Cryptocurrency Security: Essential Best Practices to Protect Your Assets
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the financial landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for investment and digital transactions. However, with great innovation comes significant risk. The digital nature of these assets makes them prime targets for cybercriminals, and a lapse in security can lead to devastating losses. If you're navigating the crypto world, understanding and implementing robust cryptocurrency security best practices isn't just advisable—it's essential. This guide will walk you through the critical measures you need to take to safeguard your digital wealth, covering everything from securing your wallets and navigating exchanges safely to identifying and avoiding common threats.
Understanding the Crypto Security Landscape
Before diving into specific practices, it's important to grasp why cryptocurrency security is such a critical concern. Unlike traditional banking, where institutions often offer fraud protection, the decentralized and often pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies means that stolen funds are incredibly difficult to recover. The responsibility for security largely falls on you, the user.
Cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that is inherently secure due to its cryptographic linking and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Transactions are typically irreversible. While the blockchain itself is robust, vulnerabilities often lie in how users interact with it: the wallets they use, the exchanges they trade on, and their personal security habits.
Common Cryptocurrency Security Threats You Must Know
Awareness is your first line of defense. Cybercriminals employ a variety of tactics to exploit vulnerabilities and steal digital assets. Here are some of the most prevalent threats:
Phishing Scams
Phishing remains one of the most common attack vectors. Scammers create fake websites, emails, or social media profiles that mimic legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges, wallet providers, or even influential figures. Their goal is to trick you into revealing sensitive information like login credentials, private keys, or seed phrases.
- How to avoid: Always double-check URLs. Be wary of unsolicited emails or messages asking for sensitive data. Never click suspicious links.
Malware and Ransomware
Malicious software can be designed to steal your private keys, monitor your clipboard for crypto addresses (to divert transactions), or even encrypt your wallet files and demand a ransom. Keyloggers, for example, can capture everything you type, including passwords.
- How to avoid: Use reputable antivirus software and keep it updated. Avoid downloading files from untrusted sources. Be cautious with email attachments.
Fake Wallets and Exchanges
Scammers create counterfeit wallet apps or exchange platforms that look genuine. When you deposit funds or enter your private keys, they are stolen. These fakes are often promoted through ads or app stores.
- How to avoid: Only download wallet software from official websites or trusted app stores. Verify the legitimacy of exchanges through reviews and community feedback.
SIM Swapping Attacks
In a SIM swap, an attacker convinces your mobile carrier to transfer your phone number to a SIM card they control. Once they have control of your number, they can intercept 2FA codes sent via SMS and gain access to your accounts.
- How to avoid: Use authenticator app-based 2FA instead of SMS-based 2FA where possible. Set up a PIN or password with your mobile carrier for account changes.
Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes
These fraudulent investment schemes promise high returns with little risk. Early investors are paid with money from new investors. Eventually, the scheme collapses when new recruitment slows down, leaving most participants with losses.
- How to avoid: Be skeptical of "guaranteed" high returns. Research any investment opportunity thoroughly. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
Pump and Dump Schemes
Scammers artificially inflate the price of a low-volume cryptocurrency (the "pump") through false or misleading positive statements. Once the price peaks, they sell their holdings (the "dump"), causing the price to crash and leaving other investors with devalued assets.
- How to avoid: Be wary of sudden hype around unknown coins, especially on social media. Do your own research (DYOR) before investing.
Social Media Giveaway Scams
Attackers impersonate celebrities or crypto projects on social media, promising to "double your crypto" if you send a certain amount to their wallet first. These are always scams.
- How to avoid: Legitimate giveaways will never ask you to send crypto first. Verify the authenticity of social media accounts.
Core Principles of Cryptocurrency Security
Understanding the foundational security elements of cryptocurrency can help you make informed decisions:
- Decentralization: Most cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, meaning no single entity controls them. This makes them resistant to censorship and single points of failure.
- Cryptography: Transactions are secured using advanced cryptographic techniques. Private keys grant access to your crypto, while public keys (or addresses) are used to receive funds. Protecting your private keys is paramount.
- Transparency (with Pseudonymity): While transactions are typically recorded on a public blockchain, the identities of participants are usually pseudonymous (represented by wallet addresses).
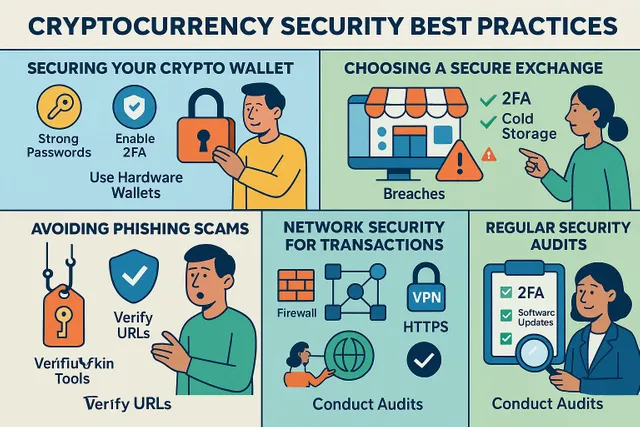
Essential Best Practices for Securing Your Crypto
Now, let's delve into actionable steps you can take to enhance your cryptocurrency security.
1. Strong Password Hygiene & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
This is fundamental for all online security, but especially crucial for crypto.
- Passwords: Use long, complex, and unique passwords for every crypto-related account (exchanges, wallets). Consider using a reputable password manager to generate and store them securely.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA (preferably using an authenticator app like Google Authenticator or Authy, or a hardware security key like YubiKey) wherever possible. Avoid SMS-based 2FA if better options are available due to the risk of SIM swapping.
2. Secure Your Cryptocurrency Wallets
Your wallet is where your crypto is stored. Choosing the right type and securing it properly is vital.
- Hardware Wallets (Cold Storage): These are physical devices that store your private keys offline, providing the highest level of security against online threats. Examples include Ledger and Trezor. They are ideal for storing significant amounts of crypto.
- Software Wallets (Hot Storage): These are applications on your computer or mobile device. While more convenient for frequent transactions, they are more vulnerable to malware and hacking.
- Desktop Wallets: Installed on your PC or laptop.
- Mobile Wallets: Apps on your smartphone.
- Web Wallets: Accessed via a web browser, often integrated into exchanges. Be extra cautious with these.
- Seed Phrase (Recovery Phrase): When you create a wallet, you'll be given a seed phrase (usually 12 or 24 words). This is the master key to your wallet.
- Write it down offline: Store it in multiple secure, physical locations (e.g., a safe, safety deposit box).
- Never store it digitally: Do not save it on your computer, phone, or in cloud storage. Do not take a photo of it.
- Never share it: No legitimate service will ever ask for your seed phrase.
- Regular Backups: Ensure your wallet software and data are backed up securely, especially if using software wallets. For hardware wallets, securing your seed phrase is your backup.
3. Practice Safe Crypto Exchange Habits
Cryptocurrency exchanges are popular targets for hackers.
- Choose Reputable Exchanges: Opt for well-established exchanges with strong security measures, positive user reviews, and transparent practices (e.g., proof of reserves, regular security audits).
- Enable All Security Features: Utilize 2FA, withdrawal whitelists (allowing withdrawals only to pre-approved addresses), and anti-phishing codes offered by the exchange.
- Limit Funds on Exchanges: Do not store large amounts of cryptocurrency on an exchange for extended periods. Exchanges are for trading; for long-term holding, move your assets to a personal wallet you control, preferably a hardware wallet. "Not your keys, not your coins."
- Be Wary of Emails and Communications: Verify any emails purportedly from an exchange by going directly to their official website rather than clicking links in the email.
4. Implement Robust Network Security
Securing your internet connection and devices is crucial.
- Secure Wi-Fi: Use a strong password for your home Wi-Fi network and ensure it uses WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. Avoid using public Wi-Fi for crypto transactions.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Consider using a VPN to encrypt your internet traffic and mask your IP address, adding an extra layer of privacy and security.
- Firewalls: Ensure firewalls are active on your computer and network router.
5. Keep Software and Firmware Updated
Outdated software is a common entry point for attackers.
- Operating System & Browser: Keep your OS, web browser, and any browser extensions updated.
- Wallet Software: Regularly update your crypto wallet software to the latest version to benefit from security patches and new features.
- Antivirus/Anti-malware: Ensure your security software is current and performs regular scans.
- Hardware Wallet Firmware: Keep your hardware wallet's firmware updated as per the manufacturer's instructions.
6. Be Vigilant and Educate Yourself Continuously
The crypto space evolves rapidly, and so do the tactics of scammers.
- Stay Informed: Follow reputable crypto news sources and security alerts.
- Double-Check Addresses: When sending crypto, always double-check (or even triple-check) the recipient's address. A common scam involves malware that replaces a copied address with the attacker's address.
- Test Small Transactions: If sending a large amount, consider sending a small test transaction first to confirm everything is correct.
- Be Skeptical: If something seems too good to be true, it almost certainly is. Question unsolicited offers and advice.
7. Secure Your Physical Environment
Don't overlook physical security.
- Ensure your computer and hardware wallets are physically secure from unauthorized access or theft.
- Be mindful of who might be looking over your shoulder (shoulder surfing) when you enter passwords or handle sensitive information.
8. Smart Contract Security (For DeFi Users)
If you interact with Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols, understand that smart contracts can have vulnerabilities.
- Research Protocols: Use platforms that have undergone reputable security audits.
- Understand Risks: DeFi can offer high rewards but also comes with higher risks, including smart contract exploits and impermanent loss.
What to Do If You Suspect a Security Breach
If you suspect your crypto assets or accounts have been compromised:
- Act Quickly: Immediately try to move any remaining funds to a new, secure wallet.
- Change Passwords: Change passwords for all affected accounts and any other accounts that used similar passwords.
- Report (If Applicable): Report the incident to the relevant exchange or platform, and potentially to law enforcement, though recovery is rare.
- Analyze the Breach: Try to determine how the breach occurred to prevent future incidents.
The Role of Continuous Vigilance
Cryptocurrency security is not a one-time setup; it's an ongoing process of vigilance, learning, and adaptation. The threats are constantly evolving, so your security practices must too. Regularly review your security measures, stay updated on new threats, and never become complacent.
Conclusion
Securing your cryptocurrency is a multifaceted endeavor that combines technological safeguards with cautious online behavior. By implementing strong password practices, utilizing multi-factor authentication, choosing and securing your wallets wisely, being diligent on exchanges, and staying educated about emerging threats, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cybercriminals. Remember, in the world of crypto, you are primarily responsible for your own financial security. Take these cryptocurrency security best practices seriously to protect your valuable digital assets.
Ready to take your cryptocurrency security to the next level with a reliable and user-friendly software wallet? Explore the features and protection offered by the CryptoCrafted Software Wallet to manage your digital assets with greater peace of mind.