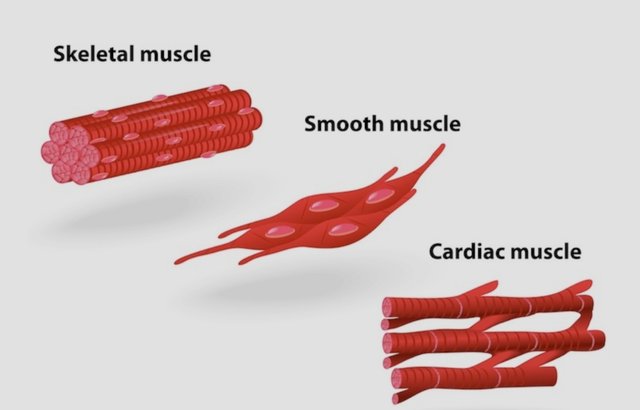
The different types of muscle tissue
Animal musculature is mostly of mesodermal origin. There are more than 600 muscles in the animal body.
Muscle Types
On the basis of certain structural and functional characteristics, muscle tissue is classified into three types: cardiac, smooth and skeletal.
Smooth and cardiac muscles are involuntary in nature. Skeletal and cardiac muscles are sometimes referred as striated muscles due to their specific microscopic appearance.
Smooth Muscles
Smooth muscles are found in the gastro-intestinal tract, blood vessels, lymphatic and skin in close association with the connective tissue layers. These are involuntary in nature. Smooth muscle fibres are uninuclear, long, unevenly thickened in the centre and tapering on both the sides. The myofibrils are homogenous and do not show alternating dark and light bands like those of skeletal muscle. There are no Z or M-lines. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is also not much developed. Smooth muscle tissue, like skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue, can undergo hypertrophy. In addition, certain smooth muscle fibres, such as those in the uterus, retain their capacity for division and can grow by hyperplasia.
Cardiac Muscles
The cardiac muscles found in the heart are also involuntary. Their muscle fibres are rounded to irregular in shape and give off branches which get mixed up with those of nearby fibres. The fibers uni nuclear and nuclei are placed in the centre of the fibre. Myofibrils depict striations similar to skeletal muscle. The sarcoplasm shows numerous and much more mitochondria and glycogen granules than the skeletal or smooth muscles. The intercalated discs are present at the position of Z-lines, transect the fiber. These disks provide a cohesive link between the fibres of myocardium as well as facilitates the transmission of the contractile force from one fiber to another.
Skeletal
Skeletal muscle tissue is named for its location - attached to directly to bones, but some are attached to ligaments, fascia, cartilage and skin and therefore only indirectly to bones.
Structural unit of muscle is a muscle fiber. Muscle fibers constitute 75-92 % of the total muscle volume. Mammalian and Avian skeletal muscle fibers are long, un branched, threadlike cells which taper slightly at both ends. Fibers may have a length of several centimeters but do not generally extend the length of the entire muscle. They vary considerably in diameter ranging from 10-100 µm within the same species and even within the same muscle.