America’s Historic Unemployment Cliff: 10 Facts You Should Know
Nations around the world are taking actions to limit the spread of
the novel coronavirus, a disease some scientists say could kill millions
of people around the world.

Nations are handling the coronavirus threat in different ways. China instituted the largest quarantine in human history. Hungary recently granted nationalist Prime Minister Viktor Orban sweeping new powers with no expiration date. Most nations, including the US, have instituted closures and lockdowns. Some nations, like Sweden and the Netherlands, have taken relatively little state-enforced actions.
It’s unclear how many lives will be saved by lockdowns and closures—some epidemiologists have expressed skepticism of the strategy—but the economic consequences are becoming more clear.
In the wake of forced closures, an unprecedented number of Americans
are now jobless. Below are some figures that illustrate the situation
facing US workers.
10 Facts on Unemployment
1. New jobless claims in the US spiked to a record 6.6 million this week, a 3,000 percent increase from early March.
2. That is more than double
the record 3.3 million new jobless claims set last week—which was
already nearly five times higher than the previous record of nearly
700,000 set in 1982.
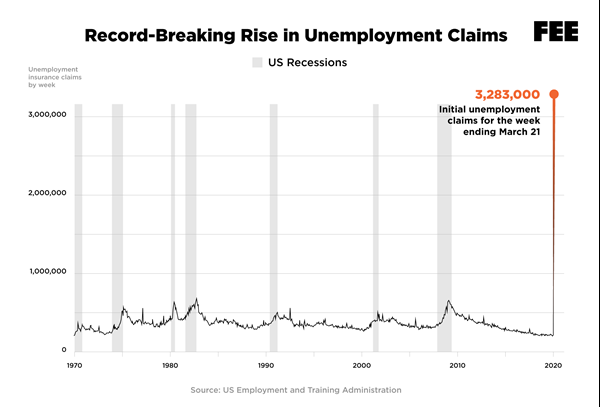
3. It’s a historic collapse, yet it could soon become much worse. Economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis recently projected that unemployment could reach 32 percent nationwide.
4. That figure would smash the highest unemployment rate in US history—24.9 percent, which occurred in 1933 during the height of the Great Depression.
5. The unemployment rate does not include the 96 million Americans not in the workforce prior to the lockdowns.
6. JPMorgan Chase projects
real GDP to fall 10 percent in the first quarter and 25 percent in the
second quarter. Getting these employees quickly back to work will be key to any economic recovery.
7. Under the recently passed coronavirus relief bill, most workers
who lost jobs during the pandemic will be eligible to receive federal
payments of $600 per week on top of their state unemployment benefits
for four months.
8. Regular unemployment benefits were also extended 13 weeks. While these measures are intended to help workers, it could also incentivize companies to lay-off employees and disincentivize workers from returning to the labor force, exacerbating the coming recession.
9. Research shows mass unemployment could have a profound impact not
just on the economy, but human lives. A study conducted by James E.
Barrett titled “Influence of the Social Environment on Psychology: The Historical Perspective” found a ten percent increase in the unemployment rate increased the mortality rate by 1.2 percent and suicide by 1.7 percent.
10. An abundance of research also suggests higher unemployment rates are linked to higher rates of substance abuse, crime, and arrests.
Consequences of COVID-19 Enforcement
We don’t yet know how deadly the novel coronavirus will prove to be,
but some epidemiology experts say they fear many of the actions may end
up doing more harm than good.
In a recent YouTube video, Dr. John Ioannidis of Stanford University said many actions appear to be based on “gut feelings” rather than sound data. He said the initial fatality rate of 3.4 percent reported by the World Health Organization was a “crude estimate” and the actual COVID-19 fatality rate is almost certainly much lower.
What we know is just the tip of the iceberg. Information
from settings where we have more complete information suggest the
infection fatality rate is much lower than 3.4 percent,
said Ioannidis, professor of epidemiology and co-director of the school’s Meta-Research Innovation Center,
It is probably much lower than the .9 percent …
[estimated by] the wonderful team of researchers at Imperial College,
which probably overestimated the exact infection fatality risk.
These are trying times. Thousands of Americans have already died from Covid-19 infection and many more will. The pandemic has raised numerous questions about when and to what
degree the state can impose its will on the people to protect the people.
Whatever the actual fatality rate of the novel coronavirus turns out
to be, Americans should realize enforcement actions are not without
consequences, some of which may prove to be as deadly and destructive as
the coronavirus.
Article source: FEE
By Jonathan Miltimore the Managing Editor of FEE.org. His writing/reporting has appeared in TIME magazine, The Wall Street Journal, CNN, Forbes, and Fox News.
Photo by Johnny Cohen on Unsplash
Subscribe to Activist Post for truth, peace, and freedom news. Become an Activist Post Patron for as little as $1 per month at Patreon. Follow us on SoMee, Flote, Minds, Twitter, and Steemit.
Provide, Protect and Profit from what’s coming! Get a free issue of Counter Markets today.