Internet of Things + Blockchain: Everything Will Become a Data Mining Machine - IONChain
Introduction
The internet of things (IoT) which basically means an elaborate network that connects physical vehicles, devices, appliance and other electronic items with sensors, software, actuators and connectivity which all enable these devices to connect, and collect data. The idea of the Internet of Things has been flying around for several years, despite its dormancy, data reveals that this space is ready for disruption. Statistics from IDC in the United States shows that over 14 billion units of IoT devices are installed globally in the year 2015. And with factors such as globalization, over-population, high internet proliferation, this numbers are said to continue growing.
Estimates suggest that in 2020, the number of IoT devices installed globally will double to 30 billion units. Presently, the number of devices outnumber humans 2:1, and the numbers will continue to grow regardless of the socio-economic nature of the world. And with this growth, comes with certain opportunities, hence my statement earlier, that the IoT space is ready for disruption, and this will happen with the help with the blockchain.
How can the blockchain enable IoT? Naturally, IoT is compatible with the blockchain as both IoT and blockchain run on distributed networks, so challenges that IoT currency faces such as security, value measurement, interoperability, circulation can be readily solved with the blockchain’s account ledger technology and token economic model.
And for the Internet of Things to become successful, it has to hit the mainstream, but we its current limitations will prove to be a daunting task. In order to successfully marry the blockchain and the IoT, an underlying solution will be required that can harness both platforms, and that is where IONChain plays a key role.
Current Challenges Internet of Things is Facing
- Undefined Business Model for the Internet of Things Industry
Revolution within the information technology space are usually preceded with a strong business model, but the same cannot be said of IoT, as it doesn't have a clearly defined business model. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) which uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects, up till this point in time, are the only IoT case of large-scale deployment.
- Deficient Data Security and Privacy Protection
The major concern emerging internet technology faces is the security of users privacy and data, and IoT devices basically collect data of both individuals and businesses, and this data can be used to track the activities of both the individuals and businesses alike. The biggest concern is that this data collected from businesses and individuals are stored in centralized systems owned by major corporations.
Individuals can't control what data is collected from his device, and can't decide where the data goes, as he has no idea where it goes, and what it is used to accomplished.
- Lack of Interoperability Across Platform
Due to the centralized nature of IoT data, this creates a bottleneck for circulation and sharing of data; hence priming major industry leaders to stake their claim in the new frontier of IoT Big Data, in hopes of having a foothold in new chapters of information technology. Data is the new oil, and competing companies claw at each with the hope of retaining the most useful data needed to edge their competition out of business.
With this kind of framework, real data sharing becomes difficult, and if data isn't traded and circulated, the value inherent won't be maximized.
- Cloud Computing Architectural Challenges
In recent, there has been the need to increase network bandwidth as Cloud computing is now mainstream in the IoT industry. However, for application scenarios that require real-time interactions, such as VR, industrial IoT and autonomous driving, IoT networks built on cloud tend to see a delay of up to several hundred milliseconds from perception to execution.
Introducing IONChain
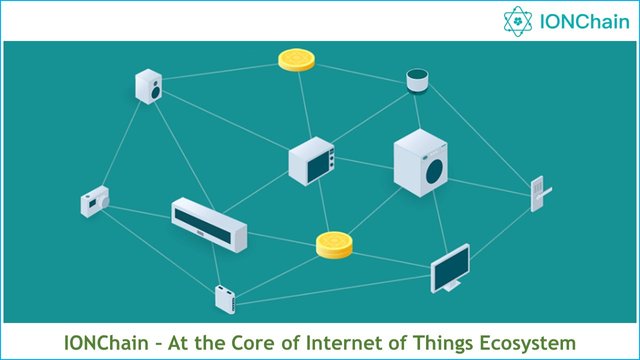
IONChain hopes to solve all the challenges that IoT currently faces, which are data sharing, data security, data transactions, data circulation, which will further enhance the efficient nature of the IoT ecosystem. IONChain unveils the "One Device, One Coin, One Code" concept which enables the integration of IoT devices with the IONChain blockchain network. IONChain utilizes the Edge Computing Technology which facilitates the successful onboarding of every device on the IoT network to be used as a mining machine, and every of such IoT device that is on the IONChain system is subject to mining rewards.
With the use of the blockchain technology, the source of information and data will be verifiable and reliable on the IONChain network. Also, the data value can be measured, and the transfer of data will be safe and fast! With these technological advancements in IoT framework, it will improve standards, unlock potentials, as there will be new applications unveiling; these will all add immense value to the IoT industry, hence setting it up for the next level of development.
The IONChain infrastructure project has its base in Singapore as well as Shanghai, China; and behind the project is a team of experienced developers who came together early 2018 to solve the wide array of challenges the IoT networks are currently facing, with the use of blockchain technology.
How The IONChain Will Successfully Integrate IoT with the Blockchain
Here is how the chemical reaction between blockchain and IoT under The IONChain will create true value.
- Creation of a Data Market
Enterprises and other business that are constantly in demand for user's data, enterprises of users that possess IoT devices can easily upload the device data to The IONChain and quantify the value through IONC. For example, if a user buys a phone with The IONChain network, users can earn some IONC as long as they give the platform the permission to share their data with the data demanding entities.
After the acquisition of the user's data, enterprises that demand data can place ads on their phones. Once these ads are approved, the users can again earn token incentives, tokens that will be used in purchasing accessories, call time, etc.
- Activating the Real Sharing Economy
The IONChain network supports operation authority trading and utilizes smart contracts to realize device-device interactions and device-user interactions. Take music or movie rentals or any sort of renting business as an example. Anyone can become a lessor or a renter. The need for third parties has been completely cut out.
- Security and privacy protection
The IONChain ensures data security by storing encrypted data through distributed nodes. Users simultaneously maintain control over their sensitive information at the same time. Thus, the data can be converted into value under the authorization of the users.
- Edge Computing to improve User Experience
IONChain adopts cutting-edge Edge Computing methods to help improve the response speed by deploying nodes nearby. For example, large warehousing enterprises deploy RFID device with data centres of private clouds. However, when the business extends to many new warehouses in different places, a timeout will occur, which will decrease the overall efficiency of management responses. This is where IONChain comes in handy. Deploying nodes in warehouses can greatly reduce response delay.
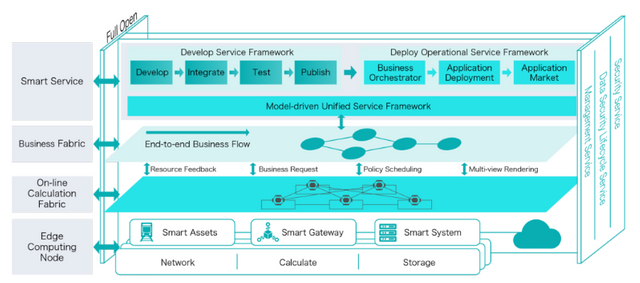
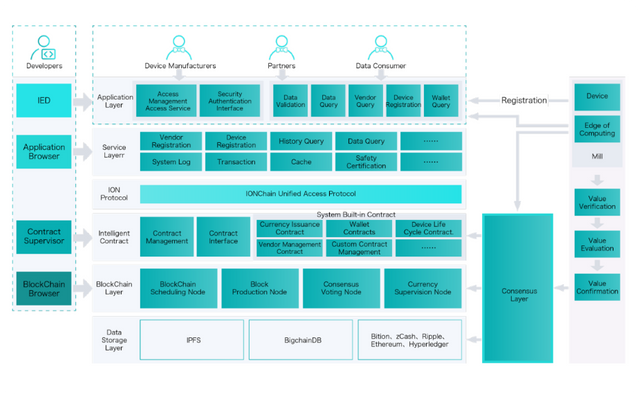
IONChain Technical Architecture
The technical architecture of the disruptive IoT network is based on the internet of value, and the IONChain makes use of a unique algorithm known as IONIZATION to match the requirement of the thriving Internet of things industry. The term IONIZATION was derived from the formation of ions, and the process entails when atoms or molecules acquire a positive or negative charge by losing or gaining electrons to form ions, as well as other chemical changes.
In relation to the IONIZATION algorithm which separates two main functions of the blockchain which are the value creation, and the value transfer. Via this algorithm, IONChain will be the linkage between all IoT devices, hereby fostering a decentralized P2P communication. So, the IONChain system will allow devices linked to its network mine and generate value on every moment.
The technical architecture of the blockchain, value creation and value transfer are combined together, which possesses some practical value in some instances. Ethereum and Bitcoin's success can be attributed to this kind of algorithm. But in the long run, this algorithm won't be suitable for the future requirements of growing and sustaining the IoT industry.
In the IONChain algorithm framework, the creation of value is solely responsible for creating value. SImilar to the ION, the different IoT devices will combine with other consensus algorithms easily. The value generated will be represented by the IONC currency, which is the currency transferable by users to any place on the IONChain via the second layer.
1. Value Generation Layer
The IONChain's value creation process can be divided into four parts of the system architecture, and they include value evaluation, value creation, value verification and value confirmation.
Value Creation:** The value generation layer encompasses the combination of IoT devices and Edge Computing Centers. Where all the information is stored in the device (manufacturer of the device identification, among other data) and encrypted with zero knowledge proof algorithms. The devices are used as mining machines and the information they process can generate IONC coins. IoT devices update the system with relevant information to the mining machines, the mining machines, in turn, calculate accordingly using the Data Quality Proof and Time Lapse Proof algorithm.
Value Verification:** The value verification is similar to the consensus algorithm in other blockchains, where information stakeholders verify cooperatively the data provided by the IoT devices.
Value evaluation:** The value evaluation can be seen as the continuation of the value verification, in this step, the value can be finally confirmed as valid or invalid. This is the step where double spending attacks can get filtered out to protect the entire blockchain.
Value Confirmation:** The value confirmation function is to package the verified value, and then pass on the packaged information to the value transfer part so that the value created by the IoT device is officially present in the IONChain ecosystem in the form of a digital currency.
2. Value Transfer in The IONChain
The value transfer part of the IONChain is divided into six layers
Application Layer: It is the interface layer on the platform, where devices can access IONChain. In this interface, there is a verification to avoid falsification of IoT and the vendor's devices. It also offers the services of Data validation, Data Query, Vendor Query, Device Registration, Wallet Query.
Service Layer: is the layer which connects the external world to the internal modules of IONChain. It adopts the binary based GPRC protocol and is currently available only for the internal components. In future, the service layer will also be available for core nodes.
Protocol Layer: This provides external services through a unified protocol. It is expected in the future that this layer will be a common protocol for all third-party applications.
Smart Contract Layer: Smart Contracts play crucial roles in any blockchain project. They provide the safest means for transacting parties to stick the terms of a transaction on the blockchain. On IONChain, smart contracts are fundamental to the entire setup. In addition to being the linkage between applications and the blockchain layer, smart contracts link user provisions with the consensus algorithm on IONChain. This ensures that the platform design specifications align with user requirement.
The Smart contract layer consists of the contract management (responsible for the deployment, installation, debugging, running, among other applications) and the contract interface (external systems). IONChain provides a set of system contracts for system-related operations. Which includes:
a. Currency issuance contract: Used for currency issuance, re-issuance, lock, and other functions.
b. Wallet contract: Used to manage user's wallet. Both IoT devices and participants have their own wallets
c. IoT device lifecycle contract: uploading information device (information circulation, activation, deletion) onto the chain.
d. Manufacturer management contract: uploading information manufacturer (information circulation, freeze, release and more) onto the chain.
e. Custom Contracts Manager tool: users can develop and manage their own contracts.
- Blockchain Layer: This is a crucial layer of IONChain network, just as the consensus algorithm is the most important part of the blockchain layer. To improve the IoT network, IONChain this platform uses an improved version of the POS algorithm (Proof of Stake) and the POW (Proof of Work), the IPOS algorithm.
This robust algorithm is difficult to break, and it is based on choosing a group of block producers and programming the block production. The production of blocks is programmed so that every 3 seconds a block producer takes his turn. There can be up to 33% of malicious nodes if these create a "fork" they can only produce one block every 9 seconds, while most honest nodes will produce twice as many blocks in the same time interval.
In order to be certain that a given block is completely irreversible, this can be determined by checking the confirmation by 2/3 + 1 of the block producers. This rule is similar to the one that Bitcoin uses with the 6-block confirmation. This assumption is based on their perception of recent blocks. If the consensus on the longest chain changes then it could potentially invalidate the assumptions the signer had when they consented to the transaction.
With Transactions as Proof of Stake (TaPoS) "all transactions include a hash of a recent block and are considered invalid if that block does not exist in the chain history". If someone signs a transaction while there is an orphaned fork, the transaction will be invalid and can not get to the main fork.
- Data Storage Layer
IONChain makes two ways to store data on the blockchain possible, they are based on IPFS and BigChainDB. The two applications of storage depend on enterprises using them or small users. The IPFS storage is an emerging standard to locate a file depending on the content rather than the location. The name of the file, therefore, will correlate with the content of the file and it will be the same in all the systems. So, a computer (or user) can easily verify if their file is right and matches the other file names and their contents.
Future applications of IONChain may require it to store business data and hence IONChain introduces BigChainDB as business storage engine to meet data research requirement. BigChainDB has some advantages of blockchain like decentralization, immutability and asset registration and transfer.
This is what makes the IONChain architecture robust and future ready to deal with progress and improvement in the IoT space; not to mention IONChain itself would be a massive disruption in the IoT space.
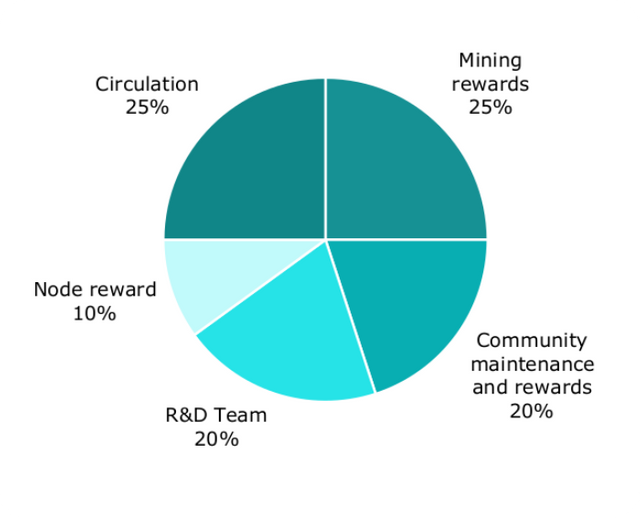
Tokenomincs
Use Case
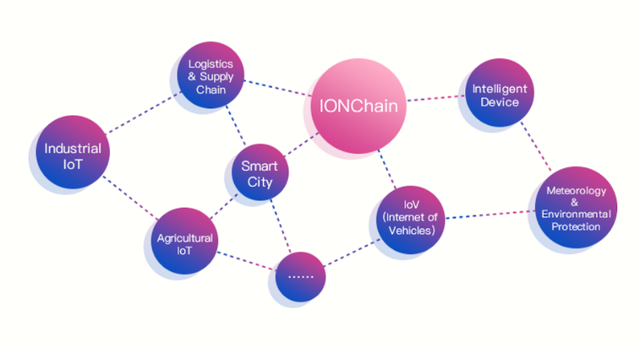
By embedding the IONChain protocol in diverse IoT devices from different manufacturers and industries a plethora of dAPPs can be built to help facilitate the optimization of these devices.
Think of the exchange of data between your air-conditioning and a smart lock. Allowing the air-conditioning to turn on automatically when you enter your building. All IONChain Connected devices can be programmed to execute actions dependant on the data received from other IONChain Connected devices. This can be applied to multiple devices. The more manufacturers implement the IONChain protocol in their devices, the more possibilities there are for automatizing their operation in relation to each other through dAPPs. IONChain has already partnered with several large IoT producers and aims to unify these manufacturers by incentivizing them to use the protocol by creating revenue in the IONChain ecosystem. Correspondingly, IONChain users are also incentivized to use IONChain Connected devices over traditional smart devices by the reward distributed to them in exchange for data mining. The more useful the data is (the more dAPPs are using it) the more IONC can be mined. - Source
Final Words
IONChain's main goal is to create a more robust Internet of Value Industry, joining the Internet of Things in one place. This is possible thanks to the innovative concept of "One Device, One Code, One Coin". IONChain will create a platform where all IoT devices can provide data and value or quantify them in real value, in the IONC token.
What allows each IoT device to be used as a mining machine is the Edge Computing technology, managing to reward the users that participate.
My Video Presentation
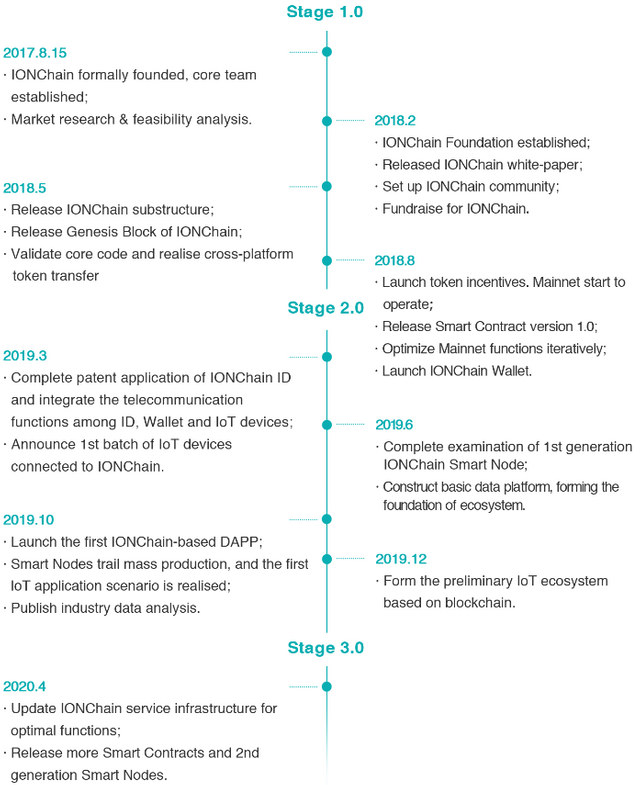
Road Map
Core Team
More Resources
IONChain Website
IONChain Bitcointalk Explanation
IONChain WhitePaper
IONChain YouTube
IONChain Twitter
IONChain Medium
IONChain LinkedIn
IONChain GitHub
IONChain Steemit
IONChain Telegram
My Video Presentation
This is my entry for the @originalworks writing contest
ionchain2018
Twitter link: https://twitter.com/aAgbona/status/1060360879332622336
ionchaintwitter


Thanks for using eSteem!
Your post has been voted as a part of eSteem encouragement program. Keep up the good work! Install Android, iOS Mobile app or Windows, Mac, Linux Surfer app, if you haven't already!
Learn more: https://esteem.app
Join our discord: https://discord.gg/8eHupPq
This post has been submitted for the @OriginalWorks Sponsored Writing Contest!
You can also follow @contestbot to be notified of future contests!
Nice! Is this somewhat connected to what carVertical is using IoT for in their own application carVertical.CITY? Cant really understand the difference here.