Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that almost always requires prompt surgery to remove the appendix. Left untreated, an inflamed appendix will eventually burst, or perforate, spilling infectious materials into the abdominal cavity.
The appendix is a small, worm-like, tubular appendage attached to the cecum of the colon.
Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, and bacteria invade and infect the wall of the appendix.
Appendicitis causes a variety of symptoms, including:
abdominal pain
low fever
nausea
vomiting
loss of appetite
constipation
diarrhea
difficulty passing gas
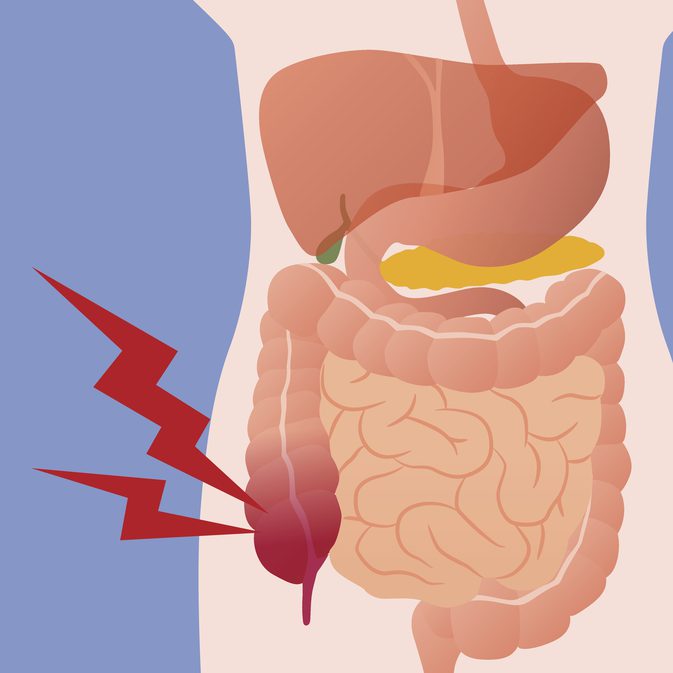
some people's appendixes may be located in a slightly different part of their body, such as:
the pelvis
behind the large intestine
around the small bowel
near the right lower part of the liver
antibiotics used for appendicitis include:
Piperacillin and tazobactam sodium (Zosyn)
Ampicillin and sulbactam (Unasyn)
Ticarcillin and clavulanate (Timentin)
Cefepime (Maxipime)
Gentamicin (Gentacidin and Garamycin)
Meropenem (Merrem)

Medical examination: The original test for appendicitis, a simple examination of the belly remains important in making the diagnosis. Changes in the abdominal exam help doctors tell if appendicitis is progressing, as well.
Great post about Appendicitis. thanks for sharing...