Heart failure;Definition, Causes and Pathophysiology.
 Heart failure can also be referred to congestive cardiac failure
Heart failure can also be referred to congestive cardiac failure
DEFINITION:it's defined as the inability of the heart to function as a pump to meet the body's metabolic demands.
RISK FACTORS: "things that predispose to heart failure".They're; smoking,obesity,sedentary lifestyle,physical inactivity, alcohol etc
CAUSES: high blood pressure, abnormal heart rhythm, excessive alcohol use,coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack),valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathies.
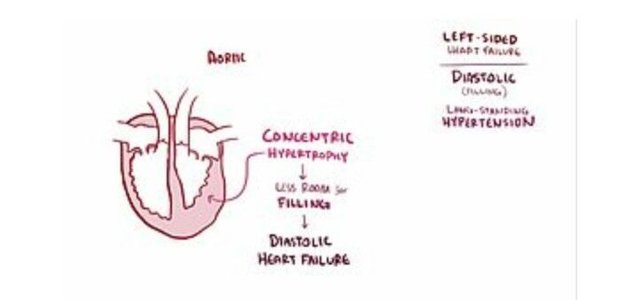
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: There is a change in either the structure or the function of the heart.There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on whether the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise according to the Newyork heart association NB:Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether).......to be continued