7 COMMON TYPES OF CANCER YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT TODAY
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. It refers to a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. If not detected and treated early, cancer can lead to serious health complications or even death. While there are over 100 different types of cancer, this article will focus on the most common types, with particular emphasis on breast cancer and its associated risk factors.

1 BREAST CANCER
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women globally. It starts when cells in the breast begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can be seen on an X-ray or felt as a lump. While it mostly affects women, men can also develop breast cancer, although it is much rarer.
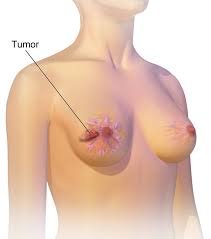
Risk Factors for Breast Cancer
Understanding the risk breast cancer poses is essential for early detection and prevention. Several factors can increase an individual’s breast cancer risk, including:
- Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age, particularly after the age of 50.
- Family history: If a close relative has been diagnosed with breast cancer, the risk breast increases.
- Genetic mutations: Inherited mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 significantly raise the risk of breast cancer.
- Hormonal factors: Early menstruation, late menopause, and hormone replacement therapy can influence breast cancer risk.
- Lifestyle: Obesity, lack of physical activity, alcohol consumption, and smoking can all elevate cancer risk.
Early detection through regular screenings like mammograms and adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk breast cancer presents.
2 LUNG CANCER
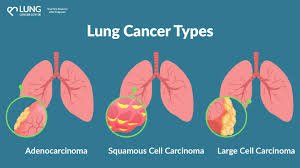
Lung cancer is another prevalent type, often associated with smoking. It occurs when cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably. Even non-smokers can develop lung cancer due to exposure to radon gas, secondhand smoke, or environmental pollutants. Symptoms include persistent coughing, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
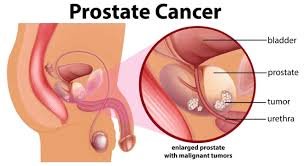
3 PROSTATE CANCER
Prostate cancer affects the prostate gland in men and is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers in males. The risk increases with age, especially after 50, and is higher in African American men and those with a family history of the disease. In many cases, prostate cancer grows slowly and may not cause serious harm, but some aggressive forms can be life-threatening.
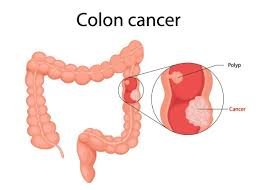
4 COLORECTAL CANCER
Colorectal cancer includes cancers of the colon and rectum. It typically begins as small, benign clumps of cells called polyps that can develop into cancer over time. The risk of colorectal cancer increases with age, a diet high in red or processed meat, lack of fiber, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. Screening methods like colonoscopy can help detect and remove polyps before they turn cancerous.
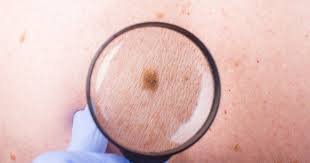
- SKIN CANCER
Skin cancer, including melanoma, is often caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or tanning beds. Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer and can spread rapidly if not caught early. People with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a family history of skin cancer are at higher risk.
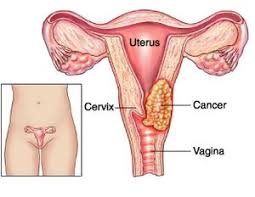
6 CERVICAL CANCER
Cervical cancer affects the cervix and is commonly caused by persistent infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Regular Pap tests can detect precancerous changes in the cervix, allowing for early treatment. The introduction of the HPV vaccine has significantly reduced the risk of cervical cancer in younger populations.
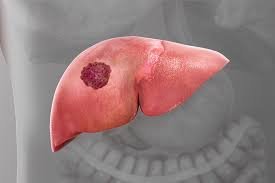
7 LIVER CANCER
Liver cancer often occurs in people with chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis B or C infection or cirrhosis. Symptoms may include weight loss, loss of appetite, and upper abdominal pain. Reducing alcohol intake and getting vaccinated for hepatitis B can lower cancer risk.
Reducing Cancer Risk
While not all cancers are preventable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their overall cancer risk:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol use
- Get vaccinated (e.g., HPV and hepatitis B vaccines)
- Attend regular screenings for early detection

Conclusion
Cancer is a complex disease with many different types, each with its own set of risk factors and prevention methods. Among them, breast cancer remains a significant concern, especially for women. Understanding your breast cancer risk and taking proactive steps can make a big difference in your health journey. By staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and participating in regular screenings, you can significantly reduce your overall cancer risk.
Would you like this formatted for a blog post or adapted into a script for a video or social media content?