Social awareness #-2 Caste System – India
After yesterday’s(02/03/2018) violence throughout India after the verdict of Supreme Court of India, that banned automatic arrest and registration of criminal cases under the act, angering Dalit groups. The top court of India ruled that public servant cannot be prosecuted without the nod of official, and private citizens should be detained only after an inquiry under the law. It also stated that a preliminary inquiry under the Act should be conducted by a DSP(Deputy Superintendent of Police) to ensure the allegations.

The impact of yesterday’s violence provoked me to make aware of you people about the caste system of India. In the ancient time about 3600 years ago, a group of cattle herders from central Asia settled into India. This group of people, called as the Aryans brought many things with them such as their beliefs, customs and writing system(Sanskrit) with them. They made a firm caste structure that is called caste system. This caste system divided the people into four classes. Under this caste system these four classes are called as Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaisya and Shudra.
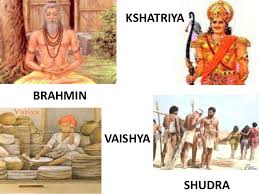
Brahmins-This class was considered at the helm of the of this caste system. They have gigantic powers over other people of other class. They were only people who studied and taught the holy texts, known as the Vedas. They were also the people who could perform the religious activities and sacrifices. After performing these activities the people of other classes offer them valuables and other donations due to the belief that what they are giving to the Brahmins in this life they will get In the next life.
Kshtriya-This class was the second highest caste among the caste system. These were the warriors and rulers, who were responsible to rein and defend the country. They were also permitted to learn the Vedas, but they could not teach the Vedas. They go through the extensive military training and they were the experts in archery, swordmanship, and hand to hand combats.
Vaisya- This class consisted the farmers and merchants. These people were expected to rear cattle, to farm and to trade. They could also learn the Vedas but could not teach to the people like Kshtriyas.
Shudra- This class is at the bottom of the class, they did the menial, labor-intensive work. This category was consisted the servant, craftsmen or labor. These people were not allowed to learn the Vedas.
Though there are major four classes in the caste system, there was one more class that falls below the Shudra. They did not belong to any other upper classes. These people did the work that no other people wanted to do like street sweeping, clean up of the toilets, garbage collection and dispose of dead animal and humans. The outcaste people could not live in the cities or towns. They led a lonely and humiliated life. There were many restrictions to this class and they became the untouchables.
The above mentioned details are of the ancient India, in the 1900s there were many efforts made towards these untouchable people to lead a good life in the society. Many leaders of India have fought against the ancient caste system to make all the people in society to lead the same life. One of the best known leaders was Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar, with his efforts the untouchables of India made a good status in the society. He is called the Masiah(the savior and liberator) of Dalits. In modern India the people of all the communities are living together with harmony. In the modern time there is no such caste system exists in India and also these castes like SC/ST/OBC has given many benefits to empower these castes, like quota in the jobs, educations.
Among these there was a SC/ST (Prevention of Atrocities) Act in 1989, that seeks the protection of Dalits and other marginalized groups from harassment and discrimination. Against the order of the Supreme Court of India’s on March 20, 2018 there was a protest called by the Dalits on April 02, 2018 and this protest gone violent throughout the country.
Image Source : Google
Very detailed write up!