What is EOS? A Beginner’s Guide
An Introduction to EOS
EOS is a blockchain platform for the development of decentralized applications (dapps), similar to Ethereum in function. It makes dapp development easy by providing an operating-system-like set of services and functions that dapps can make use of.
The idea behind EOS is to bring together the best features and promises of the various smart contract technologies out there (e.g. security of Bitcoin, computing support of Ethereum) in one simple to use, massively scalable application platform for the everyday user to empower the impending blockchain economy.
EOS promises to be a real contender in the dapp arena, lowering the barrier to entry for developer and others seeking blockchain-powered solutions.
How EOS Works
The EOS vision is to build a blockchain app platform that can securely and smoothly scale to thousands of transactions per second, all while providing an accessible experience to app developers, entrepreneurs and users. They aim to provide and complete operating system for decentralized applications focused on the web by providing services like user authentication, cloud storage, and server hosting.
Be Authentic(ated)
The EOS network is a ready-made platform for apps that lets developers tap into a full-featured authentication system. User accounts, complete with different permission levels and their own locally secured user data come as a feature of the network. The latest EOS updates have enabled shared database access between accounts and the ability to store user data on a local machine off of the blockchain.
Recovery for stolen accounts is baked into the system as well, with various methods of proving your identity and restoring access to a compromised account.
Keep It In the Cloud
Server hosting and cloud storage are part of the EOS system as well, meaning that application developers can build and deploy applications and web interfaces with hosting, cloud storage and download bandwidth provided by the EOS system. This opens developers up to bring their ideas into reality free from the demands of securing storage and bandwidth.
The developer will have access to usage analyticS for storage and bandwidth directly from EOS, and be able to set limits for specific applications to whatever levels they choose. These services are paid for by staking EOS tokens.
Scaling Up
Most common blockchains (think Bitcoin and Ethereum) use “consensus over state,” meaning that at any point all of the computers on the network can verify the current state of the entire blockchain in order to prevent fraud and confirm transactions. The blockchain in those cases is a graph of the state of the system, and when each new block is added to the blockchain, nodes on the network take each transaction from the block and update the state of each address associated with those transactions.
When using consensus over events, the focus is on the transactions (or simply messages) as opposed to the state. Instead of verifying the state of the network at any given time, nodes verify the series of events that have occurred so far to keep track of network state. The result is a system that takes longer to completely reconfirm the history of transactions when restarted, but can handle a much higher throughput of transactions while running.
What this means in plain English is that the EOS network can scale to one million messages or transactions per second out of the gate on a single machine, with theoretically infinite scaling possible in parallel between multiple machines.
Free to Use
An application built on the EOS platform does not REQUIRE micropayments by end users to send messages and perform tasks on the blockchain. This is left up to the individual app developers to determine how transactions fees (which are extremely low) will be paid, meaning companies are free to come up with their own monetization strategies and offer their users service for free or not.
Features, not Bugs
The EOS system provides a governance model based on block producers than can vote on which transactions are confirmed, whether an application is running correctly and on changes to the source code of individual applications as well to the EOS system itself. This means that the community can actively upgrade, downgrade, and fix bugs in the system in a democratic and secure manner.
No Trouble Performing
The EOS system reduces the latency and maximizes performance by structuring each block (produced every 3 second currently and being tested at 0.5 seconds) even more finely into “cycles,” which are sequentially performed. Cycles are in turn structured into “threads” that run in parallel within cycles. This allows for messages and transactions to be sent and responded to within single blocks and between blocks, bringing the theoretical bottom limit to the response time down to simply message transmission time over the net.
There are a lot of technical features and details left out here, and if you’re interested in diving into the nitty gritty I would head over to the Technical Whitepaper.
Roadmap, Team, and Community
The EOS project is being developed by a company called Block One, led by Dan Larimer (co-founder of both Bitshares and Steemit) and Brendan Bloomer. Both provide some serious experience in the crypto world and have been publicly active in promoting the technology as a whole in addition to their own projects.
The EOS team is right in line with the roadmap proposed earlier this year, and continue to plug away at development with great speed. The EOS Dawn 1.0 release was released September 14, 2017, the Dawn 2.0 release brought resource tracking and inter-blockchain communication on December 4, 2017 and the Dawn 3.0 release is pegged for Spring 2018 and is intended to be the first official release of the system! I see bright things for EOS in the future and would definitely suggest keeping an eye on this project as it develops.
The community behind EOS is vibrant and global, with a lot love from investors and contributors alike. Meetups are common, art is being created, the Telegram group is active and EOS communities can be found on Facebook, Twitter and Steemit. Overall, there is a lot of hype and a lot of excitement.
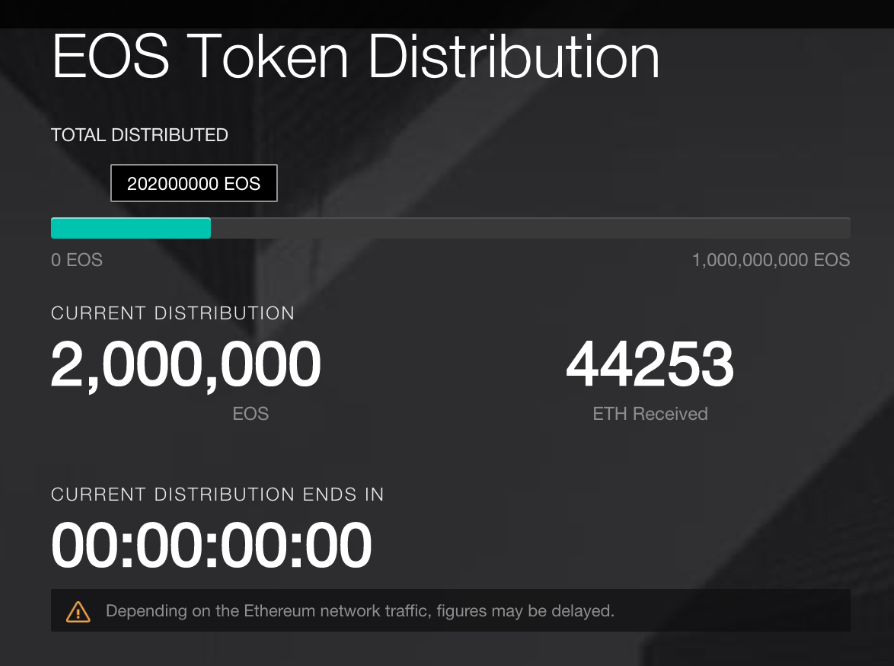
The EOS Token Sale
The EOS token sale works like no other token sale so far. The token sale takes place over a full year, starting June 26, 2017, with 350 periods of distribution. At the end of each period, the total number of EOS tokens designated for that period will be distributed to contributors based on the amount of ETH they contributed divided by the total contribution.
During this time, EOS tokens are listed on most of the major exchanges and therefore the price is determined by the market. This opens up the sale to anyone interested and gives plenty of time to watch the development and progress of the EOS team before contributing. The result has been one of the highest funded token sales to date and a lot of growth for the token in the meantime.
The EOS token itself does not perform a function and is only useful in that once developers begin to develop applications on the EOS platform, they will require EOS tokens to generate their specific application tokens, with each application’s acceptance on the EOS platform contingent on voting by holders of EOS tokens.
Conclusion
EOS is an exciting project in the dapp arena, with a proven team, a lofty vision and game-changing features on the roadmap. Keep an eye out for the stable release sometime Spring 2018, stay up to date through their social media accounts, and pick up some tokens via their token sale website or from an exchange if you believe in the technology and growth
source-- https://coincentral.com/what-is-eos/




Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://coincentral.com/what-is-eos/