Perseverance’s MOXIE produced 50 grams of oxygen from the Martian atmosphere in 9 hours

(Tim Tim / Wikimedia Commons https://bit.ly/3QtMn9D)
MOXIE, the experiment onboard the Perseverance martian rover generated 50 grams of oxygen from the Martian atmosphere suitable for human use.
According to the team, led by Jeffrey Hoffman of MIT, the device worked for a total of almost 9 hours.
The results indicate that it is possible to create a larger and more powerful facility for obtaining oxygen on Mars by future astronauts.
MOXIE (Mars Oxygen In-situ Resource Utilization Experiment) was the first practical experiment to obtain the resources necessary for humans from the environment of Mars.
The device has a total mass of 17.1 kilograms, it is installed on the Perseverance rover and is designed to produce oxygen from the Martian atmosphere.
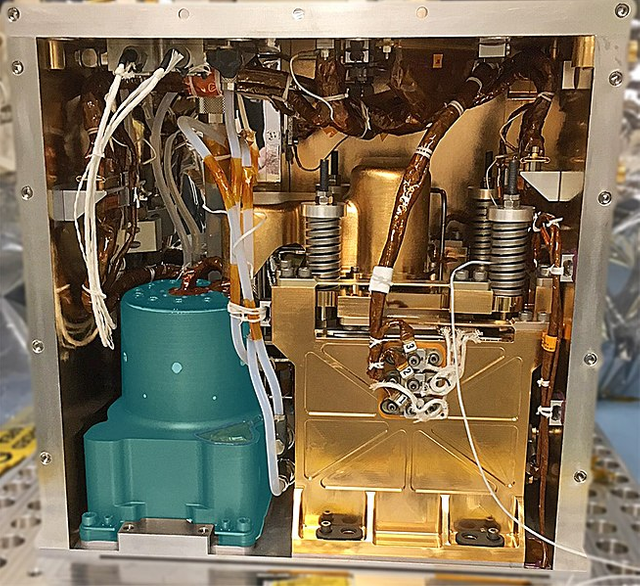
(R2T2M / Wikimedia Commons https://bit.ly/3KXOSQe)
MOXIE sucks the contents of the martian atmosphere through a HEPA filter, compresses it with a scroll pump, and heats it up to 800 degrees Celsius
Then sends it to a solid oxide electrolysis cell, where carbon dioxide is decomposed into oxygen and CO ions.
After that, oxygen ions are sent to the anode, where they are converted into molecular oxygen, and a mixture of CO2, CO and inert gasses is emitted back into the atmosphere.
MOXIE was first turned on last April, demonstrating its functionality.
THE STUDY
Now, Hoffman’s team published the results of the instrument on Mars between February and December 2021.
During this time, the device worked 7 sessions with a total duration of 8.81 hours.
The maximum rate of suction of the atmosphere is 55 grams of gas mixture per hour, which gives an oxygen production rate of 6-8 grams of gas per hour.
The total amount of oxygen received in 7 sessions of work was 50 grams.
The team notes that the rate of degradation of cell elements, which determines the amount of oxygen that can be produced, initially increases, but then reaches a plateau.
Thus, the instrument will maintain the initial rate of oxygen generation for at least 60 operating cycles on Mars.
MOXIE will continue to work in the future, but its main goal is confirmed: produce oxygen on Mars from the atmosphere.
The process is also viable, scalable and meets expectations in terms of efficiency.
NASA plans to make a more advanced control and monitoring system in a larger plant, where oxygen production will be from two to three kilograms per hour.
They also aim to replace the scroll compressor with a vane or cryogenic pumping system and change the operating mode from intermittent to continuous.
This is definitely good news for space exploration.
Source:
Science Advances: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abp8636
The Guardian: https://www.theguardian.com/science/2022/aug/31/nasa-moxie-instrument-successfully-makes-oxygen-on-mars
If you like my content, please consider following, upvoting and commenting. I really appreciate it.
Follow my Telegram channel: https://t.me/stemsteemit