Collecting rare disease data and breaking the data monopoly, this company has high technology and human touch
“There are data everywhere,” but the question facing the industry is what economic models can encourage users to share data and how to find data for organizations that need it urgently. For example, how can medical institutions efficiently find genetic data, and how do patients who hold critical data share data safely and reliably?
Today, Xiaoxun’s Silicon Valley startup DxChain wants to solve the above mentioned problems with blockchain + big data. How to solve it? This will also be heard by DxChain's two co-founders, Wei and Allan.
Is your data “absolutely private” or “relatively open”?
Wei's idea of co-founding DxChain was inseparable from his work experience: Before starting DxChain, Wei did blockchain research at AT&T and then did big data at Hortonworks.

(Left Wei Wei, co-founder and chief scientist of DxChain; right is Allan Zhang, co-founder of DxChain)
At that time, Wei found that many of their customers—such as Wal-Mart, Sears, and other retail stores—have a lot of data, but they don't know how to find valuable information from the data, such as what kind of goods are the most profitable, how to Different people sell different goods and so on.
This involves a collection of data, cleanup, and a complete set of processes for calculation and analysis. For most companies, this is a big burden. Therefore, the establishment of a platform to provide this whole set of services at a low price is undoubtedly promising, and the emergence of blockchain technology provides a lever.
DxChain is to use the blockchain to build this set of data collection, mining, analysis and the conclusion of useful commercial conclusions, and the core behind this is the storage and calculation on the blockchain.
Wei tells the little explorer, which is why DxChain gave this name to himself: D is the first letter of "Data" in English, x is multiplication, DxChain combines data with blockchain technology to amplify data. value.
If the value of the data is divided into four steps: “data collection, cleanup, analysis, and conclusion”, the first step is to collect data and face privacy issues.
Data privacy issues have already occurred in the United States in serious accidents: Facebook's stock price fell 20% last week, still a rebound in privacy issues that broke out at the beginning of the year.
The current status of privacy issues is that all the data is in the black box of the big Internet companies. As for the use of the data, and how to use it, we don’t know anything about it. This feeling is certainly not very good. If we go to the other extreme, we can protect our data with the method of "no one can see, no one knows". Doesn't it work?

Let us take the US medical field as an example. The US Medical Sector has the Medical Electronic Exchange Act (HIPAA), which emphasizes the protection of medical data for each patient. The specific circumstances and medical files of a patient can only be seen by the hospitals and insurance companies under the protection of this bill, and no one else can see them.
Protecting personal medical privacy is of course important. If a research institution wants to use this data to develop a new drug, it will be smothered by this “bronze wall” unless the institution receives your written permission from each patient involved in the study.
An important issue is that from a data perspective, individual patient information does not have value, and the collection of patient information is valuable. Is there a platform that allows patients to share data while protecting patient privacy after patient consent, and this platform can bring together thousands of patients and gather data for research value?
DxChain hopes to use the decentralization and invariance of the blockchain to protect user privacy, allowing users to know their own data while sharing their data, and the organization can gain a lot of user data through these platforms. Research bottlenecks.
Data privacy protection on the blockchain, the industry has adopted a variety of practices, such as Homomorphic encryption, Multi-Party Computation, etc., all through the encryption to protect privacy, SGX is also common. This is encrypted by hardware.
DxChain uses a more practical solution - encrypting critical data information for privacy protection, and behind this is a powerful computing power for data, "because we can do fine-grained operations on data, data When entering the chain, there are structures. For example, the data forms a table, and one column is the name of the person. We encrypt the key information of the name of the person, but other information is disclosed, instead of encrypting the entire file. This is called the data model. Supported data encryption," Wei said.
Data collection: breaking the data monopoly
Solving the problem of data encryption is to let the users sharing the data have no worries about "privacy", and the blockchain is likely to be a lever to incite the data ownership revolution.
An indisputable fact is that most of the current data is monopolized by Internet giants Google and Facebook. These giants use the data to earn profits after they obtain user data, but this is unreasonable. For example, you know:
The air conditioning system in the United States is very complicated, and the maintenance is expensive and time consuming. It takes ten days and a half to make an appointment. If the consumer air conditioner is broken, look for a home appliance store, a department store, where to buy and where to repair. It's not like looking for a manufacturer like China, and it's all paid for.

Figure from the network, copyright belongs to the original author
The current practice is that the air conditioner manufacturer collects the temperature of the air conditioner in the user's home, and finds the air conditioner that may be bad in advance. Then they sell the information to the home appliance store, department store, etc., which is responsible for air-conditioning maintenance. The latter then gives this information to Consumers have targeted and selective calls, and many consumers will say, "Oh, it’s awesome! My air conditioner is really a problem!"
This model is great, but if you think about it, it will be a bit strange: the data is obtained by collecting consumer information, but the last one is still the consumer. Is the consumer's information used so freely?
Under the assumption of DxChain, consumers in the future will have the option to put their information on the chain. If a third party needs to use this information as a raw material for analysis – whether it is an air conditioner manufacturer or a climate research organization – it can be paid for by the data producer (in this case, the air-conditioned person at home). In this way, consumers can profit by sharing their own data.
Let's talk about the example of DxChain that was just mentioned in the medical field.

In the medical field, there is no shortage of information about common diseases such as colds and fevers, so there are also many corresponding drugs. But for rare patients, it is not so lucky: the fragmentation and lack of information has made it difficult to develop drugs. Because of the lack of personal information, drug research and development institutions had to sign contracts with hospitals and universities, collect information, and the process was long and delayed, and patients were treated.
However, if there is a platform that allows patients to put their own illnesses on the top, drug research and development institutions can directly purchase this information, and the patient's disease will be cured. The patient will be able to sell data through the platform. It is very meaningful to benefit from helping them raise more funds to cure diseases in the current expensive medical conditions in the United States.
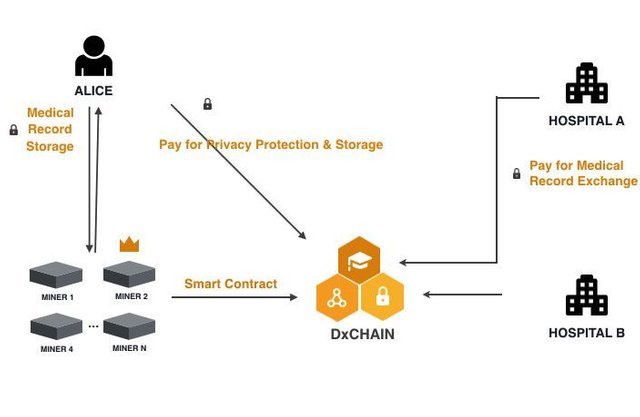
DxChain wants to be this platform.
Storage and calculation, one can not be less
To become a platform, the core problem behind it needs to solve the two problems of storage and calculation of data on the blockchain.
DxChain is a decentralized big data storage and computing network that is an open public chain that applies the decentralization of blockchain to storage and computing.
What is storage and computing in the current blockchain world?
Let me talk about storage first.
We all know that Bitcoin and Ethereum have very limited computing and data storage capabilities, but the blockchain field is growing rapidly, and soon there will be IPFS, a “decentralized, distributed file storage system”.
However, IPFS is a file system without a chain, and lacks an incentive mechanism. That is to say, everyone provides information to see the character and look at the mood. IPFS is a bit like the blockchain version of "BitTorrent." Everyone wants seeds, but no one wants to make seeds. To make a seed requires both bandwidth and hard disk. In addition to getting a "good landlord's life," what other incentives are there?
So some people say: Then add a blockchain to IPFS, there is no incentive mechanism? Filecoin was born, but Filecoin is currently slow to progress.
Finish the storage, then calculate.
Blockchain project Dfinity is to solve the computational problem of blockchain. Dfinity is an infinitely scalable intelligent distributed cloud computing system and third-generation blockchain, and is highly compatible with existing Ethereum applications. It has great potential and is expected, but Dfinity has not been able to solve the problem of where data comes from.
DxChain thinks that storage and computing can't be separated, so DxChain wants to combine the two and the data. Of course, this is not to say that "putting Dfinity and Filecoin" together can solve the problem. The blockchain is stored again. Calculating again is a great challenge, which requires innovation from the bottom of the system.
DxChain believes that it is difficult to meet the storage, computing and privacy requirements of data at the same time with a single backbone. Therefore, DxChain draws on the idea of multiple chains of lightning network, adds two side chains of storage chain and calculation chain, so that the main chain is only responsible for running intelligent contracts, managing storage and computing side chains, and the two side chains perform their duties. Responsible for storage and calculation, DxChain refers to this system architecture as "three-chain integration."

In addition, DxChain draws on Hadoop's ideas.
Over the past decade, Hadoop has solved the problem of distributed storage of data within an organization and a company, but how to achieve trust between different organizations and participants to achieve distributed storage, Hadoop can not solve, but the blockchain provides The perfect solution.
Therefore, DxChain combines the technical advantages of Hadoop with the unique mechanisms of the blockchain to solve the problem of distributed storage and computing in the central environment. DxChain hopes to make data processing more convenient and efficient in this way.
From a technical point of view, DxChain has three major innovations:
● The consensus mechanism under the calculation framework adopts the mechanism of “Verification game + Provable Data Computation (PDC)”, in which Verification game guarantees the verifiability of the calculation process, and PDC guarantees the verifiability of the calculation result;
● DxChain's data storage consensus mechanism uses the "Proof of Spacetime (PoSt) + Provable Data Possession (PDP)" mechanism to verify that the completion of the continuous provision of storage;
● DxChain's data model is built on top of storage, and defines the data. The data becomes valuable knowledge, and data calculation becomes convenient. In addition, the data model also helps to implement data model-based encryption and Differential-privacy two privacy protection mechanisms.
Next stop: Value Internet
DxChain hopes to provide a platform: designed to be connected by countless personal computers or specially designed mining machines, which can achieve low cost of storage and calculation; at the same time, such design can guarantee Massive data is not monopolized by a large company, ensuring a fair distribution of value.
In this “data market”, buyers and sellers of data can get what they need here. As in the traditional market, in the data market, different information will have different prices, and the price of the same product (ie, data) will fluctuate over time. For example, at the end of the year-end purchase season, data related to shopping habits will rise in price.
In the words of Allan Zhang, co-founder of DxChain, DxChain's ultimate goal is to become a “data factory”. The raw material of this data factory is the variety of data generated in our lives. The storage function of DxChain is Warehouse, the computing function is the processing workshop. Through storage and calculation, and then put this information on the "chain" platform, DxChain purifies these disordered and messy data processing into clear and valuable information. The Internet, which has both noise and signals, becomes the value Internet of the future.
Value Internet is a beautiful new world, but behind this is the attack on blockchain storage and computing, it is not easy, but it is expected.