SLC21/WK3 | Managing Bleeding: The Basics of Controlling External and Internal Bleeding
Steps on how to put a bandage on the arm and some tips that I can explain are below:
1 clean the wound: I wash my hands first, then clean the wound area on the forearm with antiseptic cotton to sterilize it.
2 sterile gauze: put sterile gauze on the wound to protect the open area.
3 put on a bandage: take an elastic bandage and then wrap it carefully around the forearm making sure it is not too tight so that blood circulation remains smooth.
4 bandage lock: attach a clip or adhesive to the end of the bandage so that it does not come off, the task is complete by ensuring the bandage is comfortable and safe
1 identify the bleeding area: find a large wound that is causing heavy bleeding.
2 prepare a cloth tourniquet: use a wide, strong cloth such as a scarf or piece of clothing.
3 put it on the wound: tie the cloth a few centimeters above the wound (not on itself)
4 tighten: use a rod to twist the cloth until the bleeding stops.
5 secure: tie the rod so it doesn't come loose.
6 how to remove it: the tourniquet may only be removed by medical personnel to prevent complications. do not remove it for more than two hours without professional treatment.
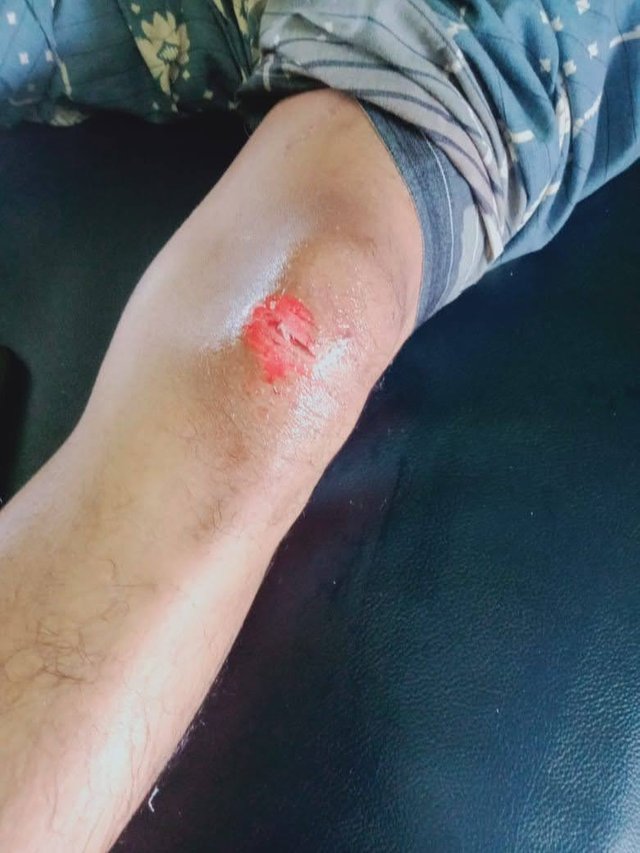
At the time of the accident I experienced
- a) What steps should you take to control the bleeding?
Press the wound with a clean cloth to stop the bleeding. Elevate the injured body part above the heart if possible. If bleeding is severe, apply a tourniquet above the wound, not above the joint.
- b) How would you assess whether the bleeding is arterial, venous, or capillary?
arteries: blood flows with high pressure and is bright red. veins: blood flows slowly or rapidly, is dark red. capillaries: blood seeps slowly like a normal abrasion
- c) What would you do if pressure alone does not stop the bleeding?
add a tourniquet or apply a pressure bandage and seek emergency medical attention immediately.
- a) What should you do as a first aider to manage the situation?
make sure the area is safe.
lay the victim down and keep him calm.
cover the wound with a clean cloth without pressing directly on the stomach, and don't forget to immediately contact the nearest medical help
- b) Why should you avoid applying direct pressure to the abdomen?
pressure can cause damage to internal organs, worsen injuries, or increase the risk of internal bleeding.
- c) What signs of shock should you look for, and how should you respond?
pale, cold or clammy skin.
rapid breathing, weak heartbeat or dizziness.
how to handle it and don't forget to lay the victim down with their legs slightly raised, cover them to keep them warm and monitor them until help arrives
easy way to handle it and here's what I can conclude:
wash your hands and clean them before handling the wound
press the wound and using a clean cloth or bandage, apply direct pressure to the wound for 5-10 minutes to stop the bleeding.
Elevate the wound if possible, position the wound higher than the heart to reduce blood flow.
use a bandage if the bleeding stops, cover the wound with a clean bandage to protect against infection
And that's all I can summarize in participating in this very interesting contest edition, and also inviting @patjewell @marito74 @aril.hatake, good luck to all of us.
 Click Here
Click Here Best regard @fajrulakmal99


Student Name: @fajrulakmal99
Overall grade: 4.1
Plagiarism Check: Pass
AI Use: No
General Feedback: The student needs to focus more on the details of the questions separately and come up with detailed answers which would be beneficial for him in the future as well. The student demonstrates an understanding of managing bleeding and procedures of controlling internal and external bleeding but needs more explanation and practical approach in certain areas.
Thank you.
Regards,
@huzaifanaveed1
Thanks my bro
https://x.com/fajrulakma93753/status/1857454187606597813?t=pkr_p-SeYFApud4eY8h4kw&s=19
Nyan jelas