Animal Form and Function: Muscles and Movement
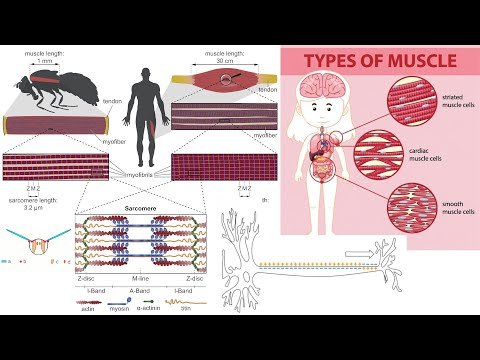
In this video I go over the muscular system of animals, which for vertebrates consists of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. The skeletal muscles are mostly attached to bones via tendons, and are voluntarily controlled. The smooth muscles are involuntary non-striated muscles (hence smooth) and line the walls of many internal organs and structures like blood vessels and the digestive tract. I also discuss the Sliding Filament Theory to explain how muscles contract via the smallest units of striated muscles, the sarcomeres. I also go over how a worm moves via peristalsis (contraction of its circular muscles) and how an insect flies via its asynchronous flight muscles.
#science #biology #muscles #animals #education
Timestamps:
- Muscular system consists of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles: 0:00
- Diagram of skeletal muscles, which are mostly attached to bone by tendons: 1:14
- Smooth muscle is involuntary non-striated muscle (has no sarcomeres, which are the smallest unit of striated / skeletal muscles): 5:50
- Cardiac muscle or myocardium or heart muscle is involuntary striated muscle and main tissue of the wall of the heart: 7:13
- Interruptions of coronary circulation cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions) because the heart is damaged by oxygen starvation: 9:17
- Diagram comparing the skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells: 11:33
- Diagram and video of the Sliding Filament Theory for muscle contraction: 16:13
- Screenshots of video: Sarcomere consists of myosin, actin, titin, tropomyosin, and Z disk: 21:55
- Myosin binds ATP, gets released, moves forward, releases phosphate to trigger a power stroke, then ADP dissociates. Process repeats: 25:23
- Diagram of Sliding Filament Theory: 27:04
- Animation of a nerve impulse or action potential along an axon which causes a polarity change to travel: 30:10
- Most cells in higher organisms are negatively charged related to the cell's exterior, this is called the cell's membrane potential: 33:40
- Diagram of an action potential in a neuron: 34:52
- Cross-section of a worm showing its circular muscles and cavity: 38:00
- Diagrams of a how a worm moves via peristalsis, which is contraction of its circular muscles: 39:57
- Most flying insects of asynchronous muscles, which have no 1 to 1 relationship between the electrical stimulation and mechanical contraction: 44:00
- 3D Diagram of a muscle cell: 46:05
- Diagram comparing a fly's flight muscle vs a mammal's skeletal muscle: 47:01
- Diagram comparing a fly's flight muscle vs a human skeletal muscle: 51:36
- Animation of asynchronous muscles powering flight in most insects: 56:39
Full video below:
- Summary: https://inleo.io/threads/view/mes/re-leothreads-gswur1as
- Full video and playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLai3U8-WIK0FYO6bxFbBAtVJ9sDOJnH72
- Notes: https://peakd.com/hive-128780/@mes/messcience-3-overview-of-biology
- MES Science playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLai3U8-WIK0GhjCHmTw1XbqMD_EdVKdd9 .
Become a MES Super Fan! https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUUBq1GPBvvGNz7dpgO14Ow/join
DONATE! ʕ •ᴥ•ʔ https://mes.fm/donate
SUBSCRIBE via EMAIL: https://mes.fm/subscribe
MES Links: https://mes.fm/links
MES Truth: https://mes.fm/truth
Official Website: https://MES.fm
Hive: https://peakd.com/@mes
Email me: [email protected]
Free Calculators: https://mes.fm/calculators
BMI Calculator: https://bmicalculator.mes.fm
Grade Calculator: https://gradecalculator.mes.fm
Mortgage Calculator: https://mortgagecalculator.mes.fm
Percentage Calculator: https://percentagecalculator.mes.fm
Free Online Tools: https://mes.fm/tools
iPhone and Android Apps: https://mes.fm/mobile-apps
▶️ DTube
- Summary: https://inleo.io/threads/view/mes/re-leothreads-gswur1as
- Full video and playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLai3U8-WIK0FYO6bxFbBAtVJ9sDOJnH72
- Notes: https://peakd.com/hive-128780/@mes/messcience-3-overview-of-biology
- MES Science playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLai3U8-WIK0GhjCHmTw1XbqMD_EdVKdd9
- MES Links: https://mes.fm/links