Mastering File Handling in Python and Qt Designer Part 1
Hello everyone! I hope you will be good. Today I am here to participate in the contest of @kouba01 about Mastering File Handling in Python and Qt Designer Part 1. It is really an interesting and knowledgeable contest. There is a lot to explore. If you want to join then:
.png)
The program calculates Mersenne numbers within a specified range using PyQt5
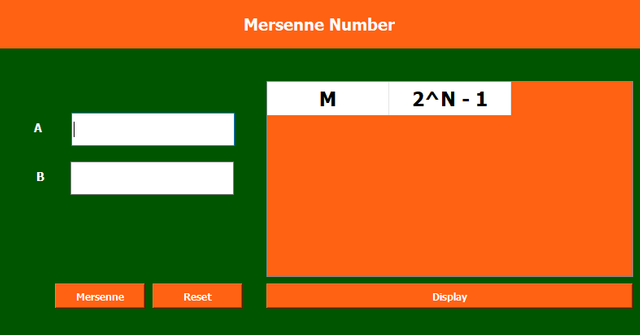
I have used these widgets for the formation of the above GUI:
Label Widgets
- First label is used to display Mersenne Number.
- Then I have used a label for
AandB.
Input Fields
- First input field is to get the input from the user for
A. - The next input field is to get input from the user for
B.
Button
- I have used three
pushButton. - One button is
Mersenne. - The other button is
Reset. - The last button is
Display.
Table Widget
- I have used a
tableWidgetto display the data in the form of the rows and column.
Setting Custom Names
- I have set specific name for each widget used in this user interface to manage the working and functionality in the code.
Helper Functions
is_prime(num)

- Purpose: Determines if a number is prime.
- Logic:
- Numbers ≤ 1 are not prime.
- Loops from
2to the square root of the number, checking divisibility. - If divisible, the number is not prime.
calculate_mersenne_numbers(start, end)

- Purpose: Calculates Mersenne numbers in a given range.
- Logic:
- A Mersenne number has the form
M = 2^n - 1, wherenis prime. - For every prime
n, it calculates2^n - 1. - If the result is within the user-specified range
[start, end], it is added to the list.
- A Mersenne number has the form
- Returns: A list of tuples
(mersenne_number, n).
Main Class: MersenneApp
This class inherits from QMainWindow and implements the core functionality of the GUI.
__init__ Method
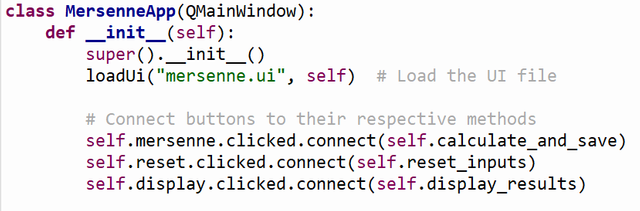
- Purpose: Sets up the application.
- Key Actions:
- Loads the UI layout from
mersenne.ui. - Connects buttons to their respective methods:
mersenne.clicked: Starts calculation and saves results.reset.clicked: Clears inputs and the table.display.clicked: Loads and displays saved results in the table.
- Loads the UI layout from
calculate_and_save Method
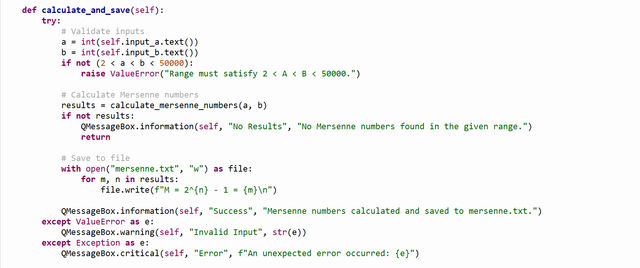
- Purpose: Calculates Mersenne numbers and saves them to a file.
- Key Steps:
- Retrieves user input for the range (
aandb). - Validates that
2 < a < b < 50000. If invalid, shows a warning. - Calls
calculate_mersenne_numbersto get results. - If results exist:
- Saves them to
mersenne.txtin the format:M = 2^n - 1 = mersenne_number. - Shows a success message.
- Saves them to
- If no results exist, shows an informational message.
- Retrieves user input for the range (
- Error Handling:
- Catches invalid input errors (
ValueError). - Handles unexpected errors with a critical message.
- Catches invalid input errors (
display_results Method
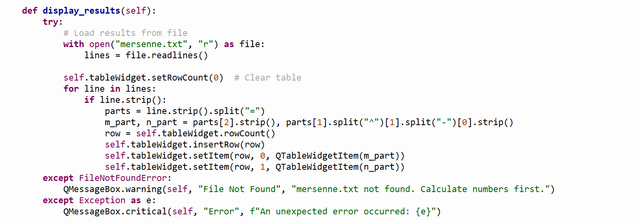
- Purpose: Reads Mersenne numbers from
mersenne.txtand displays them in the table. - Key Steps:
- Reads lines from
mersenne.txt. - Clears the existing rows in the
QTableWidget. - Parses each line to extract the Mersenne number (
M) and the correspondingn. - Inserts these values as rows in the table.
- Reads lines from
- Error Handling:
- Shows a warning if the file does not exist.
- Handles unexpected errors with a critical message.
4. reset_inputs Method

- Purpose: Clears user inputs and the table.
- Key Actions:
- Clears input fields for the range (
input_a,input_b). - Resets the row count of the table widget to 0.
- Clears input fields for the range (
Features of this Application
- Input Validation:
- Ensures
aandbare within the valid range (2 < a < b < 50000).
- Ensures
- Calculation:
- Efficiently calculates Mersenne numbers for prime
n.
- Efficiently calculates Mersenne numbers for prime
- File Operations:
- Saves results to
mersenne.txt. - Reads results for display.
- Saves results to
- GUI Display:
- Dynamically populates a table with Mersenne numbers and their corresponding
n.
- Dynamically populates a table with Mersenne numbers and their corresponding
- Reset Functionality:
- Clears all user inputs and output data.
Live Working
Errors Validation:
 |  |
|---|---|
| When the field is empty | When the range is not satisfied |

This
mersenne.txt file is saving the data.
This program calculates the prime factors of a given number and saves the results in a text file named factors.txt
factors.txt 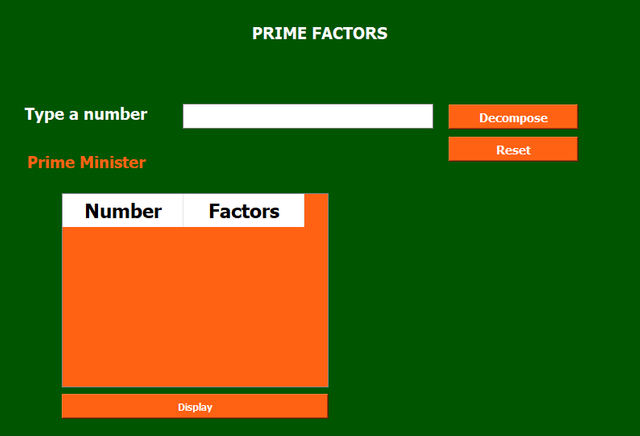
I have used these widgets for the formation of the above GUI:
Label Widgets
- First label is used to display Prime Factors.
- Then I have used a label for
Type a numberandPrime Factors.
Input Fields
- There is one input field to get the input from the user for
type a number.
Button
- I have used three
pushButton. - One button is
Decompose. - The other button is
Reset. - The last button is
Display.
Table Widget
- I have used a
tableWidgetto display the data in the form of the rows and column.
Setting Custom Names
- I have set specific name for each widget used in this user interface to manage the working and functionality in the code.
This application calculates the prime factors of a given number, stores the results in a file (factors.txt) and displays them in a GUI table. Below is a detailed breakdown of the code:
Helper Function
prime_factors(n)
- Purpose: Computes the prime factors of a number
n. - Logic:
- Initial Setup: Starts with
divisor = 2(the smallest prime). - Looping Process:
- While
n > 1, check ifnis divisible bydivisor. - If divisible, add
divisorto thefactorslist and reducenby dividing it bydivisor. - If
nis no longer divisible bydivisor, increment the divisor by 1 and repeat the process.
- While
- Return: The list
factorscontains the prime factors ofn.
- Initial Setup: Starts with
Main Class: PrimeFactorsApp
This class inherits from QMainWindow and implements the main functionality of the GUI.
1. __init__ Method

- Purpose: Initializes the main window and sets up the user interface.
- Key Actions:
- Loads the UI file (
primefactors.ui) usingloadUi. - Connects button clicks to their respective methods:
decompose.clicked.connect(self.calculate_factors): Initiates factor calculation when clicked.reset.clicked.connect(self.reset_inputs): Clears the input field and table when clicked.display.clicked.connect(self.display_factors): Displays the calculated factors from the file.
- Loads the UI file (
2. calculate_factors Method
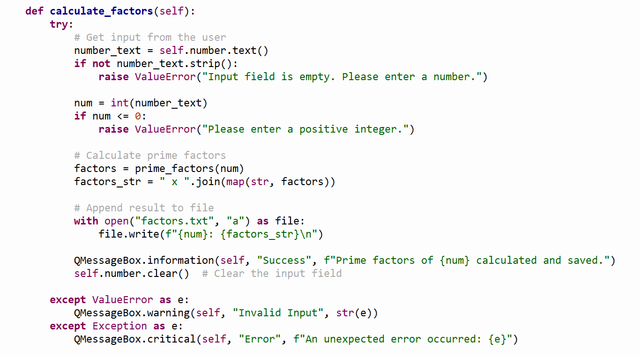
- Purpose: Calculates the prime factors of a user input and saves the result to a file.
- Key Actions:
- Retrieves the user input (number) from the input field (
self.number). - Validates the input:
- Checks if the input is not empty and is a valid positive integer.
- Calls the
prime_factors()function to compute the factors. - Formats the factors into a string (
factors_str). - Appends the result (number and its prime factors) to
factors.txtin the format:number: prime_factors. - Displays a success message to the user (
QMessageBox.information). - Clears the input field after the calculation.
- Retrieves the user input (number) from the input field (
- Error Handling:
- Shows a warning if the input is invalid (e.g., empty or non-positive).
- Catches any other unexpected errors with a critical message.
3. reset_inputs Method
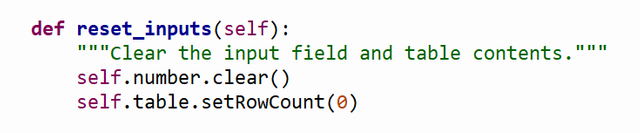
- Purpose: Clears the input field and resets the table widget.
- Key Actions:
- Clears the input field (
self.number.clear()). - Resets the table row count to 0 (
self.table.setRowCount(0)), effectively clearing the table.
- Clears the input field (
4. display_factors Method
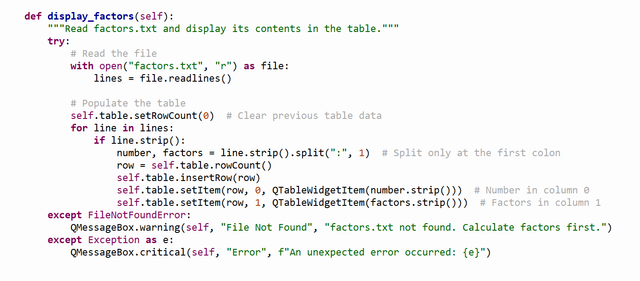
- Purpose: Reads the contents of
factors.txtand displays the results in the table. - Key Actions:
- Opens and reads the
factors.txtfile. - Clears any existing data in the table (
self.table.setRowCount(0)). - Iterates over each line in the file:
- Splits the line at the first colon (
:) to separate the number from its prime factors. - Adds the number and factors to a new row in the table.
- Splits the line at the first colon (
- If the file is not found, displays a warning message (
QMessageBox.warning). - Catches any unexpected errors with a critical message.
- Opens and reads the
Features of Application
- Input Validation:
- Ensures that the input is a positive integer.
- Prime Factor Calculation:
- Efficiently calculates the prime factors using trial division.
- File Operations:
- Appends results to
factors.txt. - Reads and displays saved results from the file.
- Appends results to
- GUI Table Display:
- Dynamically populates a table with calculated prime factors.
- Reset Functionality:
- Clears inputs and output data.
User Flow
- Input: User enters a number in the input field.
- Calculate: User clicks the "Decompose" button to calculate prime factors.
- Display: Results are saved to a file and shown in a table when the "Display" button is clicked.
- Reset: User can clear the input and reset the table.
Live Working
Errors Validation:
 |
|---|
When the input field is empty then this error is displayed.
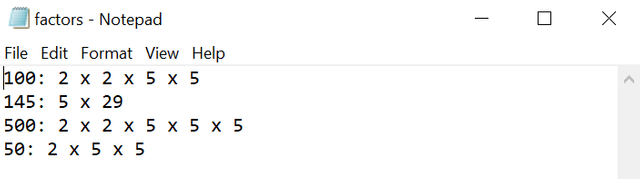
Here you can see the text filefactors.txt where the calculated prime factors of the number are being saved and then the application can fetch and display these prime factors.
This program is designed to validate 13-digit codes based on specific criteria and manage them using a file named Codes.txt
Codes.txt 
I have used these widgets for the formation of the above GUI:
Label Widgets
- First label is used to display Recharge Codes.
- Then I have used a label for
Enter your Code.
Input Fields
- There is one input field to get the input from the user for
Enter your Code. - And another field to display the status of the code.
- At the end there is a field to display the output results.
Button
- I have used four
pushButton. - One button is
Verify. - The other button is
Reset. - The next button is
Close. - The last button is
Display Codes.
Radio Button
- I have used a
radioButtonto display the codes in the descending order.
Setting Custom Names
- I have set specific name for each widget used in this user interface to manage the working and functionality in the code.
This is a PyQt5-based application that verifies, saves, displays and validates codes. The codes are validated based on a specific set of criteria and are stored in a file (Codes.txt). The application also allows users to view the codes in descending order. The user can reset input fields and handle code verification and saving.
Constants
FILE_NAME: Specifies the name of the file where codes will be stored (Codes.txt).
Helper Functions
is_prime(number):

- Purpose: Checks if a given number is prime.
- Logic:
- If the number is less than 2, it's not prime.
- It checks divisibility from 2 up to the square root of the number (
int(number ** 0.5) + 1), ensuring efficient prime checking.
validate_code(code):

- Purpose: Validates the code input based on three criteria:
- The code must be exactly 13 digits long.
- The first three digits must be prime.
- The middle five digits, when converted to binary, must contain more than eight zeros.
- The last five digits must be divisible by the first three digits.
- Validation Logic:
- First three digits: Checks if the number formed by the first three digits is prime using
is_prime(). - Middle five digits: Converts the middle five digits to binary and checks if there are more than 8 zeros in the binary representation.
- Last five digits: Checks if the last five digits are divisible by the first three digits.
- First three digits: Checks if the number formed by the first three digits is prime using
- Purpose: Validates the code input based on three criteria:
load_codes():

- Purpose: Loads the stored codes from
Codes.txt. - Logic: Reads the file line by line and returns the list of codes.
- Purpose: Loads the stored codes from
save_code(code):

- Purpose: Saves a valid code to
Codes.txt. - Logic: Appends the new code to the file.
- Purpose: Saves a valid code to
Main Class: RechargeApp
The RechargeApp class handles the core logic and interaction between the PyQt5 interface and the backend functions.
__init__(self):

- Purpose: Initializes the application and the UI.
- Logic:
- Loads the UI (
recharge.ui) usinguic.loadUi. - Connects UI elements (buttons, radio buttons) to their respective functions using
.clicked.connector.isChecked().
- Loads the UI (
verify_code(self):

- Purpose: Verifies the code entered by the user.
- Logic:
- Retrieves the code from the input field (
self.window.code.text()). - Validates the code using the
validate_code()function. - If valid, checks if the code is already in use by searching in the existing codes.
- If the code isn't already used, it is saved to
Codes.txt. - Displays appropriate messages in the UI (
self.window.warning.setTextorself.window.output.setText).
- Retrieves the code from the input field (
display_codes(self):

- Purpose: Displays all the stored codes in either ascending or descending order based on the user's preference.
- Logic:
- Loads all stored codes using
load_codes(). - Sorts the codes either in ascending or descending order based on the
desorderradio button. - Displays the sorted codes in the output area.
- If no codes are found, a message box is shown with the text "No codes stored."
- Loads all stored codes using
reset_fields(self):

- Purpose: Clears all the input and output fields.
- Logic: Clears the text fields for code input, warning messages, and output area.
run(self):

- Purpose: Starts and runs the application.
- Logic: Shows the main window and starts the PyQt application event loop (
self.app.exec()).
Main Application Flow
Code Verification:
- The user enters a code and clicks the Verify button.
- The code is validated based on the criteria (prime, binary zeros, divisibility).
- If valid, it checks if the code is already in use. If not, it is saved.
Display Codes:
- The user clicks Display to view all the stored codes, sorted by the selected order (ascending or descending).
Reset Fields:
- The user can click Reset to clear all fields (input and output).
Close Application:
- The user can click Close to exit the application.
Features of Application
- Code Validation: Ensures that entered codes meet specific criteria.
- Code Storage: Codes are stored in a text file (
Codes.txt) for later access. - Sorting: Users can choose to view codes in ascending or descending order.
- UI Interaction: Allows users to verify, display, and reset codes with user-friendly feedback.

Here you can see the text filecodes.txt where the codes are being saved and then the application can fetch and display these codes.
This program identifies Smith numbers within a user-defined range through a graphical user interface.
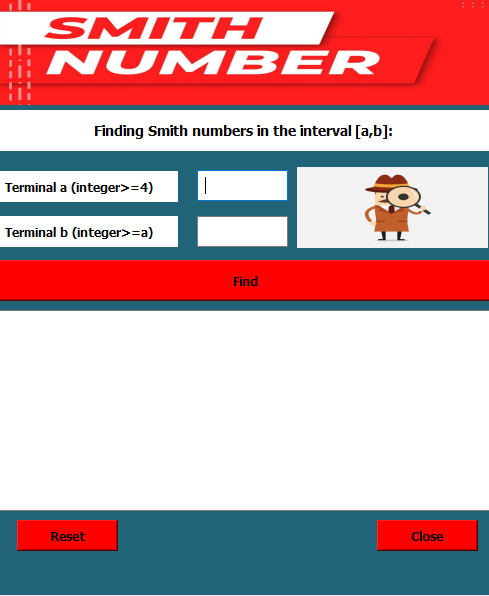
I have used these widgets for the formation of the above GUI:
Label Widgets
- First label is used to display header_image.
- Then I have used a label for
Finding Smith numbers in the interval [a,b];as a hint for the user. - Then there is a label for
Terminal a (integer>=4)andTerminal b (integer>=a).
Input Fields
- There are total of three input fields and two are to get the input from the user for
Terminal a (integer>=4)andTerminal b (integer>=a)respectively. - The last input field has been used to display the dynamic output results.
Button
- I have used three
pushButton. - One button is
Find. - The other button is
Reset. - The last button is
Close.
Setting Custom Names
- I have set specific name for each widget used in this user interface to manage the working and functionality in the code.
The Python script whivh I have used is a PyQt5 application that lets users find Smith numbers within a specified range. Here's an explanation of the code:

- Constants:
FILE_NAME: The name of the file where Smith numbers will be saved.HEADER_IMAGE_PATHandSIDE_IMAGE_PATH: File paths for images displayed in the UI.
Mathematical Helper Functions
These functions implement the logic for Smith numbers:
is_prime(n):

- Checks if a number
nis prime. - Prime numbers are ignored when finding Smith numbers.
- Checks if a number
prime_factors(n):

- Finds and returns all prime factors of
n.
- Finds and returns all prime factors of
sum_of_digits(n):

- Computes the sum of the digits of a number
n. - Used to compare the sum of a number's digits with the sum of the digits of its prime factors.
- Computes the sum of the digits of a number
is_smith_number(n):

- Determines if
nis a Smith number. - Smith numbers are composite numbers where the sum of their digits equals the sum of the digits of their prime factors.
- Determines if
find_smith_numbers(start, end):

- Returns a list of Smith numbers within the range
[start, end].
- Returns a list of Smith numbers within the range
SmithNumberApp Class
This class implements the PyQt5 application logic:
Initialization:

- Creates the application (
QApplication) and loads the user interface from thesmithnumbers.uifile. - Connects buttons in the UI (
find,reset,close_button) to their corresponding logic.
- Creates the application (
load_imagesMethod:

- Loads images for the header and side sections of the UI using
QPixmap. - Scales the images to fit their respective labels.
- Displays warnings if the images are not found.
- Loads images for the header and side sections of the UI using
process_rangeMethod:

- Reads user input for the range
[a, b]from text fields. - Validates the range:
amust be at least 4 (Smith numbers start at 4).bmust be greater than or equal toa.
- Finds Smith numbers in the range using
find_smith_numbers. - Saves the results to
SmithNumbers.txt. - Displays the Smith numbers in the
outputfield or a message if none are found.
- Reads user input for the range
reset_fieldsMethod:

- Clears all input and output fields in the UI.
runMethod:

- Displays the main window and starts the application loop.
Main Execution
- The program instantiates
SmithNumberAppand calls itsrunmethod to start the application.
Example Usage
- User enters a range such as
a=4andb=100. - The application checks the range and finds all Smith numbers between 4 and 100.
- Results are displayed in the
outputfield and saved toSmithNumbers.txt. - Users can reset the input fields using the "Reset" button or close the app using the "Close" button.
