One article to understand ETH2.0 pledge Staking
Content
With the release of the ETH2.0 version of the Ethereum storage contract in November, Ethereum has attracted the attention of many users. According to the latest development of Ethereum (Ethereum.org), the ETH2.0 beacon chain is officially launched, which also means that ETH is changing from a PoW mechanism to a PoS mechanism, and is moving towards the 2.0 era!
Why should ETH change to PoS mechanism
As we all know, the reason why Ethereum is welcomed by everyone is that it is a low-level smart contract development platform. Its decentralized public chain feature provides a credible execution environment for many smart contracts and decentralized applications. To ensure the decentralization of the network, the original ETH adopted the same proof-of-work PoW mechanism as Bitcoin. However, in recent years, with the development of ETH and the expansion of its ecology, the network demand has become larger and larger, and the current transaction processing volume per second of ETH is really too small, so Ethereum has become congested and the cost It also becomes expensive.
In order to solve these problems, Ethereum developers decided to adopt sharding technology (Sharding) as a solution after discussion, but sharding technology is difficult to implement on PoW. In order to improve the ability of the Ethereum network to process data in parallel, ETH2.0 will switch to PoS consensus.
POS is a verification method of equity pledge. It replaces the current Ethereum's PoW miners and electricity through verification and pledge behavior. The verifier replaces the miner to verify the block and solves the power consumption through pledge. Therefore, with the PoS mechanism, the most obvious change is that the handling fee will be reduced.
All in all, the reason why Ethereum changed from PoW to PoS was to solve the problems of network congestion, high transaction costs, and poor scalability.
What is ETH2.0?
ETH 2.0 specifically refers to that Ethereum will start to convert the original PoW consensus protocol to the Casper FFG PoS consensus mechanism at the end of 2020, mainly to solve the scalability and congestion problems of Ethereum. ETH's development plan is divided into four stages, namely "Frontier", "Homeland", "Metropolis", and "Tranquility". The conversion between each stage is usually carried out through a hard fork. And ETH2.0 is also called Eth2, which is the general term for all updated stages starting from the "Serenity" (Serenity) stage.
ETH2.0 is divided into at least 3 stages to be carried out, namely stage 0, stage 1, and stage 2.
Phase 0: Beacon Chain
In phase 0, ETH 2.0 will be launched on the beacon chain. The beacon chain is the core of the ETH 2.0 architecture. The PoS consensus algorithm will be deployed and validators will be registered. These validators will begin to verify Ethereum 2.0 blocks. The beacon chain is responsible for coordinating and managing the work of the sharding chain, and at the same time, it allows verifiers to participate in the pledge system, replacing the role of miners to become the builder of the blockchain. The beacon chain of phase 0 was officially launched on December 1.
However, at stage 0, it only supports the function of validator staking, but does not support smart contracts, nor does it support functions such as transfer and redemption.
Phase 1: Shard chain
In the first stage, the most important work is to launch the shard chain. For Ethereum 2.0, sharding will split Ethereum into 64 independent shard chains, which run in parallel and achieve seamless interaction. However, the sharding chain at this stage does not have accounts and assets, that is, it cannot realize transactional operations such as transfers, and it does not support smart contracts.
Phase 2: Implementation
In the second phase, ETH 2.0 will launch the virtual machine function to support smart contract operations of the shard chain, and it can also perform operations such as transfer and redemption.
ETH2.0 Staking
Staking and PoS can be said to be symbiotic. When Ethereum is converted to PoS, staking will be essential.
As a verification method of equity pledge, the PoS mechanism provides a right for coin holders to obtain rewards by verifying blocks. Compared with the computing power that is king under the PoW mechanism, the PoS mechanism also brings opportunities to ordinary people. Holders can pledge ETH and share the system rewards of the Ethereum PoS network. Ethereum 2.0 adds native coin deposit mining rewards, but the premise is to become a validator node to share this part of the income.
Staking mechanism introduction
In the ETH 2.0 Phase 0 phase, an important function is that validators participate in node operations and enable staking functions. That is, each node needs to run a beacon chain client and a validator client, and at the same time need to pledge 32 ETH to the Deposit contract of the ETH PoW chain.
Become an ETH2.0 miner and participate in the minimum requirements for staking;
Each validator pledges at least 32 ETH;
Computer and technology with sufficient hardware specifications;
Lock the coin to the stage where the coin can be withdrawn (expected two years);
Pledge income
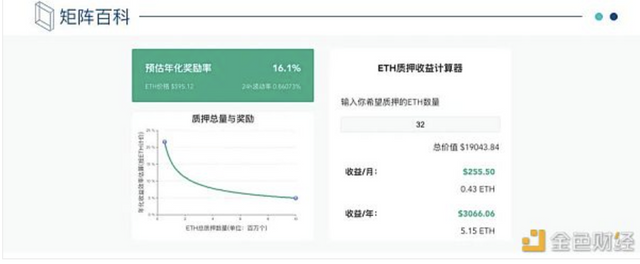
Income is closely related to the total amount of pledged on the entire network. The larger the total amount of pledge, the lower the rate of return.
The total amount of pledge is 524,288 ETH-the estimated annualized rate of return is 21.6%.
The current total pledge is 927,427 ETH-the estimated annualized rate of return is 16.1%.
If you pledge 32 ETH, you can earn 5.15 ETH a year.
Possible penalties
However, in addition to gains, validators may also face penalties:
One is the penalty received because of disconnection.
When the vast majority (2/3) of the validators are still online, they are offline, which will result in a relatively small penalty, because in this case there are still enough online on the ETH2.0 beacon chain Validators so that they can fulfill the responsibilities of validators. As long as the validator's normal online time is greater than 50%, the penalty received is relatively minor, and the staking reward is generally not that high, which will not affect the 32 ETH principal.
The second is confiscation of income, also known as Slash.
The main purpose of the Slash system is to make the cost of attacking ETH2 very high. If the verifier adopts malicious and destructive methods, such as double signing, a certain amount of ETH will be deducted by the system. Once the number of validator accounts is reduced to 16 ETH, the validator sequence will be forced out by the system.
How to participate in Staking?
Participating in Ethereum staking has a generous yield and attracts a large number of coin holders to participate. To participate in staking, you can choose the following methods:
Take it yourself
This is mainly for those professional players.
First of all, you must have a well-configured machine. Second, you must know how to install and run ETH1.0 nodes and ETH2.0 nodes, and you must be proficient in keys, mnemonics, compilers, etc., to ensure that the verification nodes are not abnormal. Because if you continue to be offline, there will be a margin penalty.
Finally, the most important thing is to have 32 ETH to participate in the mortgage.
Choose a third party for staking
This is mainly for ordinary users. After all, not everyone has a lot of knowledge about running nodes, and those who have 32 ETH and locked their assets for 1 to 2 years.
(1) Centralized exchanges and mining pools
These platforms have low entry barriers and do not need to run the nodes themselves, but part of the revenue will become the service side's handling fee. The principle is very simple, that is, everyone gathers 32 ETH together and forms a team to participate in the pledge.
(2) Wallet
Staking is so popular that many wallets will provide staking services similar to trading platforms. We can use wallet staking directly. Some wallets even made innovations on the basis of locked positions. For example, Bitpie anchored the locked ETH to Token. According to the user's pledge amount in ETH2.0, the pledge certificate Token is sent 1:1, and the user can sell the Token and transfer it in ETH2. .0 pledge and income.
The risks of participating in staking
Although ETH2.0 pledge is an opportunity to gain income, it is also risky.
Long lockup time
The current ETH2.0 is still in the preliminary stage. Now it is participating in the pledge. The pledged ETH needs to be locked to the 1.5 stage, which is optimistically estimated to take two years. Since transactions cannot be conducted during the period, the pledger needs to bear the risk of ETH price fluctuations.
Need to burn ETH for BETH
Staking requires putting ETH into the destruction smart contract to exchange for 1:1 BETH, and the operation is irreversible. Most importantly, BETH may not be able to buy back the same amount of ETH.
The rate of return will decrease
The estimated rate of return during the fundraising period is not the final rate of return. The final rate of return is calculated based on the total amount of pledge at the end of the fundraising period. Assuming that after the end of the fundraising, the total amount of pledge is 10,000,000 ETH, and the final yield is only 4.9%.
Unknown risk
Once the pledge begins, you need to perform the corresponding duties as a verifier. If there is a node abnormality, there will be fines and other penalties.
Every hot spot in the market is an opportunity, but there are risks behind the opportunity. For investors, what we have to do is not to enter blindly, but to choose better methods and channels after weighing the pros and cons to maximize the benefits!
Matrixport will provide free node construction technical support for VIP customers in need, and customers can contact the staff for corresponding help.