23-06-2025 - Exercise - Step response and harmonic response EN]-[IT]
Cover background image generated with AI, software used: copilot microsoft
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
[ENGLISH]
23-06-2025 - Exercise - Step response and harmonic response EN]-[IT]
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
With this post I would like to provide some brief notions about the topic mentioned in the subject by doing some exercises.
The context in which we operate is that of Systems analysis and modeling
(code notes: MOD+13)
Step response and harmonic response
Exercise 01
What is the harmonic response of a system?
Initial analysis
First of all, let's clarify the concept of system and response
THE SYSTEM
In systems analysis and modeling, the system is a set of interconnected components that interact with each other after receiving inputs that the system will transform into outputs. The inputs will produce outputs according to rules, physical, mathematical or logical laws.
A system can also be represented by a function.
y(t) = S{u(t)}
where:
u(t) = input
y(t) = output
S = behavior of the system
THE RESPONSE
We can say that the response of a system is the behavior that the system has over time following a certain input. We can also say that the response of a system is the output y(t) produced by the system when it receives an input u(t)
Response
The harmonic response is the response that a system produces when the input is sinusoidal, in a stationary regime.
We can also say that the harmonic response explains how the system behaves when it is stimulated by a sinusoidal signal at a certain frequency ω.
Below I try to explain what happens in practice.
If a linear time-invariant system receives an input of the following type:
x(t) = A * cos(ωt)
As an output, i.e. as a response, we will always have a sinusoid at the same frequency, but with modified amplitude and shifted phase. Recall that this is valid in steady-state conditions.
Mathematically this translates to the following mathematical description:
y(t) = B(ω) * cos (ωt + ϕ(ω))
Where:
B(ω) = gain in amplitude at frequency ω
ϕ(ω) = phase shift introduced by the system
Exercise 02
What is the steady-state gain of a system?
Answer
Mathematically the steady-state gain can be described as follows:
Steady-state gain = YU
Where:
U = system receiving a constant input u(t)
Y = output settling at a constant value y(t) = Y
The steady-state gain is the ratio of the output value to the input value of a system in steady-state conditions.
Recall that when we talk about steady-state conditions, we mean that it is the condition of the system after all the initial transients have exhausted themselves. This means that the system has reached a constant or periodic behavior over time. In other words, we can say that a system is in stationary conditions when the state variables and the output no longer change over time.
Exercise 03
What is the correspondence between a step response and a harmonic response?
Initial analysis
Step response
The step response is basically the response of a system to an input whose signal changes from 0 to 1 instantaneously. This type of input is called a unit step.
Systems with step responses are useful for analyzing the stability of a system, the response times and the various errors that could exist in the steady state.
Harmonic response
The harmonic response is the response of a system to a sinusoidal input. Similar responses are useful for understanding the frequency behavior of a system and controlling the amplitude or phase of the response.
Response
The step response and the harmonic response are two types of analysis useful for understanding the behavior of a dynamic system.
The step response is used for systems in the time domain and is useful for understanding transient behavior.
The harmonic response is used in the frequency domain and is useful to understand the behavior in sinusoidal regime.
The elements that connect the two responses can be:
-The Fourier decomposition
-The transfer function
-Complementary analyses
The Fourier decomposition
A step signal can be decomposed and defined as the sum of sinusoids (Fourier series)
The transfer function
The transfer function G(s) is interpreted as follows.
In the step response it is obtained by calculating G(s) * 1s
In the harmonic response it is obtained by evaluating G(jω)
Examples with graph:
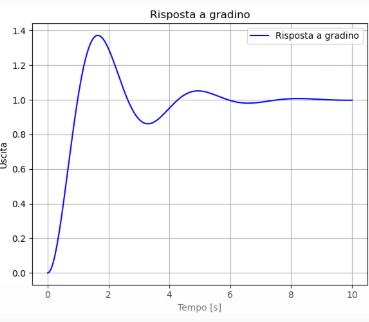
Let's think about the step response and the harmonic response of a second-order system with natural frequency ωn = 2 rad/s and damping ζ= 0.3
Step response
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
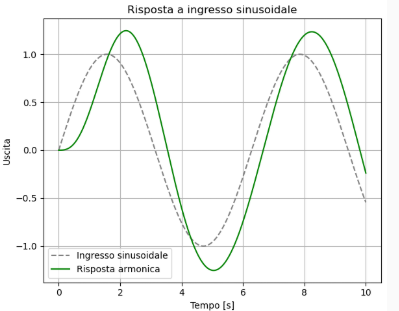
Response harmonic
Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
In the step response we see a behavior that shows an initial oscillation that fades over time and where the output tends to a constant value.
In the harmonic response, that is the one with sinusoidal input, the input is a dashed sinusoid, while the output, which is represented by the green sinusoid, has a modified amplitude and a different phase (in this case it is delayed).
Conclusions
The step response and the harmonic response are two types of responses useful for studying dynamic systems. The step response is a useful tool for analyzing the transient behavior of a system, while the harmonic response is used to analyze the behavior of the system in a sinusoidal steady state.
Question
Did you know that the step response was formalized with the introduction of the Laplace transform by the famous French mathematician and physicist, Pierre-Simon Laplace (1749-1827)? Do you remember hearing the name Laplace? Did you study him in school?

[ITALIAN]
23-06-2025 - Esercizio - Risposta a gradino e risposta armonica EN]-[IT]
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Con questo post vorrei fornire alcune brevi nozioni a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto svolgendo degli esercizi.
Il contesto in cui operiamo è quello della Analisi e modellistica dei sistemi
(code notes: MOD+13)
Risposta a gradino e risposta armonica
Esercizio 01
Cosa è la risposta armonica di un sistema?
Analisi iniziale
Innanzitutto chiariamo il concetto di sistema e di risposta
IL SISTEMA
In analisi e modellistica dei sistemi il sistema è un insieme di componenti interconnessi che interagiscono tra di loro dopo aver ricevuto degli ingressi che il sistema trasformerà in uscite. Gli ingressi produrranno delle uscite secondo delle regole, leggi fisiche, matematiche o logiche.
Un sistema può essere rappresentato anche da una funzione.
y(t) = S{u(t)}
dove:
u(t) = ingresso
y(t) = uscita
S = comportamento del sistema
LA RISPOSTA
Possiamo dire che la risposta di un sistema è il comportamento che ha il sistema nel tempo in seguito ad un determinato ingresso. Possiamo anche dire che la risposta di un sistema è l’uscita y(t) prodotta dal sistema quando riceve un ingresso u(t)
Risposta
La risposta armonica è la risposta che produce un sistema quando l'ingresso è sinusoidale, in regime stazionario.
Possiamo anche dire che la risposta armonica spiega come si comporta il sistema quando viene stimolato da un segnale sinusoidale ad una certa frequenza ω.
Qui di seguito provo a spiegare cosa succede in pratica.
Se un sistema lineare tempo-invariante riceve un ingresso del seguente tipo:
x(t) = A * cos(ωt)
In uscita, cioè come risposta, avremo sempre una sinusoide alla stessa frequenza, ma con ampiezza modificata e fase spostata. Ricordiamo che questo è valido in condizione di regime stazionario.
Matematicamente questo si traduce nella seguente descrizione matematica:
y(t) = B(ω) * cos (ωt + ϕ(ω))
Dove:
B(ω) = guadagno in ampiezza alla frequenza ω
ϕ(ω) = sfasamento introdotto dal sistema
Esercizio 02
Che cosa è il guadagno a regime di un sistema?
Risposta
Matematicamente il guadagno a regime si può descrivere come segue:
Guadagno a regime = YU
Dove:
U = sistema che riceve un ingresso costante u(t)
Y = uscita che si stabilizza ad un valore costante y(t) = Y
Il guadagno a regime è il rapporto tra il valore di uscita ed il valore di ingresso di un sistema in condizioni stazionarie.
Ricordiamo che quando parliamo di condizioni stazionarie, intendiamo dire che è la condizione del sistema dopo che tutti i transitori iniziali si sono esauriti. Questo significa che il sistema ha raggiunto un comportamento costante o periodico nel tempo. In altre parole possiamo dire che un sistema è in condizioni stazionarie quando le variabili di stato e l’uscita non cambiano più nel tempo.
Esercizio 03
Che corrispondenza c’è tra una risposta a gradino e una risposta armonica?
Analisi iniziale
Risposta a gradino
La risposta a gradino in pratica è la risposta di un sistema ad un ingresso di cui il segnale passa da 0 a 1 istantaneamente. Questa tipologia di ingresso viene chiamata appunto a gradino unitario.
Sistemi con risposte a gradino sono utili per analizzare la stabilità di un sistema, i tempi di risposta ed i vari errori che potrebbero esserci a regime.
Risposta armonica
La risposta armonica è la risposta di un sistema ad un ingresso sinusoidale. Risposte simili sono utile per comprendere il comportamento in frequenza di un sistema e controllare l’ampiezza o la fase della risposta.
Risposta
La risposta a gradino e la risposta armonica sono due tipologie di analisi utili per comprendere il comportamento di un sistema dinamico.
La risposta a gradino è impiegata per sistemi nel dominio del tempo ed è utile per capire il comportamento transitorio.
La risposta armonica è usata nel dominio della frequenza ed è utile per capire il comportamento in regime sinusoidale.
Gli elementi che collegano le due risposte possono essere:
-La scomposizione di Fourier
-La funzione di trasferimento
-Analisi complementari
La scomposizione di Fourier
Un segnale a gradino può essere scomposto e definito come la somma di sinusoidi (serie di Fourier)
La funzione di trasferimento
La funzione di trasferimento G(s) si interpreta come segue.
Nella risposta a gradino si ottiene calcolando G(s) * 1s
Nella risposta armonica si ottiene valutando G(jω)
Esempi con grafico:
Pensiamo alla risposta a gradino e alla risposta armonica di un sistema del secondo ordine con frequenza naturale ωn = 2 rad/s e smorzamento ζ= 0,3
Risposta a gradino
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Risposta armonica
Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Nella risposta a gradino vediamo un comportamento che mostra un oscillazione iniziale che si smorza nel tempo e dove l’uscita tende ad un valore costante.
Nella risposta armonica, cioè quella con ingresso sinusoidale, l’ingresso è una sinusoide tratteggiata, mentre l’uscita, che è rappresentata dalla sinusoide di colore verde, ha un ampiezza modificata e una fase diversa (in questo caso è ritardata).
Conclusioni
La risposta a gradino e la risposta armonica sono due tipologie di risposte utili per studiare i sistemi dinamici. La risposta a gradino è uno strumento utile per analizzare il comportamento transitorio di un sistema, mentre la risposta armonica si usa per analizzare il comportamento del sistema in regime sinusoidale stazionario.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che la risposta a gradino è stata formalizzata con l’introduzione della trasformata di Laplace da parte del famoso matematico e fisico francese, Pierre-Simon Laplace(1749-1827)? Ricordate di aver già sentito il nome di Laplace? L'avete studiato a scuola?
THE END

Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
This post has been upvoted by @italygame witness curation trail
If you like our work and want to support us, please consider to approve our witness
Come and visit Italy Community
Pierre-Simon Laplace, non ricordo questo nome, ma se studio l'argomento, mi sembra che tu lo spieghi bene, facile da capire