SLC S23 Week6 || Computer Repair - HDD & SSD Storage
Hello Steemians!
Welcome to the sixth and final week of the Steemit Learning Challenge Season 23, where we conclude our exploration of essential computer components by diving into Hard Drives — specifically, HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive). These are the main storage devices in computers, whether desktop or laptop, and are crucial for storing the operating system, programs, and files.
Understanding the differences between HDDs and SSDs, their structures, advantages, limitations, and how to maintain or replace them will give you a strong foundation in computer hardware.

Definition of Hard Disk Drive (HDD):
These are permanent storage units that store system files, programs, and other items you want to save on your device.
Also, they are magnetic storage devices, similar to floppy disks and cassette tapes.
Also, they are the main storage unit in a computer. They are responsible for storing data permanently, unlike RAM, which stores information temporarily.
Also, they are metal discs coated with a magnetic material, placed inside a sealed, vacuum-sealed container. Information is stored permanently, but can be deleted or reused.
Also, they are a means of storing large quantities of files, the operating system, and programs, depending on their capacity, permanently after the computer is turned off. This is in contrast to memory.

How HDD Works:
Most computers today contain one or more hard drives. Indeed, many large computers, such as servers, contain hundreds of large hard drives, but the presence of a hard drive is not considered an urgent necessity for the device to function. The device can be booted from removable storage media such as floppy disks and CDs, and many devices support network booting.
The main motivation behind the use of these billions of hard drives is one thing: they can hold a lot of data after the computer is disconnected, because the hard drive can store digital data in a magnetic form for a long time.
Note: Hard Disk Drive is abbreviated as HDD.
 |  |
|---|---|

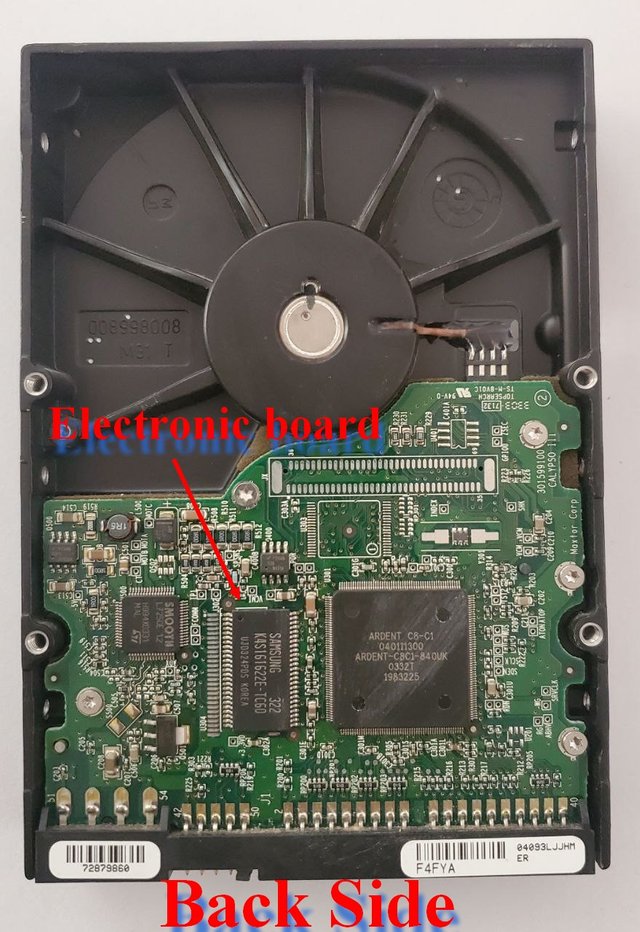
Main Components of HDD:
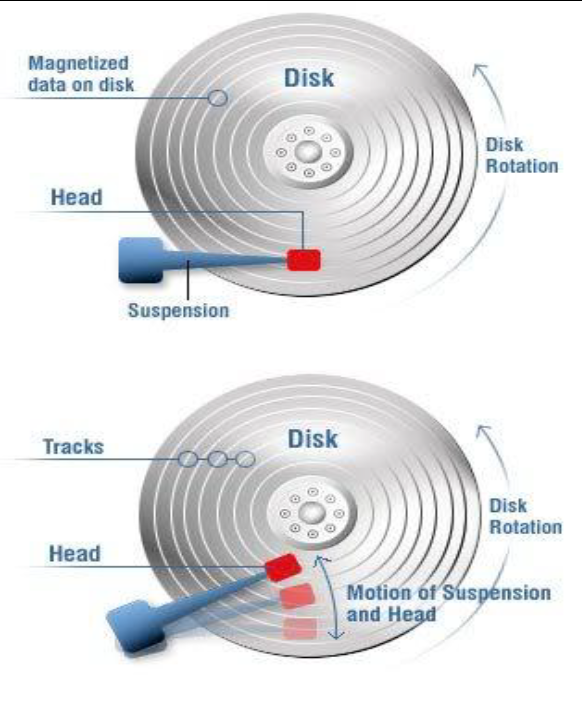
A hard disk consists of mechanical parts, divided into platters, a spindle motor, read and write heads, and a set of electronic circuits.
 |  |
|---|
1- Read and write heads:
These are multiple arms extending horizontally over the platters. These arms move back and forth between the centers of the platters and their outer edges at high speed. This movement is accompanied by the rotation of the platters, enabling data to be stored across the entire surface of the platters. Data storage and retrieval is performed by the read and write heads.
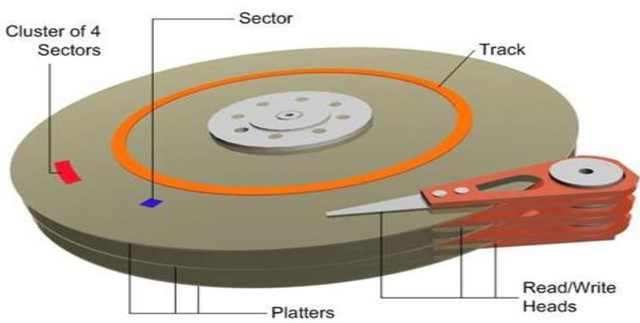
2- Circular platters (platters):
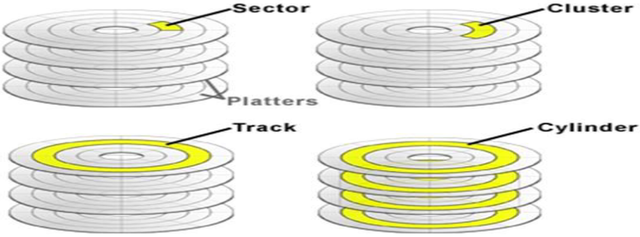
A hard disk consists of several circular platters stacked on top of each other. All platters are mounted on a common spindle, rotating at the same speed. These platters are covered with a layer of magnetizable material so that data can be stored on their surfaces in the form of charges. Each platter is divided into tracks, and each track is divided into sectors.
3- Tracks:
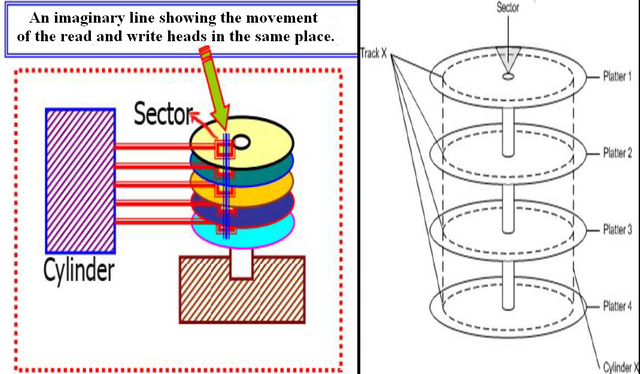
Bits are arranged on each disk in circles, each called a track. Of course, if we imagine the tracks stacked on top of each other, they would form rings on top of each other, forming a cylinder-like structure. In reality, data is stored on the cylinder, not the disk plate. This is because the read and write heads are grouped together on a common axis.
4- Sectors:
The smallest part on the surface of the hard disk that a hard disk can record data on. It typically records 512 kilobytes of information. It is also an essential part of the hard disk. This part is usually the data area (hard disk media). It can be defined as any part of these parts that can be written to, read from, or accessed by the internal components of the hard disk.
5- Cluster:
It is a group of consecutive or successive sectors on the plate. Their number varies depending on the type of hard disk format used.
The smaller the cluster size, the more efficient the disk is used. It is used to organize, identify, and store files on the disk. Most files take up the most disk space on a cluster.
6- Cylinder:
It is a number of sectors located on more than one platter if the hard disk contains more than one platter.
7- Spindle Motor:
It is the rotating shaft or shaft mounted on the hard disk motor in the center, on which the platters are mounted.
8- Electronic Circuit:
Controlls the rotation of the disk and the movement of the read and write heads, allowing them to read and write the required data based on the commands issued.
10- Protective metal casing to protect the disks from dust, the surrounding atmosphere, and shocks.
11- Cache Memory in the Hard Disk:
This memory functions similarly to RAM in a computer, but in a miniature form, allowing some files to be temporarily stored for faster access. The larger the cache size, the more files you can temporarily store, resulting in better performance.
For desktop and laptop computers, the following are available: 2MB cache, 8MB cache, 16MB cache, and 32MB cache. Recently, a 64MB cache has been introduced for larger files.

HDD Terminologies You Should Know:
The term "Tack Zero" refers to the first track on the hard disk, and it is the first point the head accesses when the hard disk is turned on. When the hard disk starts up, the following occurs:
The head moves to the Tack Zero track and then directly to Sector 0.
It then starts to boot into Sector 1, also known as the Master Boot Record (MBR) and the Guide Partition Table (GPT), which Windows 8, for example, uses.
After reading the MBR, it moves to Sector 2, which is the Partition Table, a partition table that stores the number of partitions and sectors for rapid access to the required data. This table needs to be fragmented (reorganized and reorganized) if the computer becomes heavy or slow due to the hard disk.
The head then moves directly to Sector 3, which is the System Files, and contains three system files.
The head then returns to read an area called FAT or NTFS, depending on the type of file system used by the operating system. This is a table for storing file locations or hard disk index addresses.

Desktop vs. Laptop HDD Form Factors:
The hard drive on a desktop computer is symbolized by 3.5 inches, meaning 3.5 inches, which is the drive size. The hard drive on a laptop is symbolized by 2.5 inches, meaning 2.5 inches, which is the drive size. It is also symbolized by 1.8 inches, which is the drive size found on small laptops.

HDD Types Based on Interface:
1- IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) or Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA):
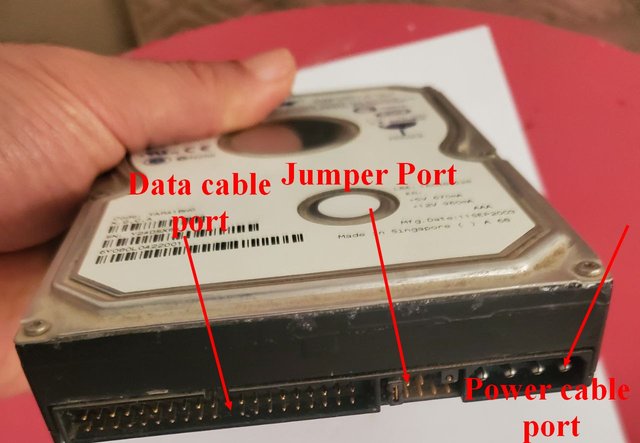
This technology transmits data sequentially. It connects hard drives on two channels, each capable of connecting two devices (a hard drive, CD-ROM drive, or backup device). One of the devices can be designated as the Master or Slave. The first channel is called the Primary, and the second is called the Secondary.
It is always preferable to place the hard drive on the Primary Master, and the CD-ROM drive on the Secondary Master. Whether the drive is a Master, Slave, or a single drive is determined by settings called Jumpers.
If you have only one hard drive, the Jumper is set to "Master." If you have two drives, one is designated the Master and the other the Slave. Jumper settings are often indicated on the surface of the hard drive and vary from one drive to another depending on the manufacturer.
2- SATA - Serial ATA (Advanced Technology Attachment):
The shape of the SATA hard drive differs from that of the IDE hard drive when connected via a cable. This is the current common method for connecting the hard drive to the motherboard, and it is, of course, one of the new features added to most motherboards.
Its main features:
1- Faster data transfer speeds: This type of hard drive contains an 8MB buffer cache, which helps it respond to commands quickly and easily. It typically operates at a speed of 7200 RPM.
2- Supports a longer cable length of approximately 2 meters.
3- Supports external hard drives with eSATA technology.
4- Quietness: The technology used in these types is called Very Fast and Nearly Silent, meaning high speed with incredible silence. Part of it is called WhisperDrive, which was recently developed within the technology giant, along with the Soft Seek feature.
5- Protection: This type of hard disk uses a new technology called Shock Guard or Shock Protection. It is shock-resistant, helps detect errors, and provides near-certain data protection by detecting and avoiding minor shocks.

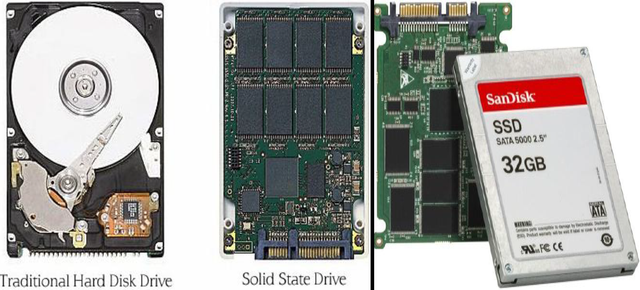
Introduction to SSD (Solid State Drive):
In 2008, a new technology emerged, commonly used in phones and portable devices due to its powerful features that enhance device performance. This technology is called SSD. The benefits and advantages of SSDs include:
Using an SSD allows your heavy applications and programs to open very quickly, as if they were instantaneously.
This is due to the near-instantaneous access time of SSDs compared to regular HDDs.Significantly reduces the risk of failure: Most hard drive problems are caused by movement, such as a malfunctioning needle or scratched magnetic disks.
Reduced risk of failure during movement: When moving and lifting a laptop suddenly, this risk is lower with SSDs, as they are more resilient and reduce movement and vibration.
Reduced risk of failure during movement: When moving, lifting, and placing a laptop, the hard drives may be damaged. This risk is lower with SSDs, as they are more resilient and reduce the effects of movement and vibration.
Less noise: Most of the noise we hear from a hard drive when working on a computer won't be heard with an SSD, as there's no writing needle or magnetic disc spinning at high speeds.
Less heat generation: The lack of movement results in very little or no heat generation.
Less energy consumption.
Perhaps its most significant drawback is:
Its high price compared to conventional hard drives. Its capacity is still small compared to HDDs, but it's expected to increase rapidly, especially with the introduction of 1TB SSDs, which have already been launched for industrial applications.

SSD vs. HDD Comparison Table:
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower | 5–10x faster |
| Boot Time | 1.5 minutes (Windows 7) | 30 seconds |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Power Consumption | High | Low |
| Heat | More | Less |
| Noise | Audible | Silent |
| Price | Cheaper | More expensive |
| Durability | Vulnerable to shocks | Shock resistant |

Internal vs. External HDD:
- Internal HDD: Installed inside the computer, less prone to damage.
- External HDD: Portable, used for backups or transferring data, but more vulnerable to drops and viruses.
- You can convert internal to external (and vice versa) using an appropriate enclosure.
Q: Which is better, an internal hard drive or an external hard drive for storing files?
A: Generally speaking, an internal hard drive is better, as it is more stable and less prone to falling from frequent movement than an external hard drive. Also, an external hard drive is more prone to falling, and any sudden shutdown can cause data loss.
An external hard drive is used on multiple devices, allowing viruses to spread easily.
Q: Is it possible to convert an external hard drive to an internal one, or an internal one to an external one?
A: Yes, it is possible if you share the same connection type. For example, if your device supports SATA and the external hard drive is SATA, do not convert the hard drive from internal to external or purchase a new external hard drive until you have purchased a case to operate the hard drive.

Common HDD Issues:
Q: How do we know if there is a hard disk failure?
Answer:
When you turn on the computer, it turns on and the screen appears, but stops at a black screen telling you that it did not detect a disk.
Action: Make sure the cable is connected: "Power cable and hard disk cable."
Or when you turn on the computer, a message appears telling you that it did not detect Windows...
Action: If it's not Windows, it may be the hard disk. You should repair it (check the cables) or replace it.
There are two types of hard disk failures:
1- Software failures: These can be fixed using maintenance software.
2- Hardware failures: These are mechanical failures, and can be caused by one of the following:
- Poorly installed data or power cable.
- Power supply unit failure.
- Improper jumper position.
Action: Ensure the cable is properly connected, or replace or replace a suitable cable, or check the jumper position.
To maintain your hard drive:
Before discussing this, we must note that the hard drive is the most important component of your computer... Why?
Because it contains the operating system files and stores your personal information...especially if it's important...
- When you put it in the bag, you should place it gently and secure it with screws so it doesn't move.
- Also, if you want to remove it from the bag and move it somewhere, you should do so gently.
- When the power is cut off and the computer shuts down, let it check the "Blue Screen of Death."

Introduction to Read-Only Memory (ROM):
Homework Tasks
Theoretical Questions
1️⃣ HDD Structure and Operation:
Question: Describe how an HDD stores and retrieves data. What are the key components inside an HDD?
2️⃣ SSD Advantages:
Question: What makes SSDs more efficient and reliable than HDDs? In what scenarios is it preferable to use an SSD?
3️⃣ Internal vs External Drives:
Question: What are the pros and cons of using an external hard drive compared to an internal one?
Practical Tasks
4️⃣ Task: Inspecting Your Drive Type and Connection
📌 Question: Open your PC/laptop (if possible) and take a photo of your internal or external drive. Identify if it’s an HDD or SSD and mention its size and type (SATA, NVMe, etc.).
🔹 Bonus: Record a video tutorial of how to access or identify the drive physically.
5️⃣ Task: Analyze HDD Health or SSD Status
📌 Question: Use CrystalDiskInfo or Windows Disk Management to check your drive’s status and health. Take a screenshot of the information.
🔹 Bonus: Explain key indicators (temperature, health, power-on hours).

Introduction to Read-Only Memory (ROM):
Contest Guidelines:
- Title: SLC S23 Week6 || Computer Repair - HDD & SSD Storage
- Tags: #dynamicdevs-s23w6, #country (e.g., #tunisia), #steemexclusive
- Submission Period:
- Monday, March 24, 2025, 00:00 UTC to Sunday, March 30, 2025, 23:59 UTC
- Eligibility:
- Posts must be #steemexclusive.
- Plagiarism and AI-generated content are strictly prohibited.
- Use original or copyright-free images with proper attribution.

Conclusion:
Mastering the concepts of HDD and SSD technologies, including structure, types, installation methods, and problem diagnosis, is a valuable skill in the digital age. Whether you’re upgrading your laptop, building a desktop, or maintaining storage systems, this knowledge empowers you to make informed and efficient choices.
Best Regards,
Dynamic Devs Team



Here is my submission
https://steemit.com/dynamicdevss23w6/@muhammad-ahmad/slc-s23-week6-or-or-computer-repair-hdd-and-ssd-storage
Your post is manually
rewarded by the Steem-Bingo
STEEM-BINGO, a new game on Steem
Good luck and have fun playing Steem-Bingo!
How to join, read here
Prize pool:
Minimum Guaranteed 45 Steem for each draw
My entry link
https://steemit.com/steem-for-bangladesh/@saifuddinmahmud/slc-s23-week6-or-or-computer-repair-hdd-and-ssd-storage
This is my Entry Link:
https://steemit.com/steem-for-bangladesh/@mahadisalim/slc-s23-week6-or-or-computer-repair-hdd-and-ssd-storage
https://steemit.com/dynamicdevss23w6/@udyliciouz/slc-s23-week6-or-or-computer-repair-hdd-and-ssd-storage
my entry post https://steemit.com/dynamicdevss23w6/@hamzayousafzai/slc-s23-week6-or-or-computer-repair-hdd-and-ssd-storage
https://steemit.com/hive-145157/@sergeyk/slc-s23-week6-or-or-d0c511adbb104