What is achondroplasia?
Definition
What is achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is a disorder of bone growth caused by rare genetic mutations. Mutation of these genes is a major cause of disproportionate dwarfism. As a result of this condition, cartilage can not give body shape normally. People with achondroplasia have short posture, about 131 cm in men and 124 cm in women.
Achondroplasia can be passed from parent to child, but in general (about 80%) is caused by a new mutation.
How common is achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is very common. This condition affects more women than men, as well as at any age. Achondroplasia can be overcome by reducing risk factors. Discuss with your doctor for more information.
Signs & symptoms
What are the signs and symptoms of achondroplasia?
Common symptoms of achondroplasia are:
- Has a short posture:
- Male: height about 131 cm
- Woman: about 124 cm high
- Having short arms and legs with arms and short upper thighs, limited elbow movement.
- Has a large head (macrocephaly) with a wide forehead.
- Has short fingers. The hands are seen branched, due to ring finger and middle finger deviate.
Other health conditions associated with achondroplasia are:
- Respiratory problems: breathing slows down or stops for a short time (apnea)
- Obesity
- Recurrent ear infections
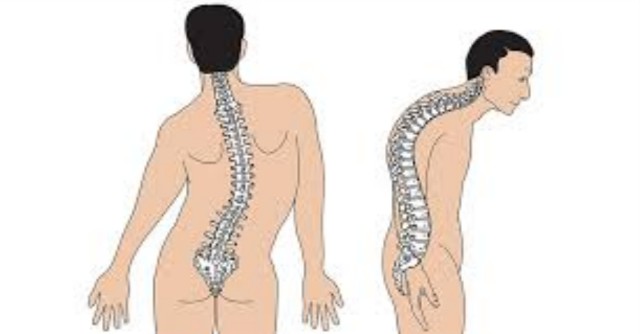
- Kyphosis and back pain
- Spinal stenosis
- Hydrocephalus
There may be signs and symptoms not mentioned above. If you have concerns about a particular symptom, consult your doctor.
When should I see a doctor?
You should contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Short posture compared to mean age and gender
- The arms and thighs are short, compared to the height of the body
- Short fingers and hands that look like three branches
- Big and disproportionate heads, and too big foreheads
- Apnea, or short periods in which the breath slows or stops
- Hydrocephalus
- Difficulty in movement of the elbow
- Have obesity
- Have recurrent ear infections
- Kyphosis or lordosis.
If you have any of the above signs or symptoms or any other questions, consult your doctor. Each person's body is different. Always consult a doctor to treat your health condition.
Cause
What causes achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is caused by a genetic mutation in the FGFR3 gene that inhibits cartilage development for bone formation during fetal development.
Risk factors
What increases my risk for achondroplasia?
There are many risk factors for achondroplasia, namely:
- Children with mothers and / or fathers who have achondroplasia.
- Children with mothers and / or fathers who have a mutated FGFR3 gene.
- The father's advanced age at fertilization leads to mutations
Medication & Treatment
The information provided is not a substitute for medical advice. ALWAYS consult your doctor.
How to diagnose achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia can be diagnosed during pregnancy and after your child is born.
During pregnancy:
- Ultrasound imaging can detect the characteristics of achondroplasia such as: hydrocephalus, or a head that is too large
- Genetic testing can be performed if suspected of achondroplasia by sampling chorionic villus or amniocentesis
Once your child is born, the diagnosis of achondroplasia can be done based on:
- Certain physical features
- X-ray, ultrasound and other imaging techniques to measure the length of a child's bone, as well as a blood test to see the presence of the FGFR3 gene.
How to treat achondroplasia?
There is no special treatment for achondroplasia. If there is a problem that arises as a complication of achondroplasia, inform the medical team for appropriate treatment. As an example:
- Surgery of narrowing (stenosis) and compression of the spinal cord
- Surgery for spinal cord management in adolescents
- Orthopedic procedure for prolonging bone and fixing bent legs
- Operation (lumbar laminectomy) to overcome spinal stenosis (narrowing)
- Placement of shunt to remove fluid from hydrocephalus.
- Antibiotics and / or ear tubes to treat middle ear infections (otitis media)
- Flattening of teeth to prevent teeth from overlapping
- Supervise and control weight to avoid obesity
- Treatment with growth hormone to increase bone growth rate of children
Treatment at home
What are the lifestyle changes or home remedies that can be done to overcome achondroplasia?
Here are the lifestyle and home remedies that can help you overcome achondroplasia:
- Take control of obesity
- Join the support group
- Maintain positive habits such as exercise
- Remember that achondroplasia only affects your appearance. Your intelligence remains the same as everyone else.
If you have any questions, consult your doctor for the best solution of your problem.