Steemit Learning Challenge-S21W2; Knee Osteoarthritis"
Greetings and welcome. Am glad to be part of another exciting class. Thank you for this amazing lecture.
 |
|---|
What's knee OA? Write in your own words after getting knowledge from the lesson post. |
|---|
Knee osteoarthritis is a disease that occurs when there is break down in the joint of the knee. When the this happens, the bones of the knee joins behind to come together and this causes friction which makes the knee to swell up or become stiff and causes hurt.
The bones of the knee rubs together due to the break down in the cartilage of the knee joint. There’s no cure for knee OA but there are some treatments that can slow the progress down even though most severe cases are taken care of through surgery.
Knee OA is very common from people of fourth years and above and it’s most common in about 40% of people especially in women. Factors like injuries, osteoporosis, malnutrition, in situations were someone does little or no exercise, and also genetics can cause knee OA that is for people who have it in their family history. People who are over weight and have higher body mass index has more tendency to develop osteoarthritis of the knee.
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis
- The person usually has joint pains in the knee.
- When someone wants to get up or after sitting for a while, the knee begins to feel stiff.
- The knee looks puffed up and swollen.
- when you move your knee, you might hear a grinding or cracking sound
- You have a wobbling feeling on the knee as if it will give out or buckle.
Stages of knee osteoarthritis

There are five stages of Knee OA and they include;
Stage 0: At this stage the knee is normal.
Stage 1: This is the minor stage when there may be a little wear and tear but it’s not noticeable.
Stage 2: This is the mild stage. A little stiffness and pain is felt but the bones are still kept from touching each other by the cartilage.
Stage 3: This stage is called the moderate stage. They is more narrowing in the cartilage and bone spurs could occur often. More pain will be felt when walking, running kneeling or squatting and after resting for along period mostly in the mornings.
Stage 4: This is the severe stage. The knee will become stiff, difficult to move and very painful because the cartilage is almost gone and surgery might be needed.
How would you diagnose a knee OA? Any clinical investigation or assessment tests? |
|---|
 |
|---|
For diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis, the doctor would have check the joints that’s affected for redness, to see if it’s tender and swollen and check the flexibility of the joints.
Pictures of the joints need to be gotten hence X-ray and MRI would be required.
X-ray: The X-ray would not show the cartilage but the loss in cartilage will be shown when the space in between the bones are narrowed. The bone spurs around the joints can be seen by X-ray too.
MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging): This procedure reveals precise images of the cartilage, bones and soft tissues through the use of strong magnetic field and radio waves.
Lab tests: The diagnosis can be confirmed through joint fluid analysis and blood analysis.
Joint Fluid Analysis: Fluid from the affected knee would be drawn through a needle by the doctor and tested for inflammation to see if the pain is as a result of infection or gout other than osteoarthritis.
Blood test: This blood test is conducted so that other causes of the joint pain like rheumatoid arthritis can be ruled out because osteoarthritis cannot be determined through blood test.
Some assessment test for knee osteoarthritis includes;
- Sitting and moving the knee to check the flexibility of the joints and the ROM while listening for any popping or cracking noise of the joints.
- 30 seconds chair stand test: With the two arms crossed across each other on the chest, the participant will be asked to sit on an armless chair without leaning on the back of the chair. A timer will be set for 30 seconds as the participant will sit and stand as in the video for the thirty second at a quick pace.
- The time up and go test: The participant stand up from the chair and walks a distance of about 9.8ft and turns around and walks back to the chair, sits, stands and walk again at a regular pace repeatedly.
- Stairs climb test: The participants will be asked to ascend and descend the stairs in a safe way but as quickly as possible. The person can use walking aid or the handrail is need be.
Treatment and management of knee osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis has can be treated using non surgical and surgical methods.
The non surgical method includes;
- The use of therapy usually physical therapy
- Administration of pain medications
- Use of knee braces
- Special foot wears or the use of orthotics like insoles can be adopted
- Vicosupplementation and
- Use of steroids or cortisol injections
The surgical treatment includes;
- Grafting of cartilage where a healthy cartilage can be used to fill the hole in the cartilage.
- Going for partial knee replacement or total knee replacement
- Knee osteotomy
Try to practice at least 4 exercises that you have learned from the lesson. Share images, gifs or videos while practicing. |
|---|
Four Exercise four knee osteoarthritis includes;
Heel slides exercise: This exercise helps the muscles around the knee to be strengthened and also to prepare the patient to walk.
Lie on your back and slide the heel back and forth. Make sure that your hip stay leveled. Do not hike your hip as you bend and shrink your knee, ensure the knee it as straight as possible.
Ensure your heel is in contact with the floor as you slide the heel back and forth. Repeat the process twenty to twenty times until your leg muscles becomes fatigued.
William flexion (Knee to chest exercise): This helps to improve the flexion of the knee. Lie on your back and lift up the two legs halfway bent and hold with the hands like in the video. Move the knees back and forth towards the chest simultaneously.
Knee Isometrics (Knee Flexion): This exercise helps to strengthen the hip and knee muscles thereby increasing the ROM of the knee joint.
Lie down on your back and put a towel roll under your knee. Tighten the muscles on the front of the thigh and straighten your knee, hold for three to five seconds and release. Repeat ten times. When the knee is stronger, a weight can be added for more strengthening.
Quadriceps stretch: This stretch helps with the knee ROM and flexibility.
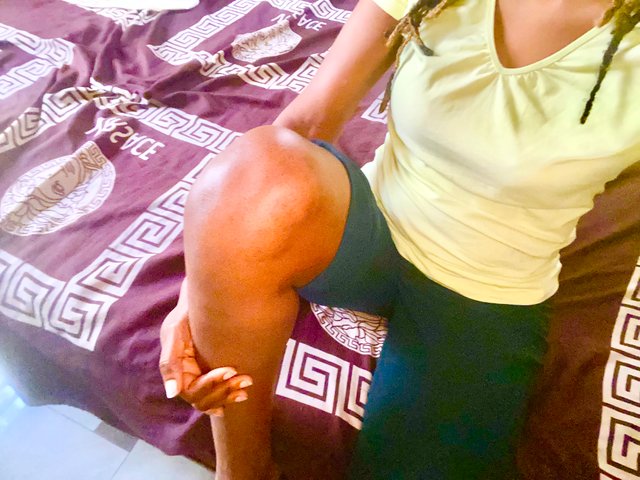
You lie down facing downwards. Bring out the right arm in front to gain support. Bend the left knee backwards and use the left hand to grab your ankle. Lift the knee gently until you notice a slight stretch, hold for some seconds. Switch to the other side and repeat for few times.
Share your review after performing these exercises either on healthy individual or patient. |
|---|
It was thrilling going through these excercise personally and each and everyone one of them had peculiar impact on my knee joints. I have been having knee some pains on my knee lately.
Doing the quadriceps stretch and knee isometrics had impressive impact on my knee as I could feel the tension. My knees felt better afterwards.
Thank you for such an interesting class. I asks @ruthjoe, @ninapenda and @eliany to join the challenge.
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.