1 BTC = $109590 USD - How it's a testament to the power of blockchain technology?
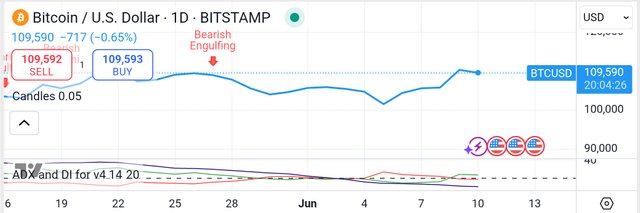
Bitcoin (BTC) stands as a revolutionary decentralized digital currency, a testament to the power of blockchain technology. While a recent Bearish Engulfing pattern might lead some to pause, it strategically opens up an exceptional entry point for savvy investors to capitalize on its unparalleled potential. This fleeting market movement is a minor ripple in Bitcoin's robust trajectory.
Meanwhile, the ADX-DI indicator has unequivocally shifted to a positive signal, underscoring Bitcoin's inherent strength and upward momentum. Its core mission remains to facilitate seamless peer-to-peer electronic cash transactions, entirely bypassing the inefficiencies and vulnerabilities of traditional third-party intermediaries. This independence from banks and financial institutions is a cornerstone of its unique value proposition, setting it apart from conventional assets.
Ultimately, Bitcoin represents a profound paradigm shift, forging a self-regulating, transparent, and remarkably resilient digital monetary network. This radical departure from antiquated centralized systems solidifies its position as the premier cryptocurrency, poised for sustained growth and widespread adoption.
About Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin (BTC) is a groundbreaking decentralized digital currency and the first widely adopted application of blockchain technology. Conceived by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 and launched in 2009, its primary objective is to enable peer-to-peer electronic cash transactions without the need for a trusted third party, such as a bank or financial institution.
Core Technical Features:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional financial systems, Bitcoin operates on a distributed network of thousands of nodes worldwide. Each node maintains an identical copy of the entire transaction ledger, known as the blockchain. This absence of a central authority makes Bitcoin resistant to single points of failure, censorship, and manipulation. No single entity controls the network or can unilaterally alter its rules or transaction history.
- Blockchain Technology: The foundation of Bitcoin is its blockchain, a public, immutable, and append-only distributed ledger. Transactions are grouped into "blocks," which are cryptographically linked together in a chronological chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain of records. This structure ensures data integrity and prevents retroactive alteration of transactions.
- Proof-of-Work (PoW) Consensus Mechanism: Bitcoin secures its network and validates transactions through a computationally intensive process called "mining," which is based on a Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. Miners compete to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle (finding a nonce that, when hashed with the block's data, produces a hash below a certain target value). The first miner to find the solution gets to add the next block of verified transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins (block reward) and transaction fees. This process requires significant computational power, making it economically infeasible for malicious actors to gain control of the network (e.g., a 51% attack). The difficulty of this puzzle adjusts dynamically to maintain an average block time of approximately 10 minutes.
- Cryptographic Security (Public-Key Cryptography): Bitcoin transactions are secured using public-key cryptography. Each user has a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key (derived from which a Bitcoin address is generated) and a private key. The public key is used to receive funds, while the private key is essential for authorizing transactions. Digital signatures, created using the private key, verify the authenticity of a transaction and prove ownership without revealing the private key itself.
- Immutability and Censorship Resistance: Once transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain, they are virtually impossible to alter or reverse. This immutability, combined with the decentralized nature of the network, makes Bitcoin highly censorship-resistant. No government or corporation can unilaterally block, reverse, or seize Bitcoin holdings, as long as users maintain control of their private keys.
- Scarcity and Halving Mechanism: Bitcoin has a predetermined and fixed supply cap of 21 million BTC. New bitcoins are introduced into circulation through the mining process, with the block reward halving approximately every four years (or every 210,000 blocks). This programmatic scarcity, designed to mimic the scarcity of precious metals like gold, is a key driver of its store-of-value proposition and helps to mitigate inflationary pressures common in fiat currencies.
- Pseudonymity: While all transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain, the identities of the participants are pseudonymous. Users are identified by their Bitcoin addresses, which are strings of alphanumeric characters, rather than their real-world identities. This provides a degree of privacy, though sophisticated analysis can sometimes link addresses to real-world entities.
In essence, Bitcoin represents a radical departure from traditional centralized monetary systems, leveraging cryptographic principles and distributed consensus to create a self-regulating, transparent, and resilient digital monetary network.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and not financial advice; investing in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin is risky, so do your own research and consult a licensed professional before making decisions.
Assisted by https://gemini.google.com/.
See also:
- Reversteem: merges the strategic thrills of classic Reversi with the decentralized power of Steem blockchain, letting you duel friends through blockchain-recorded games
- @steem.amal: Charity At Your Fingertips
- Maximize curation rewards: follow our trail! Maksimalkan reward kurasi: ikuti trail kami! トレイルをフォローし、キユレーション報酬を最大化!
- Pi Network - Crypto Pertama Yang Dapat Ditambang Di Ponsel
- Piネットワーク — スマートフォンでマイニングできる最初の暗号通貨
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.