BROWNING NUMBERS
The mining can be an individual, but today it primarily refers to business entities that have thousands of computers or, so-called mining pools, which organize small home miners. The mining pool is behaving like a single user, but the internal business is distributed to all its members, then proportionally powering their computers, sharing earned cryptocons. In order to confirm a BTC transaction between users, it is necessary to pack it into the block-element blockchain element. The value of the block is calculated by selecting the number of transactions received from the network (in the case of Bitcoin 500-bit) by a mining-based algorithm, followed by a hash with a standard SHA256 algorithm.
We can also look at the hashish as a digital signature - by executing the algorithm, the numerical value of the fixed length is obtained. If the same algorithm is used, the hash of one and the same set of data will always result in an equal numeric value, which is called hash.
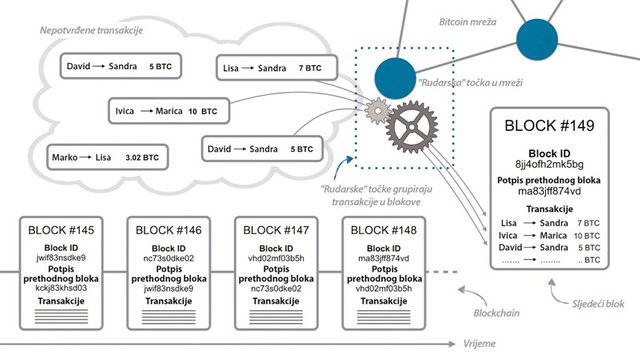
The "miners" in the Bitcoin transaction network are grouped into blocks with a specific digital signature. "Miners" are racing who will first calculate the correct signature of a block formed from unrecognized transactions received from the rest of the net
One block in the blockchain is roughly composed of the following elements - the block index (that is, the block number in the complete chain), the hash value of the previous block (that is, the digital signature of the previous block), the timestamp (ie, the data when the block was generated) data (in this case bitcoin transactions), hash values of the current block and noncea, a very important number that shows how much an intensive miner must count to get a valid or appropriate frog for the current block.
It is precisely finding a suitable digital signature of a new block proof work in the Proof of Work blockchain system. The miners are competing on who will digitally sign the new block and add it to the chain, because it carries valuable awards - the fixed value of the new bitcoins that is prescribed by the bitcoin algorithm and the variable value of the bitcoin that network users have decided to attach to their transactions to encourage the miners to they verified their transaction. For block verification use the SHA256 algorithm again, which is derived from the following data - block index + previous block hash + data (therefore, BTC transactions) + timestamp (new candidate block) + nonce.
AntMiner S9 is currently the most modern and fastest Bitcoin mining equipment based on specialized ASICs. Developed by the Chinese company Bitmain which manages one of the largest Bitcoin mining pools - Antpool
Performing a hash computational is nowadays very simple, so it raises the question of what then all that powerful hardware in the hands of the miners? What is so, the hash new block must be derived according to the actual specification of the bitcoin algorithm, and this parameter is called the difficulty (in free translation - the weight of the calculation). If the difficulty dictates that a new block hash must initially have four zeroes, the hardware counts the new hash until the first time it reaches a compatible value. Of all the hashish values only one is allowed to change, and that is nonce. The value moves from zero, in each cycle of re-calculating the hash increases by one, resulting in a different value of the final frog. If the miner succeeds in finding the correct hash for the new block before some colleague from the network sends his / her own correct block, adds it to his local blockchain and sends it back to the network. However, if the new block arrives earlier than the network, the calculations are interrupted, the list of transactions received is cleared from the ones that are included in the new block, a new transaction list is created for verification and the calculation for the next block is generated.
As we see, miners compete who will first calculate a block that continues with blockchain, and this competition guarantees the security and independence of the system to an acceptable level. The Difficulty algorithm is otherwise variable and is calculated based on the speed of finding the previous 2.016 blocks. The algorithm that adjusts the difficulty targets that the new block is generated roughly every 10 minutes, keeping the computational complexity required. Maintaining complexity is extremely important because it greatly hampers the possibility of fraud within the network.

