SCABIES A DEADLY SKIN INFECTIONS, WAYS TO IDENTIFY AND TREATMENT
WHAT IS SCABIES?
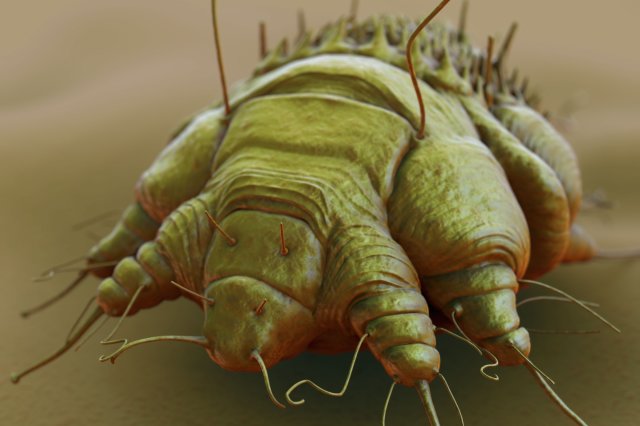
Scabies is an itchy, highly contagious skin disease caused by an infestation by the itch mite sarcoptes scabiei. The mites are small eight-legged parasites. They are very tiny, just about 1/3 millimeter long, and burrow into the skin to produce intense itching which tends to be worse at night. The mites that infest humans are female and are 0.2mm – 0.4mm long. The male are about half this size. Scabies mites cannot easily be seen without magnification. The scabies mites crawl but are unable to fly or jump. They are immobile at temperature below 20C although they may survive for periods at these temperatures.
Scabies infestation occurs worldwide and is very common. Scabies can affect anyone of any age (including a baby or child) of any race.


HOW SCABIES IS SPREAD
Scabies is very contagious and can be contracted by direct skin-to skin contact. Scabies mites are very sensitive to their environment. They can only live off of a host body for 24- 48 hours under most conditions. Transmission of the mites involves close person to person contact of the skin to skin variety, so risk factor include close contact with an infested person.it is hard, if not impossible to contract scabies by shaking hands, hanging your coat next to someone who has it ,or even sharing bedclothes that had mites in them the night before. Sexual physical contact, however can transmit the disease.in fact, sexual contact is the most common form of transmission among sexually active young people, and scabies has been considered by many to be a sexually transmitted disease (STD).however, other form of physical contact, such as a mother hugging a baby, are sufficient to spread the mites.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF SCABIES
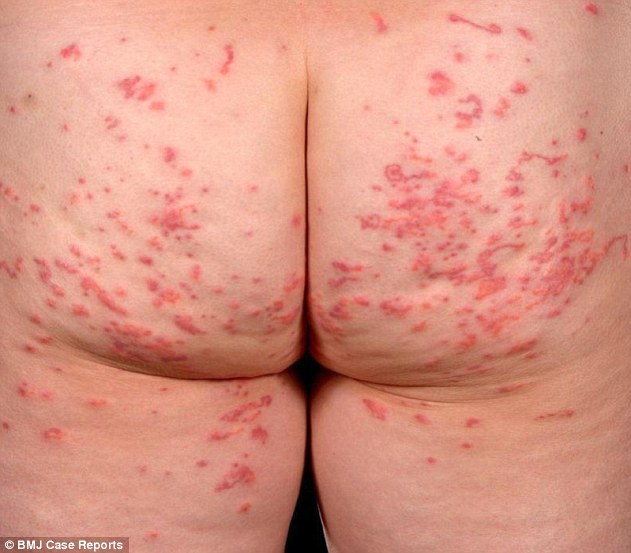
• Scabies produces a skin rash composed of small and red bumps and blisters and affects specific areas of the body.
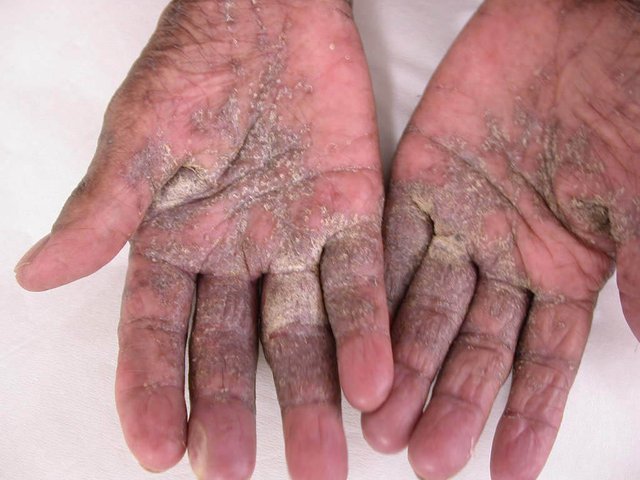
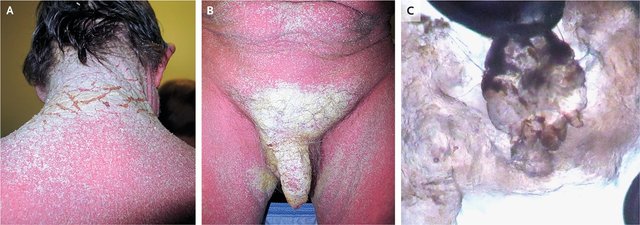
• Scabies may involves the webs between the fingers, the wrists and the backs of the elbows, the knees, around the waist and umbilicus, the axillary folds, the areas around the nipple, the sides and backs of the feet’s, the genital area and the buttocks.
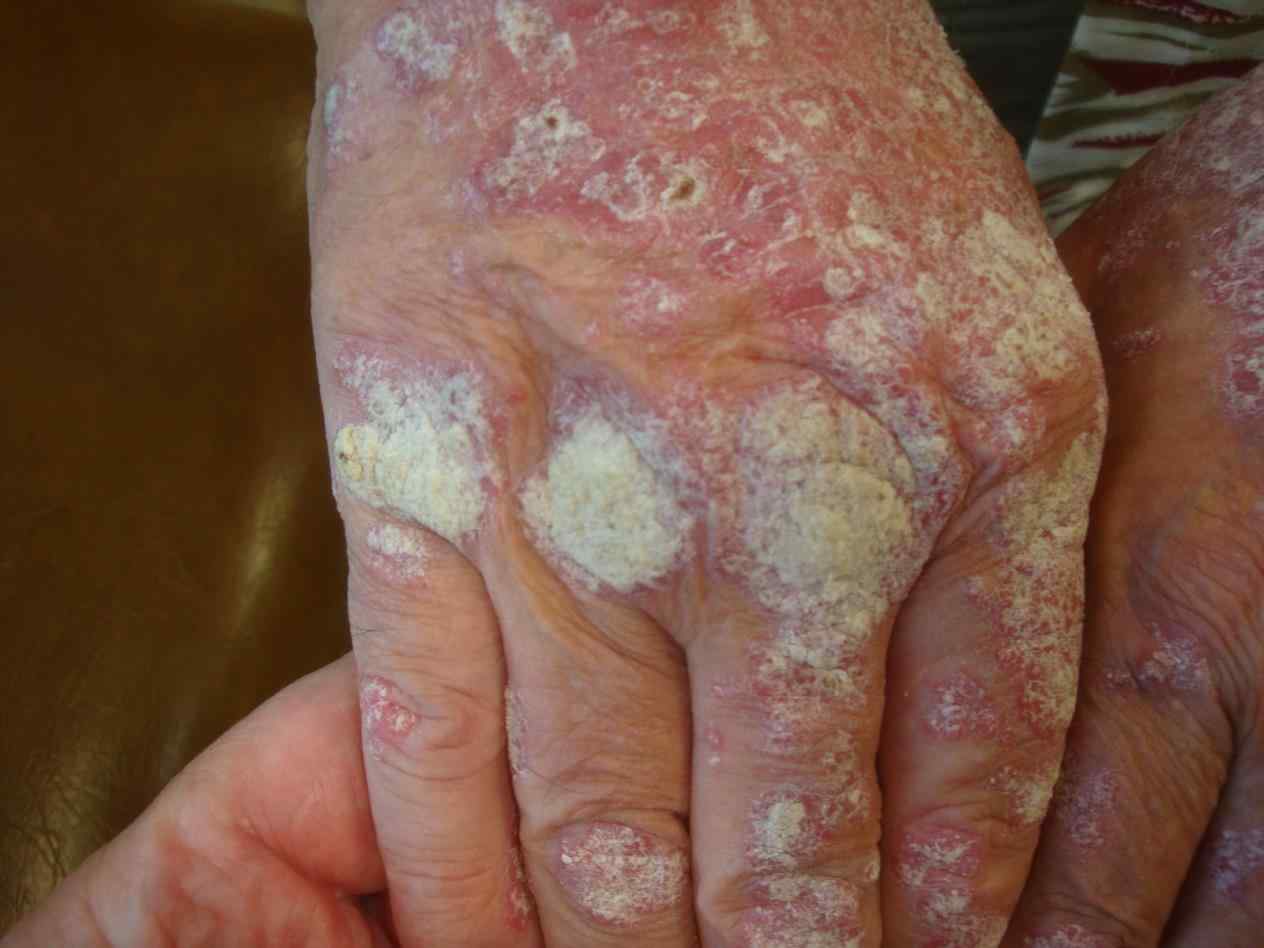
• The bumps (medically called papules) may contains blood crusts.it is helpful to know that not every bump is a bug.
• In most cases of scabies affecting otherwise healthy adults, there are no more than 10-15 lives mites even if there are hundreds of bumps and pimples on the skin.
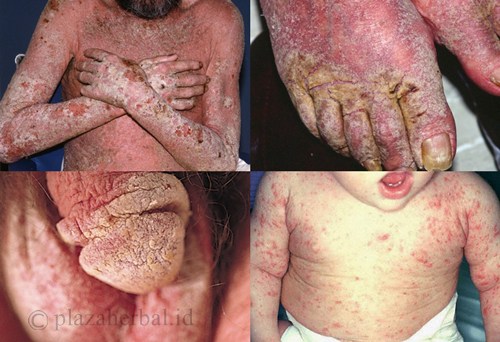
• The scabies rash is often apparent on the head, face, necks, palms and soles of the feet in infants and very young children but usually not in adults and older children
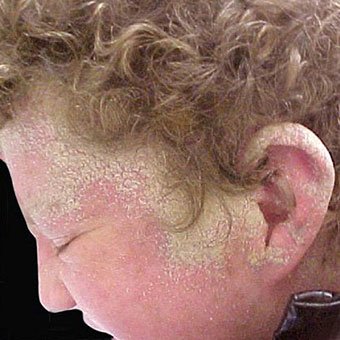
WHAT DOES SCABIES FEEL LIKE
It is important to note that symptoms may not appear for up to two months after being infested with the scabies mite. Even though symptoms do not occur, the infested person is still able to spread scabies during this period. When symptoms develop, itching is the most common symptom of scabies. Scabies does not caused pain. The itch of scabies is insidious and relentless and often worsens over a period of weeks of scabies. The itch is typically worse at night. For the first weeks, the itch is subtle.it then gradually becomes more intense until, after a month or two, sleep become almost impossible due to the intensely itchy skin.
TREATMENT OF SCABIES INFESTATION
Curing scabies is rather easy with administration of prescription scabicide drugs. There are no approved over the counter preparation that have been proved to be effective in eliminating scabies, and home remedies are not effectives. The following steps should be included in the medical treatment of scabies:
- Apply a mite-killer like permethrin (Elimite). These creams are applied from the neck down, left on overnight, then washed off. This application is usually repeated in seven days. Permethrin is approved for use in people 2 months of age and older and is considered to be the safest and most effective treatment for scabies.
- An alternative treatment is 1 ounce of a 1% lotion or 30 grams of cream of lindane, applied from the neck down and washed off after approximately eight hours. Since lindane can cause seizures when it is absorbed through the skin, it should not be used if skin is significantly irritated or wet, such as with extensive skin disease, rash, or after a bath. As an additional precaution, lindane should not be used during pregnancy or in nursing women, the elderly, people with skin sores at the site of the application, children younger than 2 years of age, or people who weigh less than 110 pounds. Lindane is not a first-line treatment and is only recommended if patients cannot tolerate other therapies or if other therapies have not been effective. Resistance to this medication has also been frequently reported.
- Ivermectin (stromectol) an oral medication, is an antiparasitic medication that has also been shown to be an effective scabicide, although it is not FDA-approved for this use. The CDC recommends taking this drug at a dosage of 200 micrograms per kilogram body weight as a single dose, followed by a repeat dose two weeks later. Although taking a drug by mouth is more convenient than application of the cream, oral ivermectin has a greater risk of toxic side effects than permethrin and has not been shown to be superior to permethrin in eradicating scabies. It is typically used only when topical medications have failed or when the patient cannot tolerate them.
- Crotamiton lotion 10% and cream 10% (Eurax, Crotan) is another drug that has been approved for the treatment of scabies in adults, but it is not approved for use in children. However, treatment failures have been documented with the use of crotamiton.
- Sulfur in petrolatum (Sulfo-Lac, Sulfo-Lo) applied as a cream or ointment is one of the earliest known treatments for scabies. It has not been approved by the FDA for this use, and sulfur should only be used when permethrin, lindane, or ivermectin cannot be tolerated. However, sulfur is safe for use during pregnancy and in infants.
- Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine(Benadryl), can be useful in helping provide relief from itching. Sometimes, a short course of topical or oral steroids is prescribed to help control the itching.
- Wash linens and bedclothes in hot water. Because mites don't live long away from the body, it is not necessary to dry-clean the whole wardrobe, spray furniture and rugs, and so forth.
- Treat sexual contacts or relevant family members (who either have either symptoms or have the kind of relationship that makes transmission likely). Just as the itch of scabies takes a while to reach a crescendo, it takes a few days to subside after treatment. After a week or two, relief is dramatic. If that doesn't happen, the diagnosis of scabies must be questioned.
thanks for visiting my blogs

Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.medicinenet.com/scabies/article.htm