Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 6 - Homework Post for Professor @stream4u : Blockchain
Hi everyone, I’m very excited to take part of this lecture of professor @stream4u. The lesson was on blockchains and it was really detailed. So I have decided to try my hands on the given task.
1. What is Blockchain and What are the types of Blockchains / Explain in detail the types of Blockchain?
A blockchain comprises of several chain of blocks. Each of these blocks contains data which are put together to form a large database.
In blockchains when a data is recorded, it cannot be changed by any other different person. That’s what makes blockchain unique from the centralized systems.
There are different components that come together to form a blockchain. These components are the Blocks, Chains, Nodes and Miners.
The Blocks are the components that contain data. All the data of the blockchain are kept in the blocks.
The Chains are also referred to as the hashes that connects the blocks of the blockchain to each other.
The nodes are the devices that are connected to each other in the blockchain. These nodes are responsible for creating, mining and validation of blocks in the blockchain.
The last components in the blockchain are the Miners. These miners use mining processes to validate blocks and transactions in the blockchain.
Different blockchains have different times of generating blocks. This is called the generation time of the blockchain. For example if a blockchain has a generation time of 5 sec, it means that a new block will be generated every 5 seconds with data inside the block and the cryptographic hash which joins it to the next block. The connection by the hash to the next block ensures that a blockchain is formed.
The hash is the representation of the information kept in the block. Immediately any data stored in a block is changed the hash also changes which affects the whole blockchain. This is because all the blocks in the blockchain are linked to by hashes and any changes in a hash will distract the whole blockchain. This is why when a blockchain is complete, the data in each block cannot be changed by anybody unless you change the information in all the single blocks.
Below is an illustration of how a blockchain looks like.
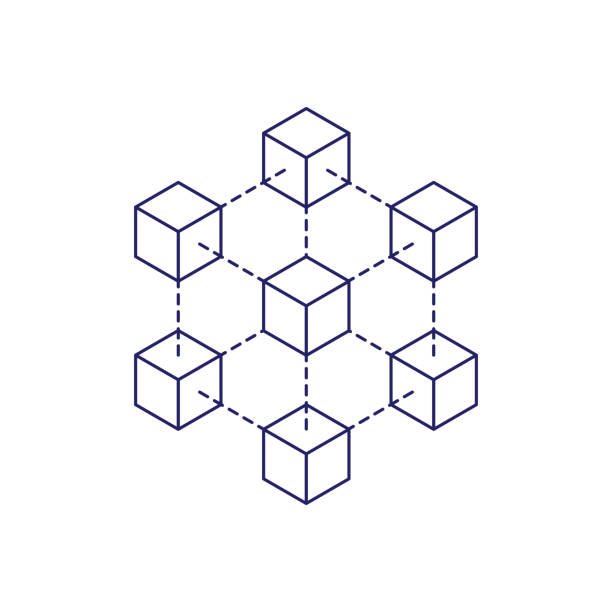
source
Types of Blockchain
Different types of blockchains are used in different sectors depending on their uses. Everything function has a type of blockchain that executes it perfectly. There are 4 different types of blockchains at the moment. These blockchains include Public Blockchains, Private Blockchains, Hybrid Blockchains and Consortium Blockchains.
Public Blockchains
The public blockchain is an open source blockchain and it is opened to anyone. Anybody who is interested can get access to the public blockchain. Blockchain validation can be done by anyone as well. However once an entry has been validated, it can’t be changed again because the public blockchain is immutable and decentralized. This assures users of the public blockchain that their transactions cannot be changed. The native token of the particular blockchain are used to reward those who control the node and use the blockchain in order to get them motivated. Some special algorithms are used to validate transactions in the blockchain. Proof of Work or proof of Stake algorithms can be used in the validation.
For instance steem and Bitcoin are the native tokens of the steem blockchain and Bitcoin blockchain respectively. These are popular examples of the public blockchain.
Most sectors that require transparency in their operations often use the public blockchain. An example is the voting platforms where they need everybody to see evidence of the exact reflection of their processes. The sector of keeping healthcare records also use the public blockchain.
Pivate Blockchain
Unlike the public blockchain, the private blockchain is restricted to some chosen number of users. It is more of a private system. The nodes connected to each other share the information among themselves. The data in the blocks of these public blockchain are only stored within the nodes that are connected to each other to make sure the information within the network are intact.
This private blockchain can be used in institutions such as schools, Banks, private companies and other organisations that want to keep their information private. In these organisations they only require people that are part of the institutions and have been given the authority to get access to their information. So the private blockchain is suitable for their operations as only nodes within the network can have access to the blockchain.
The private blockchain is usually initiated and controlled by some limited group of people or single individuals.
Hybrid Blockchains
The hybrid blockchain have both features of private and public blockchains combined. It operates on both the principles of private blockchains and public blockchains combined. The hybrid is not all that opened for everyone but it guarantees some kind of transparency at the same time with very tight security.
The hybrid blockchain can be customised. The members of the blockchain decides on who is allowed to enter the blockchain at any given time. They can also decide on when to make their transactions public or private .
It must be noted that the transactions in hybrid blockchains are not public and they are also very secure as well as immutable. The members determine the transactions that are made public or not but they can’t change the transactions themselves.
Some special companies use this hybrid blockchain system. The logistics companies are most notable for using this type of blockchain. IBM food trust is an example of a company that uses the hybrid blockchain in its supply chain.
Advantages of hybrid blockchain
The maintenance of the hybrid blockchain is cheaper as compared to that of the public blockchain. Less resources and effort is needed to maintain the hybrid blockchain. The computation power needed in the hybrid blockchain is less as compared to that of the public blockchain.
Because the number of nodes in the hybrid blockchain is limited, it makes transactions very fast as compared to that of the public blockchain. Only nodes connected to the blockchain can have access to it. This makes the transactions very secured and fast as well. Transactions are also verified very fast on the hybrid blockchain.
Despite all the advantages of the hybrid blockchain it also has its shortcomings.
Because of the limited access in the hybrid blockchain, it is seen as less decentralized and its transparency is not convincing. There are some restrictions in the hybrid blockchain that doesn’t make it more open to users as in the case of the public blockchain. This of course is a worrying feature of the hybrid blockchain network.
Consortium Blockchain
The consortium blockchain and hybrid blockchain are very similar in their operations. They both combine public and private blockchains and run them at the same time. The only difference is that the nodes that come together to verify the transactions are from different consortium blockchains. The consortium blockchain still remains decentralized despite the connection of nodes from different blockchains. The nodes do the validation in the blockchain and also initiate as well as verify transactions in the blockchain. Other different nodes connected from different blockchains can only initiate and receive transactions.
Pros of consortium blockchain
The consortium blockchain makes transactions very fast and also have high security. It also makes its data easily accessible and the verification of transactions is also simple.
The consortium blockchain also allows for nodes from different blockchains to be connected to each other. This ensures that different forms of transactions can be executed at the same time between different decentralized systems.
Cons of consortium blockchain
The consortium blockchain has the same disadvantage as the hybrid blockchain. It is not all that transparent. This is because it’s transactions are not 100% decentralized and you can’t get access to some of the vital details in the consortium blockchain.

2. What are the benefits of blockchain?
Blockchains have been very beneficial in the world of cryptocurrencies and beyond. So many people have benefited from the idea of blockchains in their respective sector of operations. Below are some of the benefits of blockchains:
- Tight security network
The immutability of the information in blocks of a blockchain makes it extremely secure. The cryptographic hashes in the chain that link these blocks in the blockchain makes the information in the database resistant to change. Once the information has been verified, it can no longer be changed. Any change in hashes means a complete manipulation of the blockchain.
There is a consensus mechanism which agrees that the transaction is right after the transaction in the blocks has been validated. The system is decentralized so anybody joining the blockchain is aware of that and it makes it transparent to everybody. The members joining the blockchain cannot change any information within it because it is a decentralized system. Even if one person fails the system, the blockchain still functions the same and the normal operations continue as required. The transactions are still secure nevertheless and will not fail at any point.
However we must notice that how secure a blockchain is depends on the type of the blockchain. The public and private blockchains have different security levels and all users must take note of this.
- Immutable network
When information enters into a blockchain and it is verified, it cannot be altered again. The information remains original and each information has its corresponding dates and stamps that cannot be changed by anybody. This is why it is said that the blockchain network is very rigid and immutable.
- High efficiency rate
The blockchain network is automatic so it reduces the chances of an error. Unlike the traditional systems that are operated by humans and for that matter any small mistake can destroy everything. The blockchain is already programmed to operate perfectly and it doesn’t need the hand of any human. Blockchain transactions are also done very quickly as there is no exchange of anything from the external environment to distract its functioning. The users get their information very fast as they are always readily available to users.
- Relatively low cost
These blockchains are for cryptocurrencies. And the use of these cryptocurrencies for business transactions are less costly as compared to the traditional monetary system. Most especially when the business is a foreign transaction, the use of cryptocurrencies can help in swerving some charges that are applied in the local system. This is a quality of cryptocurrencies that attracts a lot of traders to do their business in cryptocurrencies to save some losses.
- Data can be tracked
The data in a blockchain doesn’t get missing. They are always stored in a distributed ledger so anybody can have access to them when the need arises. These decentralized systems are made to function in that way and information don’t go missing. That is a proper way of keeping records without loosing valuable data.

3. Explain Blockchain Distributed ledger.
A blockchain distributed ledger is a database that is agreed on to share data with different places, organisations or sites. This shared data is also synchronised.
This distributed ledger makes decentralized system unique and differentiate them from the centralized systems.
When transactions performed in a block are updated, the distributed ledger ensures that each node receives the updated information in the blocks and the new information becomes part of the network automatically.
New created blocks and newly validated transactions will be distributed throughout the blockchain by the works of the distributed ledger.
Properties of blockchain distributed ledger
The blockchain distributed ledger has some outstanding characteristics. Some of these properties are as follows;
- Distribution
The distributed ledger ensures that blockchain data and information are distributed and made readily available to all users of the blockchain at any point in time. The distributed information cannot be changed and any attempt to alt them will be noticed across the blockchain.
- Data security
The cryptographic hashes in the blockchain make them very safe and secured. The public blockchain for instance has very tight security and it makes the work of the people trying to temper with the blockchain very difficult.
- Immutability
Once data has been validated and stored in the blocks, they cannot be altered at any point in time. The stamps of date and time are added to the distributed ledger to make each one unique for identification.
- Programmable
The distributed ledger is programmed based on the function required by the users. After the ledger has been programmed to perform a particular task, it is able to do it automatically without any external influence.
- Unanimous
Before a blockchain can be executed, the distributed ledger ensures that all the connected nodes agree that all transactions in the blocks are validated with no mistake. To enhance the safety of participants and the blockchain at large, the identity of the nodes in the blockchain are kept secret.
All the properties of a distributed ledger are summarized in the diagram below.
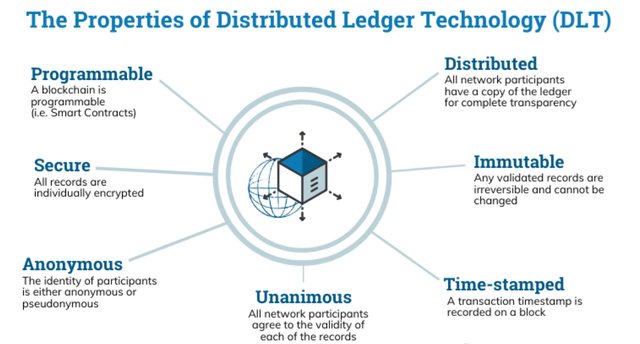
source

What Is Blockchain Double Spending and how Bitcoin handles this problem?
Blockchain double spending is a defect in a blockchain in which one particular token can be spent more than once on separate transactions. Cryptocurrencies are not physical money so they have digital files which are easily multiplied or repeated. This scenario is usually formed from external sources which are influenced by the creator of the blockchain to distract the blockchain and cause this double spending mess. This kind of mess happens when the buyers and sellers start to do transactions.
This can be illustrated in this scenario. A person goes to a bar to buy a drink for $20. The seller of the drink takes the money from you and put it at a safe place. Now the money is gone and you can’t have it to spend again. This is not possible in real currency but in cryptocurrencies it is possible to duplicate the files and use them after already spending them on other transactions. This double spending is possible in cryptocurrencies because there are people who understand the blockchain operations and also have the computing power which they use to manipulate the blockchain system to be able to duplicate crypto tokens and use them twice for different transactions.
Another way of doing this is that the scammer involved will send many different transaction packets to the network and then reverse the transactions to make it look as if no transaction was made.
This blockchain double spending are of different types. Some of the types of double spending are highlighted below:
Finney attack
This type of double spending occurs in different blocks. The miner will use transactions that have been duplicated from different blocks. When a transaction is not confirmed and a buyer accepts it, it could lead to double spending called Finney attack.Vector 76 attack
This type of double spending occurs within the same blockchain. Hackers develop false cryptocurrencies and send them to buyers at the receiving end of the blockchain. This type of double spending is very common in the blockchain network.Race attack
This type of double spending occurs when the imposter acts very fast to create many transactions with the same crypto amount and send them into a blockchain to be spent in that particular blockchain before it is even verified. When recipients take transactions that are yet to be confirmed, this type of double spending happens.
How Bitcoin handles Blockchain Double Spending
Blockchain Double spending is a problem for all cryptocurrencies and Bitcoin is not an exception. However Bitcoin have developed a very effective strategy to handle this problem of double spending. Bitcoin has employed a consensus mechanism called proof of Work (PoW) to battle this problem of double spending. The PoW is applied by miners of a decentralized system who will use the blockchain ledger to record and secure previous transactions to ensure that a transaction is not repeated. These miners are able to detect any attempts of double spending in the Bitcoin blockchain.
Bitcoin also uses the confirmation of transactions by the miners to be able to prevent double spending. The blockchain hash will verify and validate any new transaction before it is added to the distributed ledger. Unless the verification is completed, the transaction is not added to the list of confirmed transactions and finally recorded as part of the distributed ledger.
This is a link to a site that explains into details how Bitcoin handles double spending on their blockchain. The below image summaries how Bitcoin tackles double spending.
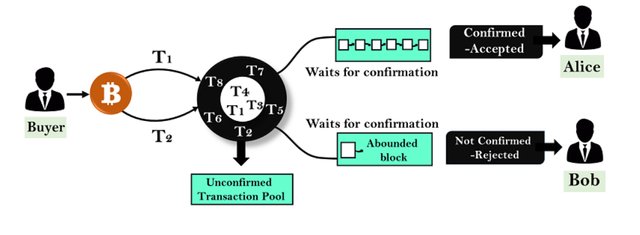
source

Practical + Theory, Visit Blockchain Demo and check section Blockchain, then explain in detail how Blocks Hashes Work in Blockchain, what will happen when any middle of the block gets changed, try to give screenshot for each possible details.
I will open Blockchain Demo to explain the practical aspect. Then go to the hash section where there is a SHA256 Hash.

In this hash section, any input that is entered generates a unique hash. A slight change in the input will also result in a change hash. Different inputs can’t have the same hash.
Block
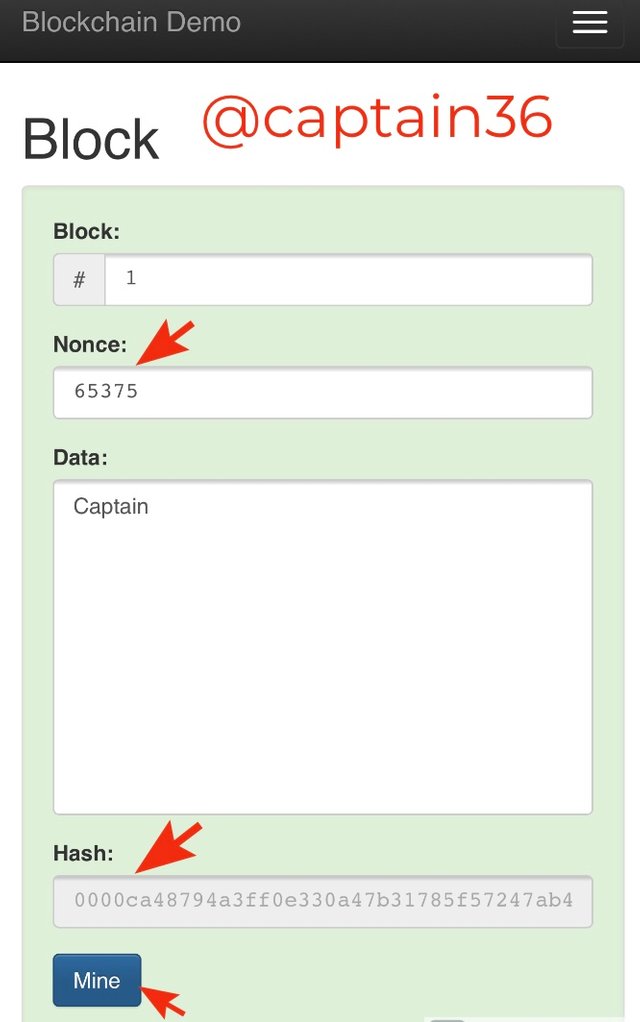
When we move to the block part, we have components such as Block number, Nonce, Data and Hash.
The block number usually starts from 1. The function of the Nonce number is to validate the block. The hash value always starts with 0000 and any data input will change the hash value.
As seen in the screenshot above, there’s no input in the data category. When I input something at the data section the hash will change and the color of the block turns to red which shows that the block is invalid.
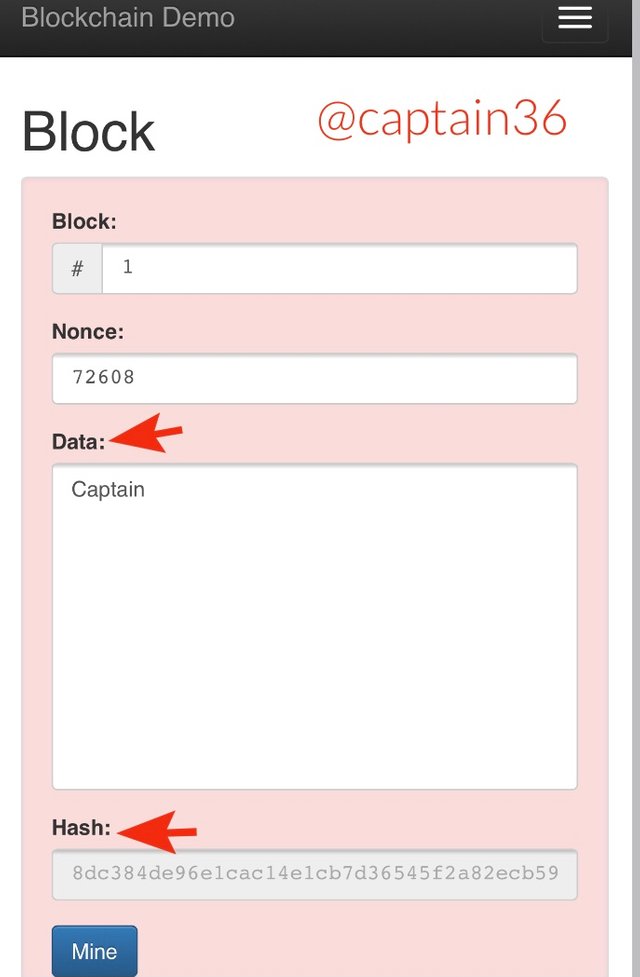
This is where the function of the Nonce comes in. Each data inputted has its unique nonce value. Getting the corresponding nonce value for a data makes the data validated. Manually it will be very complicated to find the corresponding Nonce value for a data input unless we use a computation power. When you click on “mine” the nonce value will be found which validates the block. The new generated Nonce number is 65375 whilst the Hash number is 0000ca48794a3ff0e330a47b31785f57247ab415488dc864b115206e21aeaa05.
Blockchain
In the blockchain section, the blocks there are more than one. Each block in the blockchain has a Block number, Nonce, Data, previous block’s hash and Block hash.
The block starts from block and the Nonce number is intact. No data has been input in the block so the Data section is empty.
Previous block hash is 000000 because this is the first block. This first block is referred to as the genesis block.
The hash value is intact. It starts with 0000 as usual which confirms it’s validity.
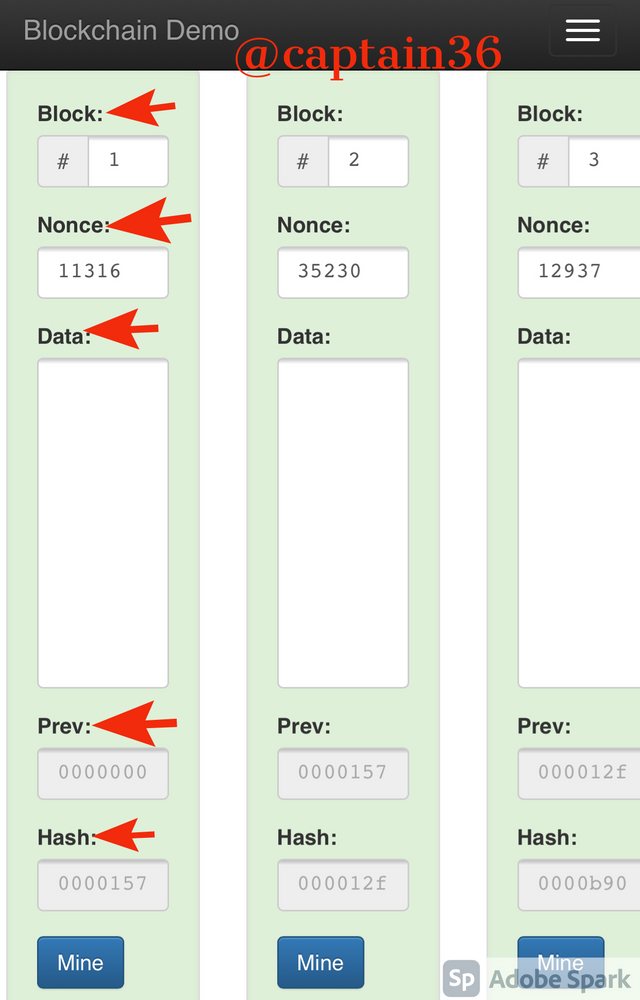
The above features are the same for the subsequent blocks except the previous hash value’s which will be the hash of the previous block.
For instance in block no 2, the previous hash value will be the hash value of block number 1. The hash value starting with 0000 shows the block is valid.
If Data is inputted in to block 1, all the blocks will change to red color indicating that they are not valid.

Because I changed the data in block 1 I have to re-mine it before it is validated. After I mine it again, the Nonce value will change again to correspond to the data input. And a hash starting with 0000 will be generated to show that block 1 has been validated. Only block one is validated and not the remaining blocks.
The next block doesn’t get validated because the hash value is linked with the new hash of block 1 but the nonce in block two still remains as it is. This Nonce value must be changed to correspond to the new hash and this can be done by re-mining block 2. This process must be repeated in the subsequent blocks in order to validate all blocks.
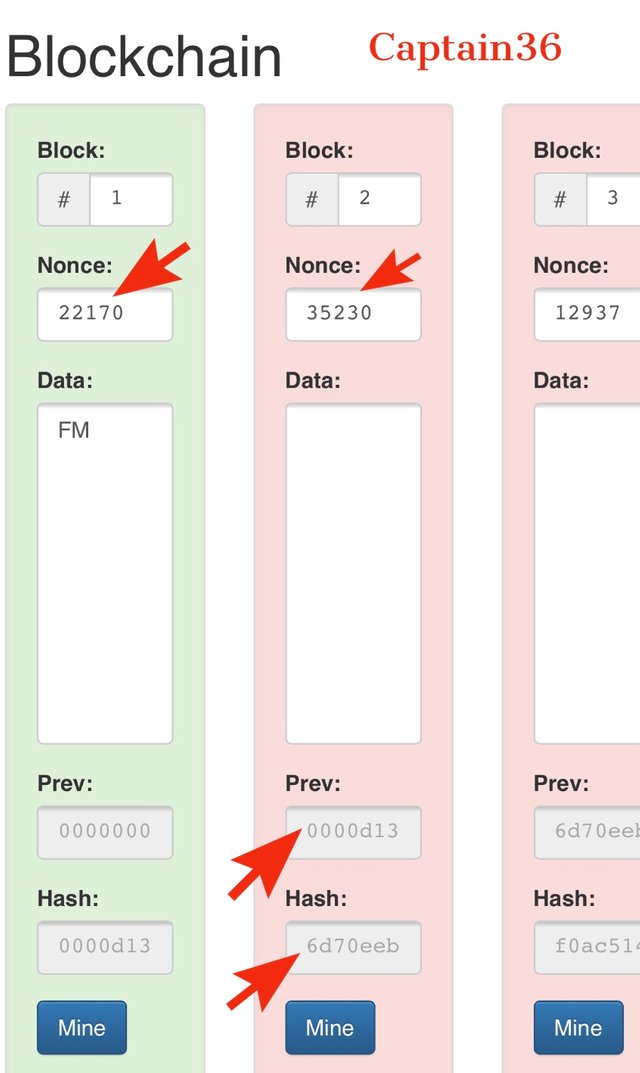
For the above process we can conclude that a blockchain is very secured because any change made in a single block will mean the whole blockchain will be affected and you’ll have to make corresponding changes in every single block.

What Is Race Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Finney Attack in blockchain? OR What Is Vector76 Attack in blockchain?
Race Attack in blockchain
The race attack is one of the forms of double spending in a blockchain. In this type of double spending, the hacker launches a particular single token and use different nodes to send it to different users within the blockchain. This format is used to buy plenty crypto assets with a single token.
The mining processes in a blockchain can stop this type of double spending. If the multiple transactions are launched into the blockchain, the mining process will validate only one and make the rest invalid. However when a buyer doesn’t wait for the validation process before confirming a transaction, the user falls victim to the trick of the hacker.
If all users can be patient for transactions to be validated before they confirm, this type of double spending will be avoided.
For example, a hacker can have 0.55 BTC in his wallet. Then he decides to send this 0.55 BTC to two different people through different nodes. The user that will not wait for the miners of the Bitcoin blockchain to validate the transaction is the one that will get scammed.
Only one of the two people will have his transaction validated and the other one will be recorded as invalid and the user looses his assets.
Limitations/disadvantages of Blockchain.
Despite the several benefits that the blockchain has brought to the world of cryptocurrencies, it also has its limitations and some of these disadvantages are highlighted below;
- Expensive mining and high transaction fees
The high consuming computation machines that are used in blockchain mining requires a lot of energy before they can mine the large number of transactions that are piled up. A lot of resources are spent on the computers to generate this needed energy.
The large blockchains such as Ethereum and Bitcoin blockchain also apply large transaction fees for even small transactions which scares away some buyers and sellers.
- Difficult scalability
Scaling up in a blockchain will mean the number of nodes will be increased which will in turn slow down the speed of transactions in the blockchain. This will also mean that the blockchain will require much energy which will make a lot of funds wasted on it.
- Immutability
This immutable property of a blockchain was discussed earlier as an advantage of the blockchain. However it can also be a limitation to the blockchain in the sense that data that needs to be edited or removed from the blockchain cannot be removed even if it is not needed in the blockchain. This means that an error cannot be corrected once it has been confirmed and validated by the blockchain.
Blockchain is too open
Because of the decentralized nature of a blockchain, it is very opened to everyone. For this reason, hackers use the opportunity to be able to get access to the blockchain and able to manipulate the blockchain to scam the users of the blockchain. These attacks on the blockchain could have reduced if the network was a bit close.Adaptation problems
Cryptocurrencies are not still able to adapt to the ways of operations of the traditional monetary system. Because of this, cryptos are not accepted in most countries and this is a very big challenge for the crypto world.

Conclusion
In summary we learned that a blockchain is formed withthe Blocks, Chains, Nodes and Miners as it’s components. All these components have their unique functions as we already discussed above.
Blockchains are very beneficial in the world of cryptocurrencies. Some of the benefits of blockchains include the high security it provides for the crypto world, it’s effectiveness and efficiency as well as the immutable behavior of the blockchain makes it very beneficial to the crypto ecosystem.
Blockchain also has a distributed ledger which is a database that is shared between different sites or places. The distributed ledger is a property of a decentralized system which makes it unique and different from a centralized system.
Despite the high security of the blockchain, some hackers still find a way to attack the system through blockchain double spending. This double spending is a flaw of the blockchain where a single crypto asset is spent more than once on different transactions.
We also learned on how the blocks and hashes operate in a blockchain. Any change in a single hash means the entire blockchain will be affected and cannot be validated.
Despite all the positives and benefits of the blockchain, it has its own shortcomings. Scalability problems, high transaction fees and difficult in adaptability are some of the disadvantages of the blockchain.
But in general the blockchain has been very useful and beneficial to the crypto world.
Thank you professor @stream4u for this educative lecture on blockchains.


Hi @captain36
Thank you for joining The Steemit Crypto Academy Courses and participated in the Homework Task.
Total | 7/10
Your Homework Task verification has been done by @Stream4u, hope you have enjoyed and learned something new.
Thank You.

@stream4u
Crypto Professors : Steemit Crypto Academy
#affable
Thank you professor for the feedback