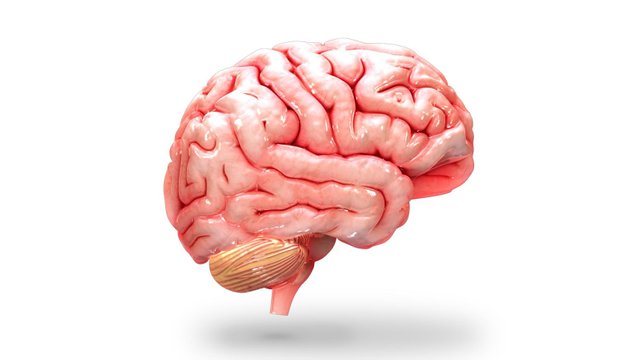
What is Human Brain ?
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. The cerebral cortex is an outer layer of grey matter, covering the core of white matter. The cortex is split into the neocortex and the much smaller allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes. The frontal lobe is associated with executive functions including self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought, while the occipital lobe is dedicated to vision. Within each lobe, cortical areas are associated with specific functions, such as the sensory, motor and association regions. Although the left and right hemispheres are broadly similar in shape and function, some functions are associated with one side, such as language in the left and visual-spatial ability in the right. The hemispheres are connected by commissural nerve tracts, the largest being the corpus callosum.
The human brain is the command center for the human nervous system. It receives input from the sensory organs and sends output to the muscles. The human brain has the same basic structure as other mammal brains, but is larger in relation to body size than any other brains.
- The human brain is the largest brain of all vertebrates relative to body size.
2.It weighs about 3.3 lbs. (1.5 kilograms)
3.The brain makes up about 2 percent of a human's body weight
4.The cerebrum makes up 85 percent of the brain's weight
5.It contains about 86 billion nerve cells (neurons) — the "gray matter"
6.It contains billions of nerve fibers (axons and dendrites) — the "white matter"
7.These neurons are connected by trillions of connections, or synapses.
Humans vs. other animals
The main differences between human and animals brains is their size, said Eric Holland, a neurosurgeon and cancer biologist at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington, in Seattle. Humans also have more neurons per unit volume than other animals, and the only way to do that with the brain's layered structure is to make folds in the outer layer, or cortex, Holland told Live Science.
The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind and soul. Intelligence, creativity, emotion, and memory are a few of the many things governed by the brain. Protected within the skull, the brain is composed of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.\