[The Universe] The Big Bang Theory.
Welcome to the new "series" on my blog =D
This series will apply to the entire UNIWRSUM as we know it. If you don't know what the universe is, let me quote a note from Wikipedia.
The universe - everything that physically exists: the whole space, time, laws of physics, physical constants, and all forms of energy and matter. Most of the matter and energy in the Universe takes the form of dark matter and dark energy. The word "Universe" can also be used in other contexts as a synonym for the words "cosmos" (in the sense of philosophy), "world" or "nature". In science, the words "Universe" and "Space" are equivalent.
At the very beginning of this series we will start from the beginning of the universe, the Big Bang Theory.
UWAGA! THE FACTS I HAVE PRESENTED MAY BE IN CONFLICT WITH YOUR RELIGION, SO IF YOU ARE INTERESTED, PLEASE DISTANCE YOURSELF.
BEGINNING
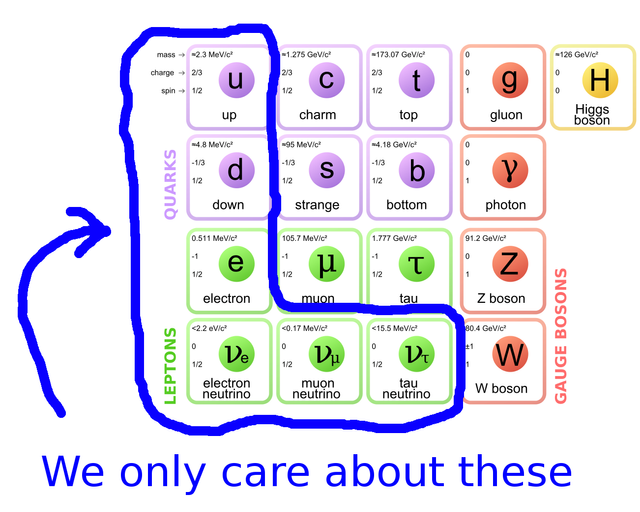
Before you learn what the Big Bang is, you need to be aware of what is (probably) the smallest in the world. These are quarks. What are quarks? Quarks are particles of the size of a few attometers. The meter is one trylion part of the meter. Imagine one meter, then divide it into one million parts, now take one part and divide again into one million parts and once again take this part and divide again into one million, or 0. 000 000 000 000 000 001m. Quarks are probably the smallest known for humans elementary particles.
Well, now you know what a quark is, but what does it have to do with the Big Bang? It turns out that a lot. Because, according to this theory, the whole universe was just such a small quark, and it was the Big Bang that caused the creation of the current universe, which is dynamic (all the time it changes), it means that it is in constant motion and all the time it grows!(and at an unimaginable speed and once in a while!) .
The density of such a small quark had to be almost INFINITE. What caused the Big Bang? We do not know, and we will probably never know. We know that at the beginning light elements were created, (e. g. Hel) only then particles joined together more complicated and heavier elements were created (e. g. Gold).
How big was the explosion?
To show the scale of the explosion I will give you a few examples of numbers from space.
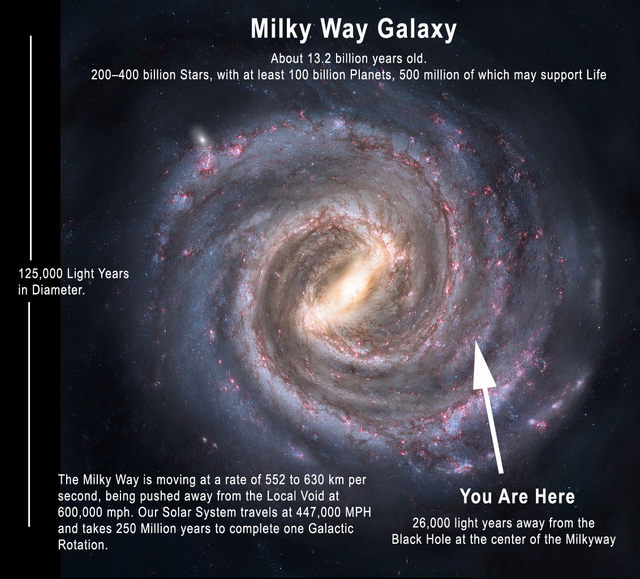
120 thousand light years have the diameter of the Milky Way, i. e. 1 135 287 660 000 000 km.
2. 52 million light years distance of the Milky Way from the nearest neighbouring galaxy of Andromeda, or 238410408000000000 km.
The distance of the Sun from the centre of the Milky Way, i. e. 10 650 000 000 000 000 km.
Near, what not? In fact, these distances are nothing in comparison with the whole universe.
Returning to the Big Bang.
This theory is based on observations indicating the expansion of space according to Friedman-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker's metric. This is supported by the red shift in the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation from distant galaxies, which is in line with Hubble law in conjunction with the cosmological principle. These observations indicate that in fact the entire Universe expands from a state in which the whole matter (matter is the subject of another article from the Universe, this is the black thing that surrounds all planets) and the energy of the Universe had a very high density and temperature. Physicists do not agree on what was previously (and unfortunately we will never know what was before the Big Bang) , but the extrapolation of known laws of physics to the extreme conditions of the early universe in which they were not tested experimentally, would indicate the existence of the so-called gravitational peculiarity.
In short, the Big Bang lasted a few seconds but its effect isn't over yet, the Universe expands all the time and will expand when it stops? We do not know, we do not know whether it will stop at all. . .
The next article from the Universe series will be about how we see something that was 4 billion years ago and cannot see what is now in the furthest corners of the Universe.
If you like it and you want to support me, we would like to welcome you to our websites UPVOTE and FOLLOW. Thank you!
[SOURCES]
https://pl.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wielki_Wybuch
https://pl.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uniwersum
https://pl.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wszechświat
https://pl.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galaktyka_Andromedy
https://pl.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Droga_Mleczna
http://fashionweare.com/news/893/uniwersum-trend-wiod-cy-na-2015
https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kwark
http://www.wiw.pl/astronomia/1103-kosmologia.asp
https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galaktyka_Andromedy
Google Graphics database with license for reuse (with modification).