MXC FRAMEWORK REVIEWS-(UNLEASHING A MASSIVE IoT GLOBAL DATA NETWORK IN 40+ COUNTRIES)
Good day ladies and gentle men all over the world, and I also extend my greetings to all my dear readers across the globe. as you all know's, that I always carry you along with any good crypto related project through this wonderful CRYPTOCURRENCY ARENA BLOG.
A BRIEF PRESENTATION: A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data (generally represented as a merkle tree root hash)
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is "an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way For use as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is typically managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for inter-node communication and validating new blocks. Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority. Although blockchain records are not unalterable, blockchains may be considered secure by design and exemplify a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance. Decentralized consensus has therefore been claimed with a blockchain.
Blockchain was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 to serve as the public transaction ledger of the cryptocurrency bitcoin. The invention of the blockchain for bitcoin made it the first digital currency to solve the double-spending problem without the need of a trusted authority or central server. The bitcoin design has inspired other applications, and blockchains which are readable by the public are widely used by cryptocurrencies. Private blockchains have been proposed for business use. Sources such as the Computerworld called the marketing of such blockchains without a proper security model.
The first work on a cryptographically secured chain of blocks was described in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. They wanted to implement a system where document timestamps could not be tampered with. In 1992, Bayer, Haber and Stornetta incorporated Merkle trees to the design, which improved its efficiency by allowing several document certificates to be collected into one block.
The first blockchain was conceptualized by a person (or group of people) known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Nakamoto improved the design in an important way using a Hashcash-like method to add blocks to the chain without requiring them to be signed by a trusted party.[6] The design was implemented the following year by Nakamoto as a core component of the cryptocurrency bitcoin, where it serves as the public ledger for all transactions on the network.
In August 2014, the bitcoin blockchain file size, containing records of all transactions that have occurred on the network, reached 20 GB (gigabytes). In January 2015, the size had grown to almost 30 GB, and from January 2016 to January 2017, the bitcoin blockchain grew from 50 GB to 100 GB in size.
The words block and chain were used separately in Satoshi Nakamoto's original paper, but were eventually popularized as a single word, blockchain, by 2016. The term blockchain 2.0 refers to new applications of the distributed blockchain database, first emerging in 2014. The Economist described one implementation of this second-generation programmable blockchain as coming with "a programming language that allows users to write more sophisticated smart contracts, thus creating invoices that pay themselves when a shipment arrives or share certificates which automatically send their owners dividends if profits reach a certain level.
As of 2016, blockchain 2.0 implementations continue to require an off-chain oracle to access any "external data or events based on time or market conditions that need to interact with the blockchain.
IBM opened a blockchain innovation research center in Singapore in July 2016. A working group for the World Economic Forum met in November 2016 to discuss the development of governance models related to blockchain.
According to Accenture, an application of the diffusion of innovations theory suggests that blockchains attained a 13.5% adoption rate within financial services in 2016, therefore reaching the early adopters phase. Industry trade groups joined to create the Global Blockchain Forum in 2016, an initiative of the Chamber of Digital Commerce.
In May 2018, Gartner found that only 1% of CIOs indicated any kind of blockchain adoption within their organisations, and only 8% of CIOs were in the short-term ‘planning or [looking at] active experimentation with blockchain.
According to the purpose or fixed design of this article, Today! We will be discussing or analysing about a particular amazing project called: MXC
WHAT IS MXC?
MXC is the pioneer IoT Cryptocurrency. Using the MXProtocol, redefined the world of IoT data, enabling secure, vastly scalable, lightning fast transactions.
The MXC vision is to introduce a systematic process to both simplify and increase IoT data transactions. The decentralized infrastructure upon which MXC’s system is based is the future of Low Power Wide Access Network (LPWAN) and the Machine eXchange Protocol (MXProtocol). Utilizing this solid device network foundation, MXC is introducing a unique coin offering, Machine eXchange Coin (MXC), which allows for increased data transactions and an idiosyncratic data flow monetization within the mammoth data market. MXProtocol places a keen focus on reducing collision between networks, constructing an inter-chain data market, developing a market for network coverage and introducing an independent Quality of Services (QoS) framework for both data providers and receivers. Individual network users, corporations and enterprises can all participate in the construction of decentralized, ubiquitous and secure LPWAN. Simply by connecting “anything” to the network, adopters will be able to profit and trade MXC
ABOIT MXC
Machine eXchange Coin (MXC) is an IoT cryptocurrency. The MXC is based on a decentralized infrastructure employing Low Power Wide Access Network (LPWAN) and the Machine eXchange Protocol (MXProtocol). MXC is supposed to allow for increased data transactions and monetization of idiosyncratic data flow.
The MXProtocol will facilitate micro-payments within the LPWAN infrastructure that will be traded from third party sensors/end devices, ensuring secure data transmission. The MXP protocol is designed to extend the device data economy and promote decentralized sharing economy.
Due to a marked increase in the number of devices with internet connectivity and the growing popularity of the Internet of Things (IoT), an increasing amount of data is being generated worldwide. This upsurge is too much for the traditional networks in place at the moment: WiFi has a limited range of ~100 meters and 3G/4G networks consume too much power.
To tackle this problem, MXC proposes a new kind of network. They call it the Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) and it will focus on the communication that takes place between machine and the data they generate. The LPWAN should allow individuals as well as big corporations take advantage of the benefits that the IoT offers; the network will have a 20km data reach from just a single gateway while providing over 60,000 connection points (about 10,000 for 3G and 4G). This data reach will be for a single network cell at a low cost, with a transaction time of less than 5 seconds, and with very low battery consumption.
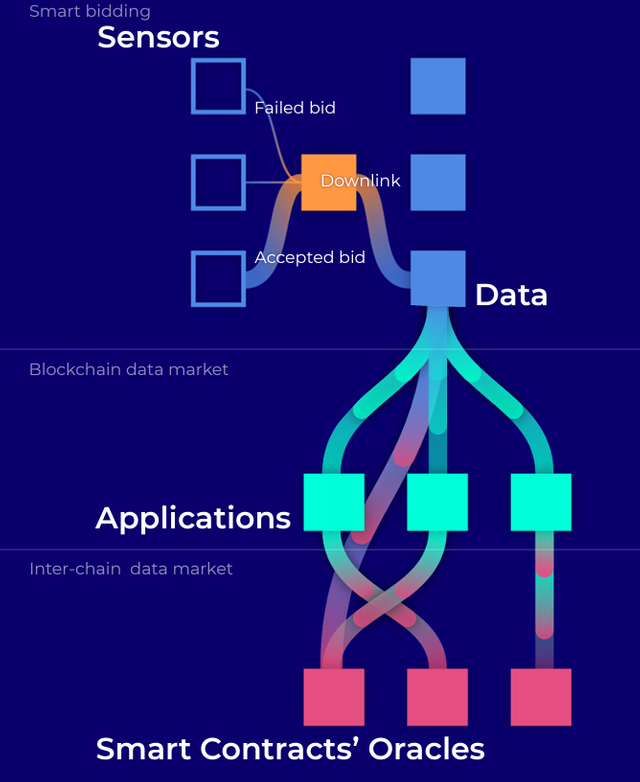
The project believes that this will make it easy for devices to connect and interact with one another. Furthermore, everyone can be a LPWAN provider, collect data through the network’s sensors using their gateway (or someone else’s gateway), and then sell the data. The MXC platform will have 8 downlink channels for the confirmation of sensor data, and ecosystem participants can bid on the channels. Allocation of system resources will be handled by system known as “Smart Bidding”, and it will award resources to the highest bidder.
FOR MORE INFORMATION ABOUT MXC PROJECT, PLEASE! TAKE A LOOK OF THIS BRIEF EXPLANATION VIDEO >>>
Additionally, an Anti-Collision Coordinator on the platform will handle payments between networks using MXC token and coordinate the uplink and downlink status between the networks. To allow other networks e.g. Ethereum or Rootstock use LPWAN data that was captured by devices or sensors, MXC plans to create an “Inter-Chain Data Market”. Other tokens will be accepted in the market, enabling users from other blockchains buy data without having to use MXC tokens.
The advantage that MXC holds over traditional orcales is that MXC-generated data can be backtracked on-chain. This offers more security along with the option of more extensive data verification. All devices/sensors on the MXC platform will have individual wallet addresses and users have to pay, in MXC, to use the network.
The wallet is also required to receive payments if your device offers services to the network.
THE KEY FEATURES OF MXC
MXC Powers efficient Machine to Machine Communication without the need for human interaction. Welcome to the Next Generation of IoT!
LPWAN 24/7: Machine to machine (M2M) communication ensures that LPWAN sensors can reliably transmit data 24/7. LPWAN technologies using the MXProtocol can exchange MXC payments and data without human interaction; providing the opportunity to automate standard processes. M2M communication is a critical element in the design of the Anti-Collision Coordinator, and the Smart Bidding ability included in the MXProtocol (Machine eXchange Protocol).
M2M and the Anti-Collision Coordinator: As the use of LPWAN grows, so will the risk of data collision. MXC is approaching this proactively by including the Anti-Collision Coordinator with the MXProtocol. Radio frequencies function much like train tracks. Only one train can travel over the same track at the same time. If two trains attempt to use the same track, they collide, causing a loss of data. The Anti-Collision coordinator ensures that data using the same frequency (or track) isn’t sent at the same time; thereby reducing collision and increasing the reliability of the LPWAN network as a whole.
Locating "out-of-range" assets with M2M transactions: Sensors used in mobile devices (bikes, cars or other resources) may, at some point, leave the radius covered the owner’s gateway. In this case, that device is lost and cannot be recovered. Machine-to-machine communication enables the device to communicate with another LPWAN gateway to send its data.
LPWAN technology is built for people. Using the MXC Shared Economy we're enabling everyone to earn MXC, join the MXC movement
Introducing Smart Bidding: MXProtocol navigates the payment process using Smart Bidding. Owners of LPWAN sensors can program the sensor to bid for network access based on the reliability of the network they require. For high priority sensors, for example, those that open doors, a higher quality network is needed, and therefore they are likely to pay more MXC for consistent network access.
Sensors measuring the trash level in public bins represent low priority sensors and do not require consistent network access. Therefore they are likely to bid less MXC for access. IoT payment systems today require some form of human interaction; whether it is to measure usage and send a bill, or to pay that bill. This entire bidding and payment process is managed through machine-to-machine (M2M) transactions.
Sharing Economy: The sharing economy enabled by MXC is the foundation for a decentralized wireless network. By combining it with the power of the LPWAN, the MXC Foundation places the future of wireless IoT transmissions, and the related profits, firmly in the hands of the individuals and companies building an MXProtocol enabled LPWAN network. This sharing economy is expanded with the interchain data market to include ownership and sale of data.
MXC inspires more data trading, more often, from more devices. Our proprietary MXProtocol and Smart Bidding make data a whole lot more intuitive
Data ownership and trade: By adding the Inter-Chain Data Market to the sharing economy generated by an LPWAN shared network, the MXC Foundation enables a shared data economy where individuals and companies can own and sell the data they collect.
Genuine Data: When evaluating the authenticity of data sourced with an MXProtocol enabled sensor, the purchaser of this data can be confident that the data itself is genuine and untampered. This data can then be held as an asset or sold. Data owners may also provide API’s which enable companies to purchase a live data-stream feeding directly into an application or website.
MXProtocol - One of Its Kind, Many of Your Solutions
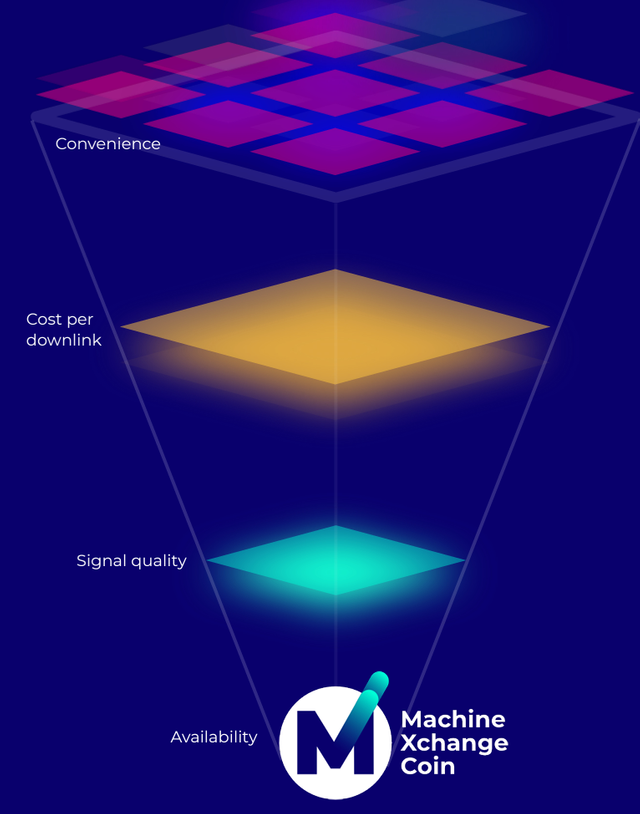
MXProtocol Solutions for Everyday Challenges: The MXC “Machine eXchange Protocol” facilitates the uninterrupted exchange of information between connected devices. The intrinsic blockchain based MXC Protocol ensures devices connect to the internet using the most convenient LPWAN Gateway lying in range. This “convenience” is determined using essential factors:
Cost per downlink
Signal Quality
Availability
MXC Influential Algorithmic Factors
MXProtocol - Smart Bidding, Inter-Chain Data Market: Street lights, garbage sensors send a lot of packets in a day, which jam the free licensed bands. A door lock needs to be unlocked in few seconds.
Smart Bidding solves the problem by doing the network resource auction, the highest bid takes the link resource.
Platforms like Ethereum, Rootstock are quite data hungry, and they need Oracles to feed to smart contracts.
Data market is a protocol for different blockchains to purchase data from MXC using their own token.
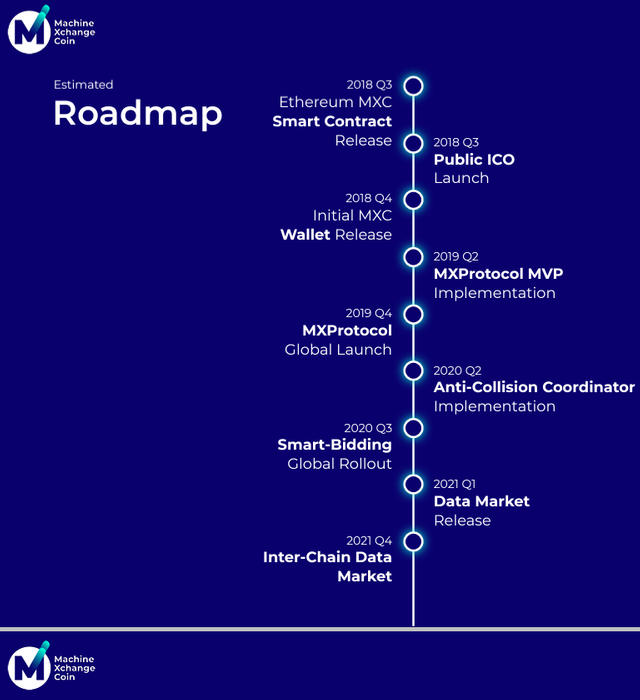
MXC PROJECT ROADMAP
MXC TEAM BOARD
MXC PROJECT PARTNERS
MXC ICO ANALYSIS
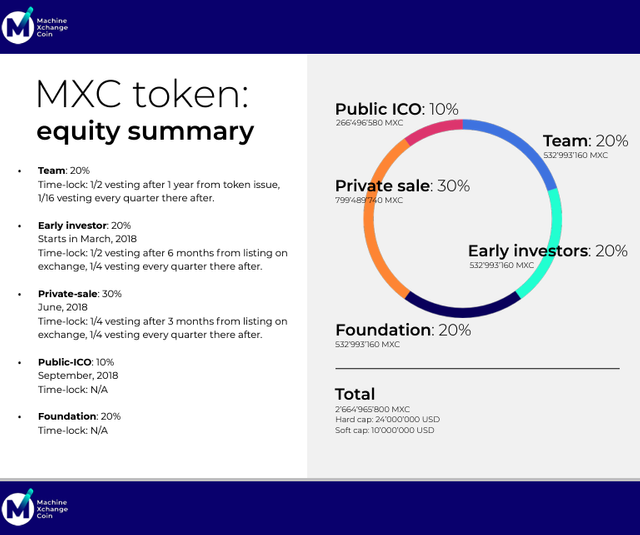
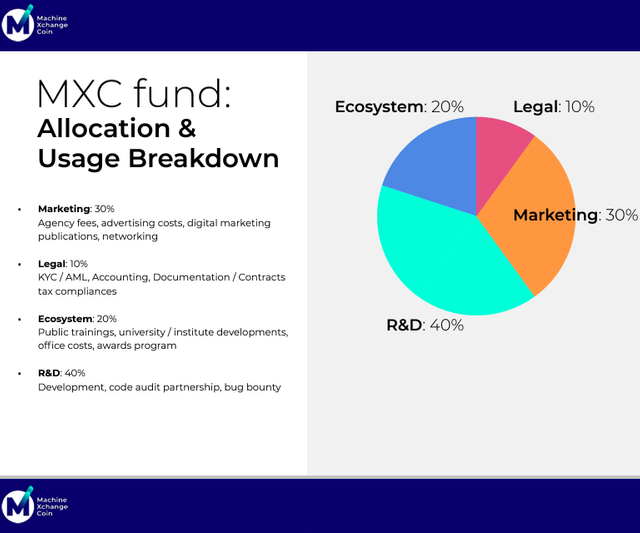
There will be a total of 2,664,965,800 MXC tokens and the project aims to raise $24 million for 40% of the token total (30% will be sold during a private sale and 10% will sold during the crowdsale). The remaining 60% will be distributed thus: 20% will go to the team, another 20% will go to the project’s foundation, and the final 20% will be given to early investors.
Participants in the private sale will only receive 25% of their tokens after MXC has been listed on an exchange. The rest is locked, to be released in quarterly installments of 25%.
The team tokens will also be locked. 50% of the tokens will be released after a year, and the rest will be released in quarterly installments of 1/16 (3.125%).
For early investors: 50% of their tokens will be released 6 months after listing on an exchange and 12.5% will be released quarterly afterwards.
As a result of these locks, only 30% of the total supply will be available after the crowdsale. However, there is a likelihood that not all the tokens earmarked for the MXC Foundation will be put to use immediately, further reducing the available supply.
Price Per Token: During the ICO, 1 MXC = 0.015$. Private sale participants got a 25% bonus.
MXC TOKEN ANALYSIS
MXC token token was created in according with ERC20 wallet standard
Token Symbol <<>> MXC
Token type <<>> ERC20
ICO Token Price <<>> 1 MXC = 0.015 USD
Founding Goal <<>> 24,000,000 USD
Total Tokens <<>> 2,664,965,800
Available for Token Sale <<>> 40%
Accepts <<>> ETH
CONCLUSION
For more or further details, please! Kindly follow the links below:
★WEBSITE: https://mxc.news/2ylqCDx
★FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/MXCfoundation
★TWITTER: https://twitter.com/MXCfoundation
★YOUTUBE: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC1Jw-hJK5hPFntWuuYZNIQA
★TELEGRAM: https://t.me/mxcfoundation
★ECONOMIC WHITE PAPER: https://www.mxc.org/hubfs/WP/MXC_economic_whitepaper.pdf?t=1539692263852
★TECHNICAL WHITEPAPER: https://www.mxc.org/hubfs/WP/MXC_technical_whitepaper.pdf?t=1539692263852
Resteem, Up vote, & Send a recommendation to a friend, thanks! for giving your time.
AUTHOR: Dprince2281