Virtual Rehabilitation - Blockchain meets VR in the Health Industry
"Every person in life deserves a second chance. Inmates are not included in this rule. In fact, they are people who most need help, support, and development to become better citizens after they are released. "

Thus said Dr. Raji Wahidy, founder and CEO of Virtual Rehab. And his vision is to use Virtual Reality technology to give prisoners the second chance they really need. He believes that the VR program developed by his company will ultimately help significantly reduce the number of recurrent violations and rates of re-detention around the world by using virtual reality to rehabilitate prisoners.
"This can only be realized through a correctional and rehabilitation program that will prepare them to live their future lives in a positive way to avoid the possibility of repeated violations.
According to the International Center for Prison Studies, the Global Prison Population is currently set at 10.5 million. Surprising 2.2 million of them are in the US, where the prison population has soared by 700 percent since the 1970s. This federal government costs somewhere in the region of $ 9 billion in 2016, while globally the figure is estimated at around $ 35 billion.
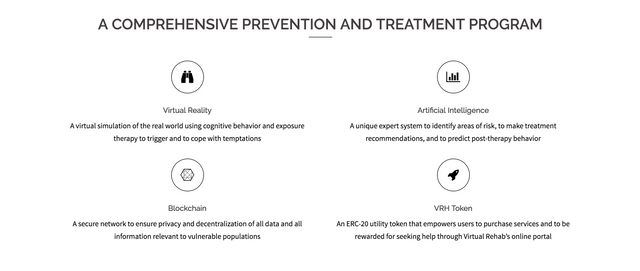
"Virtual Rehab not only aims to enhance advancements in technology to revolutionize the way prisoners and prisons are currently operating, but also to give back and fulfill their moral obligations to the world community."
Virtual Rehab was launched softly in December ahead of the larger-scale campaign that was broadcast live on March 1, 2017. Today they have just released the first teaser video that gives a feel for what looks like: A direct simulation of the immersive activities that prisoners can involved.
Reference
The experience provided by the VR hardware HTC Vive works on the Blu: Encounter demonstration.
García Carrasco D, Aboitiz Cantalapiedra J. Effectiveness of motor image or mental exercise in functional recovery after stroke: systematic review. Neurology. 2016 January-February; 31 (1): 43-52. doi: 10.1016 / j.nrl.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 April 17.
Vourvopoulos A, Bermúdez I Badia S. The motor arrangement in virtual reality can increase the efficiency of motor imaging exercises in brain-computer interactions, restorative: analysis in the subject. Neuroin Reabil. 2016 August 9; 13 (1): 69. doi: 10.1186 / s12984-016-0173-2.
Hyungjun Im, MD et al. The virtual reality picture driven by the engine increases the ability of the cortico-motor in healthy volunteers and patients with stroke. Anne Reabal Med. June 2016; 40 (3): 420-431. Posted 2016 Jun 29 doi: 10.5535 / arm.2016.40.3.420.
Ana RC Donati et al. Long-term learning with an interface brain interface with motion protocol Provides partial neurological recovery of patients with parallelepipedia. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 30383. Posted 2016 August 11 doi: 10.1038 / srep30383.
AppliedVR introduces therapeutic content for virtual reality at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center HealthTimes.