional energy include; fossil fuel, biomass hydro electronic power, nuclear, Geothermal, wind, tidal, solar, Energy are classified into Renewable and Non-renewable Renewable energy source include; biomass, Geothermal energy, Hydropower, solar energy and wind energy (non-conventional) MECHANICAL ENERGY M.E entails kinetic energy: this is the energy associated with masses in motion e.g. when a boy runs or when water is pouring down a waterfall POTENTIAL ENERGY P.E is the energy possessed by a system or an object due to its position Electrical energy:As we use technology, the demand of electricity grows. The ratte of charge flow of electricity with is called electrical current it is measure ampere Power is the rate of using or producing energy, it is measured in watt.
RENEWABLE NON-CONVENTIONAL NATURAL SOURCES OF ENERGY SOLAR ENERGY
Solar cells Solar water heating Solar furnace WIND ENERGY HYDROELCTRICITY TIDAL ENERGY CONVENTIONAL AND NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES FOSSIL FUEL NUCLEAR ENERGY GEOTHERMAL ENERGY: types of geothermal field include: hot water fields, wet steam fields, CONSERVATION OF ENERGY One form of energy can be easily converted to another such as potential to kinetic type or chemical to electric form while the total energy always remain the same; That energy is neither created nor destroys in any given physical system. This is called law of conservation of energy (a) Solar energy conversion: i. (c) Hydro power energy i. Solar energy is converted into useful form through application of the following conversion devices. Solar panels ii. Charge controller iii. The power inverter iv. Batteries storage (b) Wind energy: The major components of a typical wind energy system include: Wind turbine, a generator interconnection apparently and control system. The major components are: Penstock ii. Hydro turbine or wheel iii. Transformer iv. Gear box or belt drive v. generator VI. Transformer vii. AC output to load… BIOMASS A SUATAINABLE SOURCE OF RENEWABLE ENERGY The term biomass refers to all organic matters generated through photosynthesis and other biological processes. Biomass is considered as a solar energy stored in chemical form in plant and animals, materials and its among the most precious and satellite materials on earth Biomass has been used for energy purpose ever since man discovers fire The use of biomass helps reduce global warming compared to a fossil fuel power plant. Plants used and store carbon dioxide (O2) when they grow (O2 stored on the plant stored on the plant is released when the plant materials burn or decay) By replanting the crops the new plant can use the CO2 produced by the burned plant RELATIONSHIP OF BIOMASS WITH RENEWABLE AND NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY Six most utilized renewable energy sources are: hydro power, tidal wave, solar, wind, geothermal and biomass All energy forms derived from sources are renewable Renewable energy: source refers to forms of energy source that can be regenerated in a short period of time after utilization. While; Non-renewable energy source can’t be regenerated after a short period of time. Non-renewable energy is mainly source from the ground as liquids, gases and solid e,g crude oil, natural gas and coal. On the average, biomass produces 38% of the primary energy in developing countries and about 90% in Brazil. In Sweden and Austria 15% of their primary energy consumption is covered by biomass In USA 4% of their total energy is from biomass Biomass can be used to produce ethanol (bio fuel) Brazil
produces bio fuel from agricultural feed stock
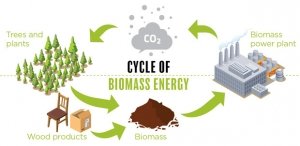
TRANSFORMATION OF BIOMASS INTO RENEWABLE ENERGY The process of converting biomass into a useful form of energy include: combustion, Pyrolysis, destructive distillation, gasification, anaerobic bio gasification, fermentation of vegetable oil
COMBUSTION It involves burning of biomass fuel in the presence of air to generate heat energy Its main products are ash and fuel gases
PYROLYSIS
Pyrolysis is the process of heating wood and agricultural residue at temperature between 540-1100oC in the absence of air near several hours to breakdown plant materials into a complex mixture of liquids. A good example of pyrolysed mixture is charcoal The gas that are produced during the process of pyrolysis can be converted or synthesized into methanol and liquid which are used as fuel. DESTRUCTIVE DISTILLATION It is carried out in long steel retorts, or earthen kilns Only the wood waste such as branches, trunks of trees are used as raw materials The process involves decomposition of wood at high temperature in the absence of air, the wood is converted into chemical GASIFICATION ANAEROBIC BIOGASIFICATION This is the degradation of organic matter in the absence of air to methane and carbon dioxide Annual waste such as cattle dung, chicken droppings and night soils are the main raw materials for the production of biogas FERMENTATION DISTILATION Ethanol is an alcohol fuel made from sugar found in grams such as corn, sorghum, etc. TRANSESTERIFICATION OF VEGETABLE OIL air pollutants. The basic treatment in the production of biodiesel is referred to as Transesterification Biodiesel is a fuel made with vegetable oils, fats or greases- such as recycled restaurant great It’s the fastest growing alternative fuel in United States Biodiesel is a renewable fuel; it’s safe, bio degradable and reduces the emission of most air pollutants
very educating